- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄24938 > 0805ZC103KA72A (AVX Corporation) General Specifications PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | 0805ZC103KA72A |
| 廠商: | AVX Corporation |
| 英文描述: | General Specifications |
| 中文描述: | 一般規(guī)格 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 5/20頁 |
| 文件大小: | 338K |
| 代理商: | 0805ZC103KA72A |
53
In specifying capacitance change with temperature for Class
2 materials, EIA expresses the capacitance change over an
operating temperature range by a 3 symbol code. The first
symbol represents the cold temperature end of the temper-
ature range, the second represents the upper limit of the
operating temperature range and the third symbol repre-
sents the capacitance change allowed over the
operating temperature range. Table 1 provides a detailed
explanation of the EIA system.
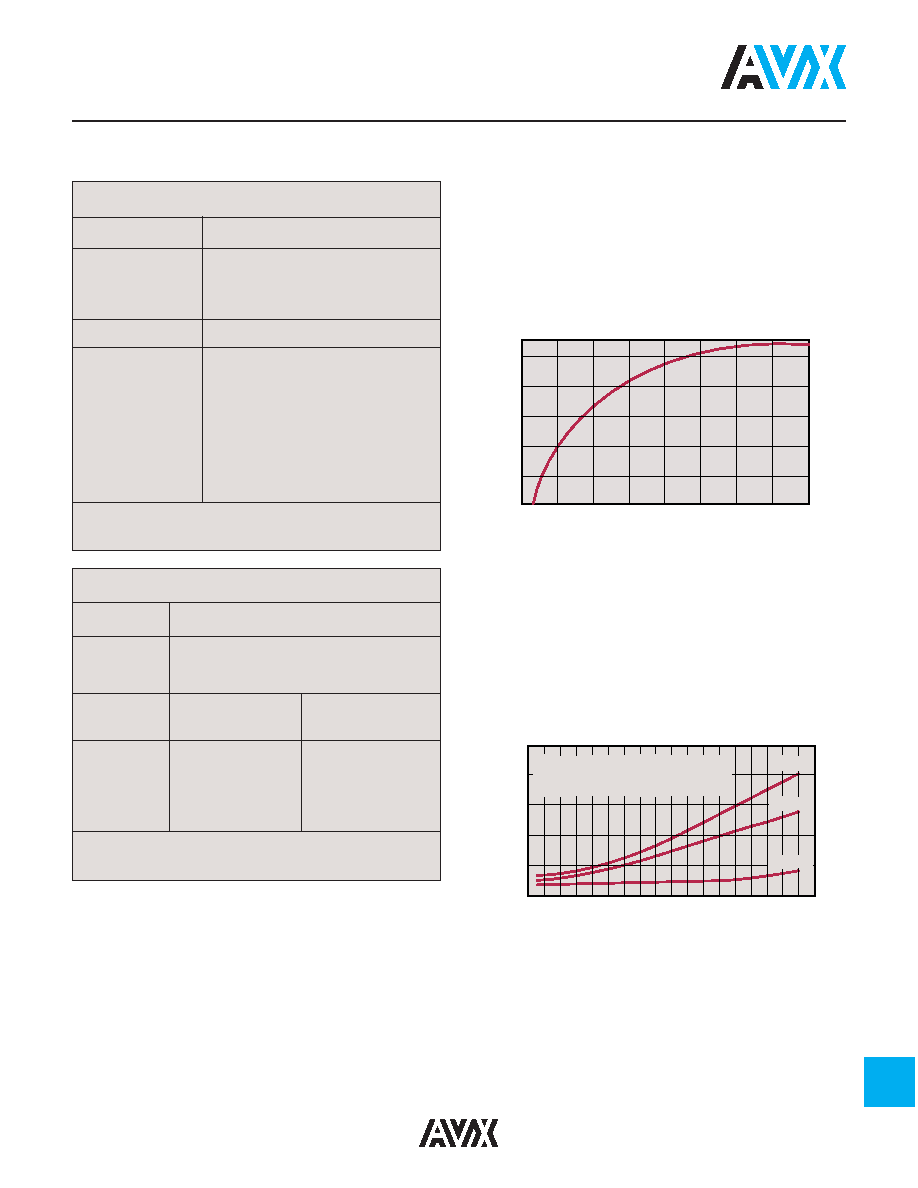
Effects of Voltage – Variations in voltage have little effect
on Class 1 dielectric but does affect the capacitance and
dissipation factor of Class 2 dielectrics. The application of
DC voltage reduces both the capacitance and dissipation
factor while the application of an AC voltage within a
reasonable range tends to increase both capacitance and
dissipation factor readings. If a high enough AC voltage is
applied, eventually it will reduce capacitance just as a DC
voltage will. Figure 2 shows the effects of AC voltage.
Capacitor specifications specify the AC voltage at which to
measure (normally 0.5 or 1 VAC) and application of the
wrong voltage can cause spurious readings. Figure 3 gives
the voltage coefficient of dissipation factor for various AC
voltages at 1 kilohertz. Applications of different frequencies
will affect the percentage changes versus voltages.
Typical effect of the application of DC voltage is shown in
Figure 4. The voltage coefficient is more pronounced for
higher K dielectrics. These figures are shown for room tem-
perature conditions. The combination characteristic known
as voltage temperature limits which shows the effects of
rated voltage over the operating temperature range is
shown in Figure 5 for the military BX characteristic.
General Description
Figure 2
50
40
30
20
10
0
12.5
25
37.5
50
Volts AC at 1.0 KHz
Capacitance
Change
Percent
Cap. Change vs. A.C. Volts
X7R
Figure 3
Curve 3 - 25 VDC Rated Capacitor
Curve 2 - 50 VDC Rated Capacitor
Curve 1 - 100 VDC Rated Capacitor
Curve 3
Curve 2
Curve 1
.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
AC Measurement Volts at 1.0 KHz
Dissipation
Factor
Percent
10.0
8.0
6.0
4.0
2.0
0
D.F. vs. A.C. Measurement Volts
X7R
EIA CODE
Percent Capacity Change Over Temperature Range
RS198
Temperature Range
X7
-55°C to +125°C
X5
-55°C to +85°C
Y5
-30°C to +85°C
Z5
+10°C to +85°C
Code
Percent Capacity Change
D±3.3%
E±4.7%
F±7.5%
P±10%
R±15%
S±22%
T
+22%, -33%
U
+22%, - 56%
V
+22%, -82%
MIL CODE
Symbol
Temperature Range
A
-55°C to +85°C
B
-55°C to +125°C
C
-55°C to +150°C
Symbol
Cap. Change
Zero Volts
Rated Volts
R
+15%, -15%
+15%, -40%
W
+22%, -56%
+22%, -66%
X
+15%, -15%
+15%, -25%
Y
+30%, -70%
+30%, -80%
Z
+20%, -20%
+20%, -30%
Table 1: EIA and MIL Temperature Stable and General
Application Codes
EXAMPLE – A capacitor is desired with the capacitance value at 25°C
to increase no more than 7.5% or decrease no more than 7.5% from
-30°C to +85°C. EIA Code will be Y5F.
Temperature characteristic is specified by combining range and
change symbols, for example BR or AW. Specification slash sheets
indicate the characteristic applicable to a given style of capacitor.
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 0805ZC103KA74A | General Specifications |
| 0805ZC103MA72A | General Specifications |
| 0805ZC103MA74A | General Specifications |
| 0805 | Case No. 0805 Device |
| 0805-T | Case No. 0805 Device |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| CP2104 | 制造商:SILABS 制造商全稱:SILABS 功能描述:USB DRIVER CUSTOMIZATION |
| CP2104EK | 功能描述:界面開發(fā)工具 Evaluation kit RoHS:否 制造商:Bourns 產品:Evaluation Boards 類型:RS-485 工具用于評估:ADM3485E 接口類型:RS-485 工作電源電壓:3.3 V |
| CP2104-F03-GM | 功能描述:輸入/輸出控制器接口集成電路 USB to UART bridge RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 產品: 輸入/輸出端數(shù)量: 工作電源電壓: 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-64 封裝:Tray |
| CP2104-F03-GMR | 功能描述:輸入/輸出控制器接口集成電路 USB to UART bridge RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 產品: 輸入/輸出端數(shù)量: 工作電源電壓: 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-64 封裝:Tray |
| CP2104-MINIEK | 制造商:Silicon Laboratories Inc 功能描述:KIT EVAL FOR CP2104-MINI |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。