- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371353 > 20BT-5 (Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc.) THERMOPILE TYPE INFRARED SENSOR PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | 20BT-5 |
| 廠商: | Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | THERMOPILE TYPE INFRARED SENSOR |
| 中文描述: | 熱電型紅外傳感器 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 33/44頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 669K |
| 代理商: | 20BT-5 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)當(dāng)前第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)
33
ZENAMIC has the forward-reverse symmetrical
electrical characteristics as shown in the figure 1.
The voltage-current curves show the varistor
characteristics in the range 1 A to 10
A, and show
the resistance characteristics for the range under
1 A and over 10
A in the figure 2.
The voltage across terminals when test current(It:
1 mA)is applied to ZENAMIC is the standard varistor
voltage(Vz), and the voltage across terminals when
a standard surge(Ip) is applied represents the
maximum suppression voltage(Vc).
Z 10 D 221
Varistor voltage
D series
Element diameter
ZENAMIC symbol
V- characteristics
A surge waveform varies according to the sources.
An EXP waveform is used for surge testing of
ZENAMIC, while a AC half-wave is used for the
energy absorption test. The EXP waveform reaches
its peak voltage (current) at [ta] as shown in the
figure 5, and then decreases as time passes and
reaches half of the peak voltage (current) at [tb].
This type of the EXP waveform is shown as a [ta/tb]
voltage (current) waveform. For surge testing
of ZENAMIC, the 8/20
sec current waveform is
used.
Surge waveform
Power lines and surge absorption units with error
display (SA series).
Applications
In the small current range, ZENAMIC features
outstanding temperature characteristics. A shunt
resistance Rp of metal oxide varistor has the
temperature characteristics which is determined by
the following equation.
Rp AeEg
/
2kT
Temperature characteristics
1.A surge excess of the specified Maximum Peak
Current may cause short circuit or mechanical
damage. The following measures are recommended.
In case that ZENAMIC is used in line to ground, the
ground fault circuit interrupter shall be applied in
location A or thermally coupled fuse shall be
applied in location C.
ZENAMIC shall not be used near heat generating
device and free from direct sunlight.
ZENAMIC shall not be used near the flammable
materials.
1) Location of the over current protector(circuit breaker
or current fuse)shall be in the power line to the
circuit(Location A)or in series with ZENAMIC
(Location B).
2) It recommended that a fuse listed in the table be put
in location A or B.
3) In case that ZENAMIC is used in line to ground, the
ground fault circuit interrupter should be applied in
location A or thermally coupled fuse should be applied
in location C.
Part Number
Rating of fuse
3A max.
Application notes(General)
Part No.
0
200
200
400
400
0
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
Current (A)
Time( s)
C
V
Fig 1
Fig 5
5
10
20
50
200
500
100
2,000
1,000
10
10
9
10
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
1
10
0
10
1
10
Current (A)
2
10
3
10
4
10
V
Fig 2
Clamping voltage
Varistor voltage
R
p
R
s
Test current
Surge current
I
C
E
10
20
50
40
30
200
500
400
300
100
10
10
9
10
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
Current (A)
2
10
1
10
V
Fig 3
100
90
50
10
0
ta
tb
T:Absolute temperature
k:Boltzmann constant
A, Eg:constants
As shown in the figure 3, the temperature dependence
characteristics are shown clearly in the low current area.
(2)
Test current
25 C
60 C 90 C 120 C
Protected
Equipment
COM
.
Surge protection of
signal Line
Surge protection of
telephone Line
Telephone
Protected
circuit
Power line
A
B
C
Protected
circuit
5A max.
7A max.
Part Number
Rating of fuse
Refer to the related Safety Standards.
10A max.
15A max.
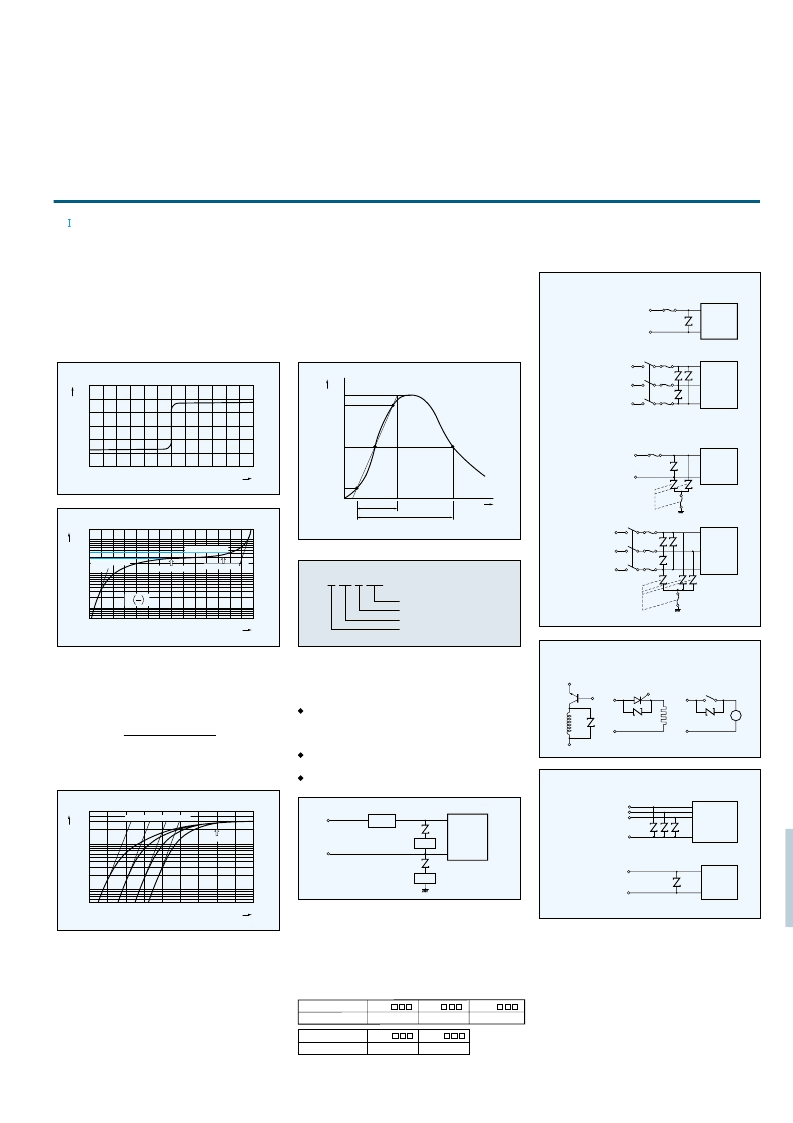
Line to line protection
Line to line and line to ground protection
Single line and telephone line surge protection
DC
AC single phase
AC three phase
Protected
circuit
f
Protected
circuit
DC
AC single phase
Switching surge
protection
Semiconductor
protection
Contact spark
suppression
f
f
f
f
f
AC three phase
Protected
circuit
f
f
f
f
Thermal
coupling
Thermal
coupling
M
Motor
Z5D
Z7D
Z10D
Z15D
Z21D
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 20BT-6 | THERMOPILE TYPE INFRARED SENSOR |
| 20KD-5 | THERMOPILE TYPE INFRARED SENSOR |
| 200FXG13 | DIODE (HIGH SPEED RECTIFIER APPLICATIONS) |
| 200FXH13 | DIODE (HIGH SPEED RECTIFIER APPLICATIONS) |
| 200GA120DN2 | IGBT Module |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| 20BT-6 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:THERMOPILE TYPE INFRARED SENSOR |
| 20C005G | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:Industrial Control IC |
| 20C010G | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:Industrial Control IC |
| 20C015G | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱(chēng):未知廠家 功能描述:Industrial Control IC |
| 20C02 | 制造商:THORDARSON 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。