- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371370 > 2184 (Analog Devices, Inc.) DSP Microcomputer PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | 2184 |
| 廠商: | Analog Devices, Inc. |
| 元件分類: | 數(shù)字信號處理 |
| 英文描述: | DSP Microcomputer |
| 中文描述: | DSP微機 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 4/31頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 213K |
| 代理商: | 2184 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁當前第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁
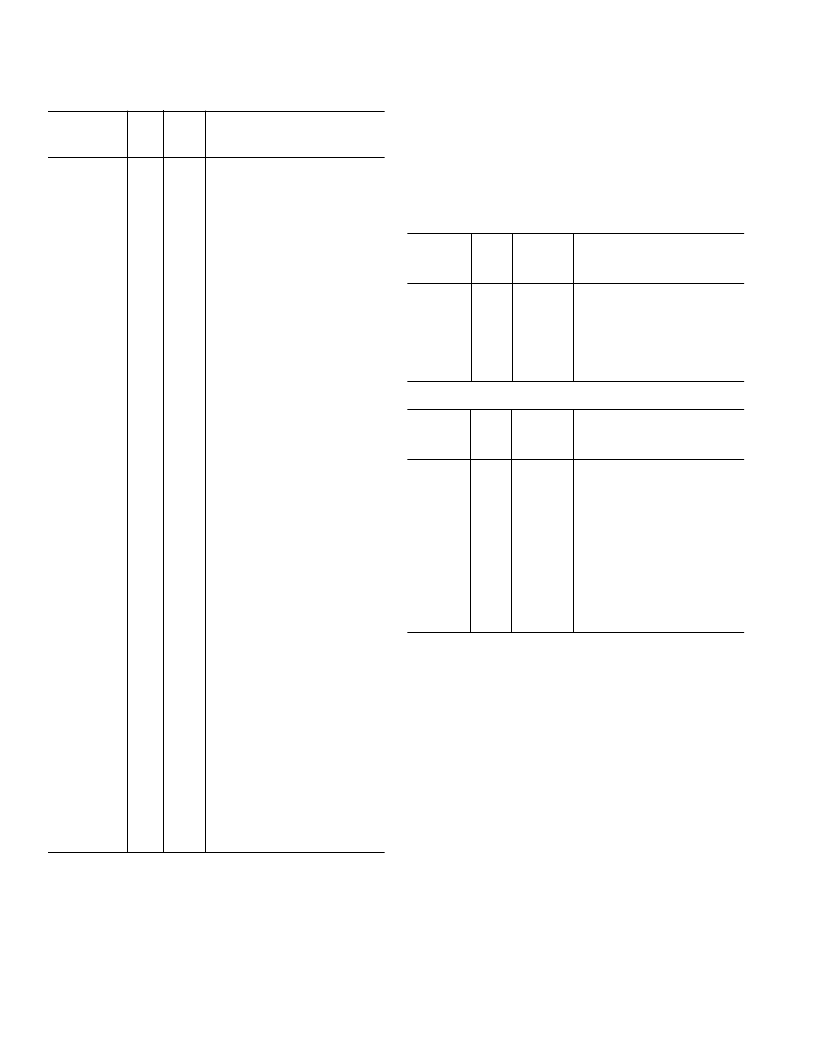
ADSP-2184
–4–
REV. 0
Common-Mode Pins
#
of
Pins put
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Input/
Out-
Pin
Name(s)
RESET
BR
BG
BGH
DMS
PMS
IOMS
BMS
CMS
RD
WR
IRQ2/
Function
Processor Reset Input
Bus Request Input
Bus Grant Output
Bus Grant Hung Output
Data Memory Select Output
Program Memory Select Output
I/O Memory Select Output
Byte Memory Select Output
Combined Memory Select Output
Memory Read Enable Output
Memory Write Enable Output
Edge- or Level-Sensitive
Interrupt Request
1
Programmable I/O Pin
Level-Sensitive Interrupt Requests
1
Programmable I/O Pin
Level-Sensitive Interrupt Requests
1
Programmable I/O Pin
Edge-Sensitive Interrupt Requests
1
Programmable I/O Pin
Programmable I/O Pin
Mode Select Input—Checked
only During
RESET
Programmable I/O Pin During
Normal Operation
Mode Select Input—Checked
only During
RESET
Programmable I/O Pin During
Normal Operation
Mode Select Input—Checked
only During
RESET
Programmable I/O Pin During
Normal Operation
Clock or Quartz Crystal Input
Processor Clock Output
Serial Port I/O Pins
Serial Port I/O Pins
Edge- or Level-Sensitive Interrupts,
Flag In, Flag Out
2
Power-Down Control Input
Power-Down Control Output
Output Flags
Power and Ground
For Emulation Use
I
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
I
PF7
IRQL0/
PF5
IRQL1/
PF6
IRQE/
PF4
PF3
Mode C/
I/O
I
I/O
I
I/O
I
I/O
I/O
I
1
1
1
1
1
PF2
I/O
Mode B/
1
I
PF1
I/O
Mode A/
1
I
PF0
I/O
CLKIN, XTAL
CLKOUT
SPORT0
SPORT1/
IRQ1:0
FI, FO
PWD
PWDACK
FL0, FL1, FL2
V
DD
and GND
EZ-Port
2
1
5
5
I
O
I/O
I/O
1
1
3
16
9
I
O
O
I
I/O
NOTES
1
Interrupt/Flag pins retain both functions concurrently. If IMASK is set to
enable the corresponding interrupts, the DSP will vector to the appropriate
interrupt vector address when the pin is asserted, either by external devices or
set as a programmable flag.
2
SPORT configuration determined by the DSP System Control Register. Soft-
ware configurable.
Memory Interface Pins
The ADSP-2184 processor can be used in one of two modes:
Full Memory Mode, which allows BDMA operation with full
external overlay memory and I/O capability, or Host Mode,
which allows IDMA operation with limited external addressing
capabilities. The operating mode is determined by the state of
the Mode C pin during RESET and cannot be changed while
the processor is running.
Full Memory Mode Pins (Mode C = 0)
#
of
Input/
Pin Name
Pins
Output
Function
A13:0
14
O
Address Output Pins for Pro-
gram, Data, Byte and I/O Spaces
Data I/O Pins for Program,
Data, Byte and I/O Spaces
(8 MSBs Are Also Used as
Byte Memory Addresses)
D23:0
24
I/O
Host Mode Pins (Mode C = 1)
#
of
Pin Name
Pins
Input/
Output
Function
IAD15:0
A0
16
1
I/O
O
IDMA Port Address/Data Bus
Address Pin for External I/O,
Program, Data, or Byte Access
Data I/O Pins for Program,
Data Byte and I/O Spaces
IDMA Write Enable
IDMA Read Enable
IDMA Address Latch Pin
IDMA Select
IDMA Port Acknowledge
D23:8
16
I/O
IWR
IRD
IAL
IS
IACK
1
1
1
1
1
I
I
I
I
O
In Host Mode, external peripheral addresses can be decoded using the A0,
BMS
,
CMS
,
PMS
,
DMS
, and
IOMS
signals.
Setting Memory Mode
Memory Mode selection for the ADSP-2184 is made during
chip reset through the use of the Mode C pin. This pin is multi-
plexed with the DSP’s PF2 pin, so care must be taken in how
the mode selection is made. The two methods for selecting the
value of Mode C are passive and active.
Passive configuration involves the use a pull-up or pull-down
resistor connected to the Mode C pin. To minimize power
consumption, or if the PF2 pin is to be used as an output in the
DSP application, a weak pull-up or pull-down, on the order of
100 k
, can be used. This value should be sufficient to pull the
pin to the desired level and still allow the pin to operate as a
programmable flag output without undue strain on the processor’s
output driver. For minimum power consumption during
power-down, reconfigure PF2 to be an input, as the pull-up or
pull-down will hold the pin in a known state, and will not switch.
Active configuration involves the use of a three-stateable exter-
nal driver connected to the Mode C pin. A driver’s output en-
able should be connected to the DSP’s
RESET
signal such that
it only drives the PF2 pin when
RESET
is active (low). After
RESET
is deasserted, the driver should three-state, thus allow-
ing full use of the PF2 pin as either an input or output.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 218 | Interface IC |
| 21904 | MARKER LABORATORY BLACK |
| 21906 | Low-Frequency, Spread-Spectrum EconOscillator |
| 2191G140IP | Low-Frequency, Spread-Spectrum EconOscillator |
| 2191G-160IP | Low-Frequency, Spread-Spectrum EconOscillator |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| 218-4"x60yd | 功能描述:膠帶 218 4 X 60 YD BULK RoHS:否 制造商:3M Electronic Specialty 產(chǎn)品:Tapes 類型:Shielding 描述/功能:EMI/RFI Foil Shielding Tape 顏色: 材料:Copper Foil 寬度:1 in x 18 yds |
| 218400 | 制造商:LITTELFUSE 制造商全稱:Littelfuse 功能描述:5 x 20 mm Time Lag Fuse (Slo-Blo) Fuse |
| 2-1840026-1 | 制造商:TRP CONNECTOR LTD. 功能描述:MAG45(TM) RJ45/USB 10/100 UR204P12 W LED - Trays 制造商:TRP CONNECTOR B.V. 功能描述:MAG45 RJ45/USB 10/100 UR204P12 |
| 218400P | 制造商:LITTELFUSE 制造商全稱:Littelfuse 功能描述:5 x 20 mm Time Lag Fuse (Slo-Blo) Fuse |
| 218402-000 | 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:CBL 1CNDCTR 16AWG 1.96MM NKL PLTD CPPR RD 600VAC - Cable Rools/Shrink Tubing 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:22759/41-16-2 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:High Performance Cable 1Conductors 16AWG 1.96mm Nickel Plated Copper Red 600VAC |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。