- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄30694 > 473CT-4 (Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc.) THERMOPILE TYPE INFRARED SENSOR PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | 473CT-4 |
| 廠商: | Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | THERMOPILE TYPE INFRARED SENSOR |
| 中文描述: | 熱電型紅外傳感器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 15/44頁 |
| 文件大小: | 669K |
| 代理商: | 473CT-4 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁當(dāng)前第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁
22
Thermal time constant
If ambient temperature of a thermistor is changed
to T1 from T2 suddenly, temperature of the thermistor
changes slowly.
The time constant means the time when temperature
of the thermistor reaches 63% of the temperature
difference.
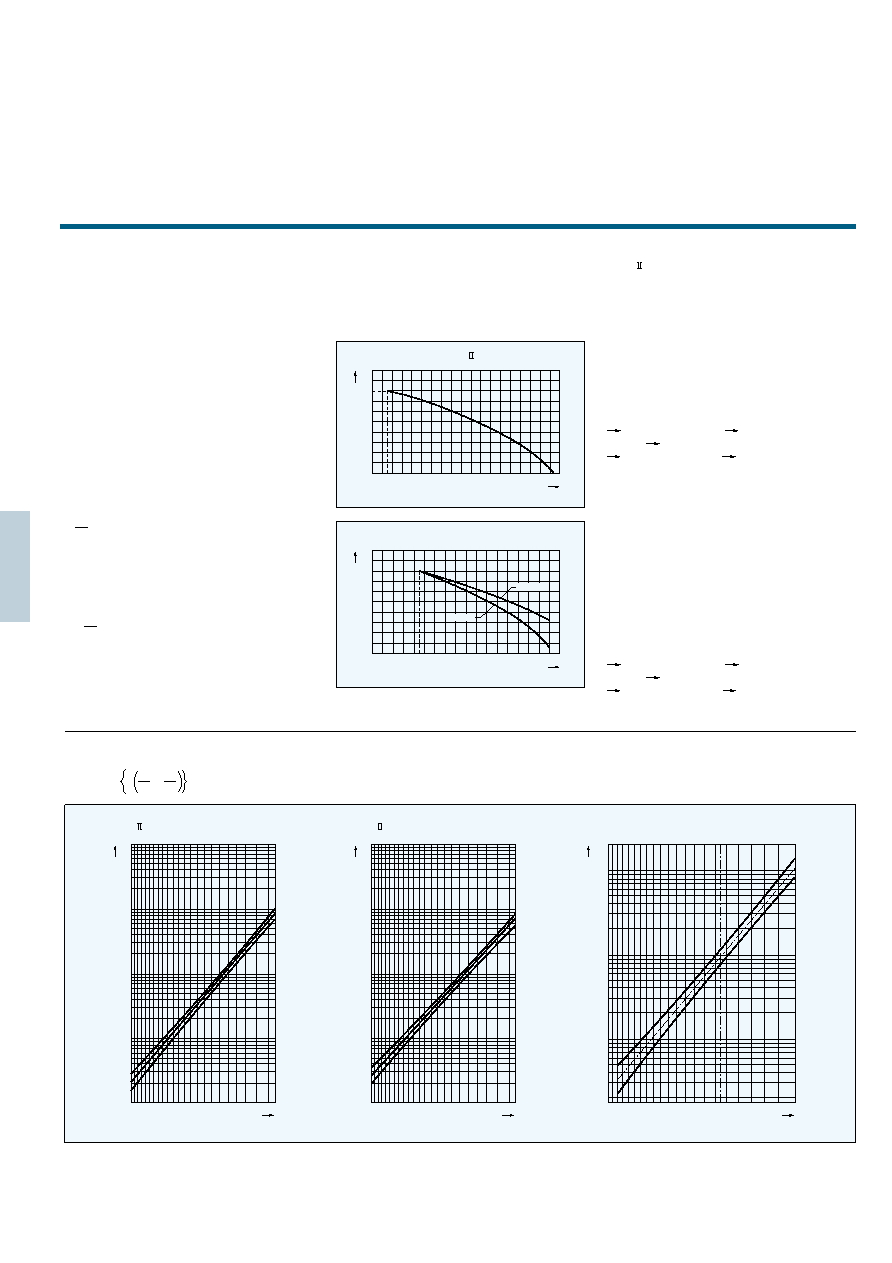
Maximum permissible current
If the maximum permissible current flows to a
thermistor at 25 C, temperature of the thermistor
rises to 200 C, (160 C). When ambient temperature is
above 25 C, the maximum permissible current shall be
over reduced as the maximum permissible current
reduction curve.
Reliability tests
Dry heat test
MARK
Test sample is exposed in air at 200 C for 1,000
hours.
R25/R25
20%
Damp heat test
Test sample is exposed in atmosphere of 95%RH at
40 C for 1,000 hours.
R25/R25
10%
Load test
Test sample is applied the maximum rating current
in air at 25 C for 1,000 hours.
R25/R25
20%
Change of temperature
Test sample is given 10 times of the following
temperature cycle,
40 C for 30 minutes
room temperature for 5
minutes
200 C for 30 minutes
room temperature for 5
minutes.
R25/R25
10%
Residual resistance
If current is flowed through a thermistor, any heat
will be generated in the thermistor by which its
resistance will be decreased, however, a decrease
of a resistance will be stabilized at a saturation
resistance value which is determined by impressed
electric power and a dissipation constant. The
residual resistance value means maximum
saturation resistance value when the maximum
permissible current is flowed through the thermistor.
Temperature coefficient
The temperature coefficient of a thermistor is
expressed by the following equation ;
Dissipation factor
If small voltage is applied to a thermistor, small
current will flow which produce enough heat in the
thermistor. Dissipation factor is electric power
which make 1 C raise by heat in a thermistor.
Resistance-temperature characteristics
The theoretical characteristics of a thermistor is expressed by following equation.
P is applied electric power.
t is rised temperature of the thermistor.
New Power Thermistor MARK
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200
Ambient temperature ( C)
Current
derating
ratio
Power Thermistor
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
20
10
10 0
30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160
Ambient temperature ( C)
Temperature ( C)
Resistance
change
ratio
Current
derating
ratio
D TYPE
W TYPE
(%/ C)
T2
B
exp B
T1
R1
R1 is the zero-power resistance at absolute temperature T1
R2 is the zero-power resistance at absolute temperature T2
R2
1
T2
1
(mW/ C)
t
P
MARK
B : 3150K
Dry heat test
POWER THERMISTOR
Test sample is exposed in air at 160 C for 1,000
hours.
R25/R25
10%
Damp heat test
Test sample is exposed in atmosphere of 95%RH at
40 C for 1,000 hours.
R25/R25
10%
Load test
Test sample is applied the maximum rating current
in air at 25 C for 1,000 hours.
R25/R25
10%
Change of temperature
Test sample is given 10 times of the following
temperature cycle,
30 C for 30 minutes
room temperature for 5
minutes
160 C for 30 minutes
room temperature for 5
minutes.
R25/R25
10%
B is constant which depends on the material used to
make the thermistor. Unless otherwise specified, all
values of B are determined from measurements made
at 25 C and 85 C.
200
0.01
0.1
1.0
10
100
160
100
50
25
0
Temperature ( C)
Resistance
change
ratio
MARK
B : 2900K
200
0.01
0.1
1.0
10
100
160
100
50
25
0
Temperature ( C)
Resistance
change
ratio
Power Thermistor
B : 3250K
0.02
0.03
0.05
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.5
1.0
2.0
3.0
5.0
10.0
20.0
160
100
50
25
30
0
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 473F04PP460R | POLYPROPYLENE-FOIL SELF CASED AXIAL LEADS |
| 473F04PP481R | POLYPROPYLENE-FOIL SELF CASED AXIAL LEADS |
| 473F04PP580R | CONV DC/DC 5VIN ADJ OUT 15A SMD |
| 473F06PP460R | POLYPROPYLENE-FOIL SELF CASED AXIAL LEADS |
| 473F06PP481R | CONV DC/DC 5VIN ADJ OUT 22A |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| 473F04PP460R | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:POLYPROPYLENE-FOIL SELF CASED AXIAL LEADS |
| 473F04PP481R | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:POLYPROPYLENE-FOIL SELF CASED AXIAL LEADS |
| 473F04PP580R | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:POLYPROPYLENE-FOIL SELF CASED AXIAL LEADS |
| 473F06PP460R | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:POLYPROPYLENE-FOIL SELF CASED AXIAL LEADS |
| 473F06PP481R | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:POLYPROPYLENE-FOIL SELF CASED AXIAL LEADS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。