- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄24804 > 935263377025 (NXP SEMICONDUCTORS) SPECIALTY TELECOM CIRCUIT, UUC8 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | 935263377025 |
| 廠商: | NXP SEMICONDUCTORS |
| 元件分類: | 通信及網(wǎng)絡 |
| 英文描述: | SPECIALTY TELECOM CIRCUIT, UUC8 |
| 封裝: | DIE-8 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 14/18頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 156K |
| 代理商: | 935263377025 |
1998 Jul 08
5
Philips Semiconductors
Objective specication
SDH/SONET STM1/OC3 transimpedance amplier
TZA3033
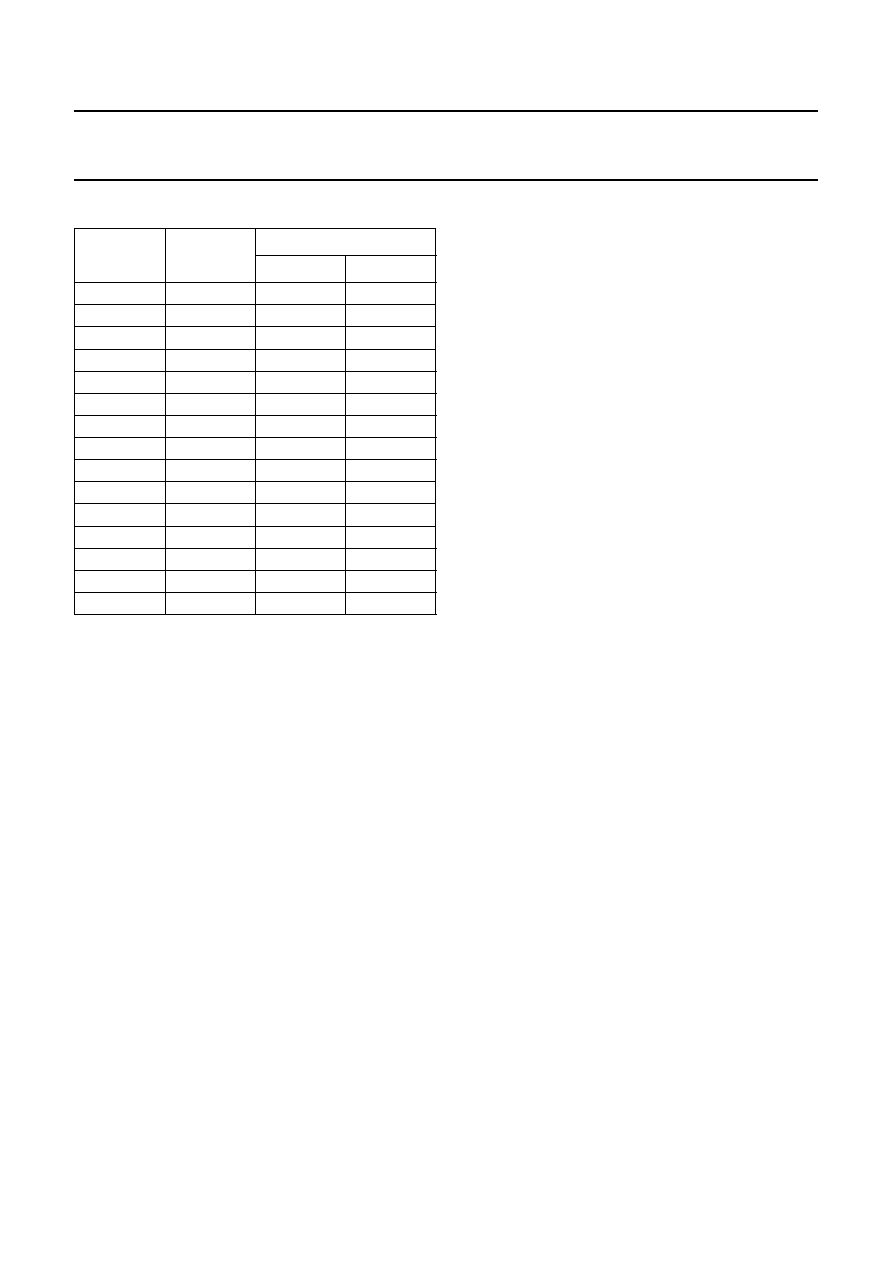
Pad centre locations
Note
1. All coordinates (
m) are measured with respect to the
bottom left-hand corner of the die.
SYMBOL
PAD
COORDINATES(1)
xy
DREF
1
95
881
TESTA
2
95
735
GND
3
95
618
GND
4
95
473
IPhoto
5
95
285
TESTB
6
95
147
GND
7
215
95
GND
8
360
95
GND
9
549
95
GND
10
691
95
OUT
11
785
501
OUTQ
12
785
641
VCC
13
567
1055
VCC
14
424
1055
AGC
15
259
1055
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TZA3033 is a transimpedance amplifier intended for
use in fibre optic links for signal recovery in STM1/OC3
applications. It amplifies the current generated by a photo
detector (PIN diode or avalanche photodiode) and
transforms it into a differential output voltage. The most
important characteristics of the TZA3033 are high receiver
sensitivity and wide dynamic range.
High receiver sensitivity is achieved by minimizing noise in
the transimpedance amplifier.
The signal current generated by a PIN diode can vary
between 0.25
A to 1.6 mA (peak-to-peak value).
An AGC loop (see Fig.1) is implemented to make it
possible to handle such a wide dynamic range.
The AGC loop increases the dynamic range of the
receiver by reducing the feedback resistance of the
preamplifier. The AGC loop hold capacitor is integrated
on-chip, so an external capacitor is not needed for AGC.
The AGC voltage can be monitored at pad 15 on the naked
die (TZA3033U). Pad 15 is not bonded in the packaged
device (TZA3033T). This pad can be left unconnected
during normal operation. It can also be used to force an
external AGC voltage. If pad 15 (AGC) is connected to
VCC, the internal AGC loop is disabled and the receiver
gain is at a maximum. The maximum input current is then
about 10
A.
A differential amplifier converts the output of the
preamplifier to a differential voltage. The data output circuit
is given in Fig.4.
The logic level symbol definitions are shown in Fig.5.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 07CM-20S12L | Bus Converter 48V Input / 12V Output / 20A |
| 07CM-30S08L | Bus Converter 48V Input / 12V Output / 20A |
| 07CM-30S08HG | DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| 0RCM-20S12HG | DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| 0RCM-30S08LG | DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| 935264217557 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:SUB ONLY IC |
| 935267356112 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:IC TEA1507PN |
| 935268081112 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:SUB ONLY IC |
| 935268721125 | 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:Buffer/Line Driver 1-CH Non-Inverting 3-ST CMOS 5-Pin TSSOP T/R |
| 935269304128 | 制造商:ST-Ericsson 功能描述:IC AUDIO CODEC W/TCH SCRN 48LQFP |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。