- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄366453 > AM29LV004T-90REC (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC) CAP TANT LOWESR 68UF 10V 20% SMD PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | AM29LV004T-90REC |
| 廠商: | ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC |
| 元件分類: | PROM |
| 英文描述: | CAP TANT LOWESR 68UF 10V 20% SMD |
| 中文描述: | 512K X 8 FLASH 3V PROM, 90 ns, PDSO40 |
| 封裝: | TSOP-40 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 12/36頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 455K |
| 代理商: | AM29LV004T-90REC |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁當(dāng)前第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁
12
Am29LV004
P R E L I M I N A R Y
Autoselect Command Sequence
The autoselect command sequence allows the host
system to access the manufacturer and devices codes,
and determine whether or not a sector is protected.
Table 5 shows the address and data requirements.
This method is an alternative to that shown in Table 4,
which is intended for PROM programmers and requires
V
ID
on address bit A9.
The autoselect command sequence is initiated by writ-
ing two unlock cycles, followed by the autoselect com-
mand. The device then enters the autoselect mode,
and the system may read at any address any number
of times, without initiating another command sequence.
A read cycle at address XX00h retrieves the manufac-
turer code. A read cycle at address XX01h returns the
device code. A read cycle containing a sector address
(SA) and the address 02h returns 01h if that sector is
protected, or 00h if it is unprotected. Refer to Tables 2
and 3 for valid sector addresses.
The system must write the reset command to exit the
autoselect mode and return to reading array data.
Byte Program Command Sequence
Programming is a four-bus-cycle operation. The pro-
gram command sequence is initiated by writing two un-
lock write cycles, followed by the program set-up
command. The program address and data are written
next, which in turn initiate the Embedded Program al-
gorithm. The system is notrequired to provide further
controls or timings. The device automatically provides
internally generated program pulses and verify the pro-
grammed cell margin. Table 5 shows the address and
data requirements for the byte program command se-
quence.
When the Embedded Program algorithm is complete,
the device then returns to reading array data and ad-
dresses are no longer latched. The system can deter-
mine the status of the program operation by using
DQ7, DQ6, or RY/BY#. See “Write Operation Status”
for information on these status bits.
Any commands written to the device during the Em-
bedded Program Algorithm are ignored. Note that a
hardware reset
immediately terminates the program-
ming operation. The Byte Program command se-
quence should be reinitiated once the device has reset
to reading array data, to ensure data integrity.
Programming is allowed in any sequence and across
sector boundaries.
A bit cannot be programmed
from a “0” back to a “1”.
Attempting to do so may halt
the operation and set DQ5 to “1”, or cause the Data#
Polling algorithm to indicate the operation was suc-
cessful. However, a succeeding read will show that the
data is still “0”. Only erase operations can convert a “0”
to a “1”.
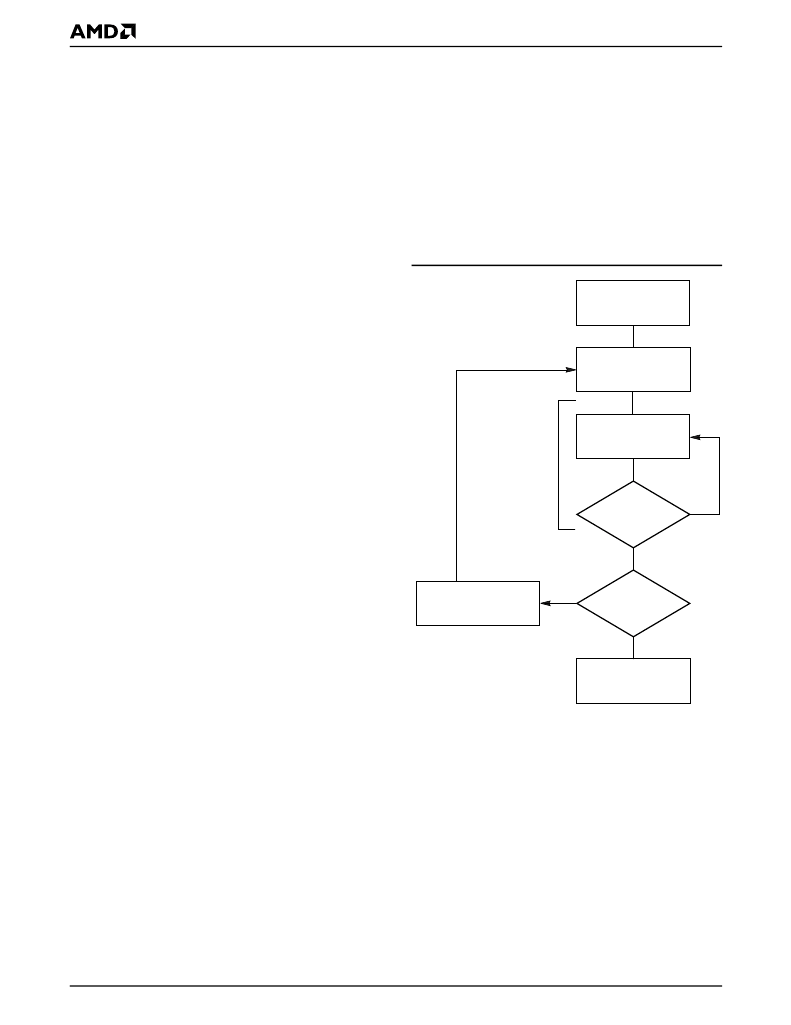
Figure 2 illustrates the algorithm for the program oper-
ation. See the Erase/Program Operations table in “AC
Characteristics” for parameters, and to Figure 14 for
timing diagrams.
Note:
See Table 5 for program command sequence.
Figure 2.
Program Operation
START
Write Program
Command Sequence
Data Poll
from System
Verify Data
No
Yes
Last Address
No
Yes
Programming
Completed
Increment Address
Embedded
Program
algorithm
in progress
21522A-4
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| AM29LV004B-90REC | 4 Megabit (512 K x 8-Bit) CMOS 3.0 Volt-only Boot Sector Flash Memory |
| Am29LV004T-90RFEB | 4 Megabit (512 K x 8-Bit) CMOS 3.0 Volt-only Boot Sector Flash Memory |
| Am29LV004B-90RFEB | 4 Megabit (512 K x 8-Bit) CMOS 3.0 Volt-only Boot Sector Flash Memory |
| AM29LV004B-150EC | 4 Megabit (512 K x 8-Bit) CMOS 3.0 Volt-only Boot Sector Flash Memory |
| AM29LV004T-120EC | 4 Megabit (512 K x 8-Bit) CMOS 3.0 Volt-only Boot Sector Flash Memory |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| AM29LV008BB-120ECT | 制造商:Spansion 功能描述:IC 8MEG X8, 3 V FLASH BOTTOM B |
| AM29LV008BB-120ED | 制造商:Spansion 功能描述:IC SM FLASH 3V 8MB |
| AM29LV008BB-120ED | 制造商:Spansion 功能描述:FLASH MEMORY IC |
| AM29LV008BB-80EC | 制造商:Spansion 功能描述:IC 8MEG X8, 3 V FLASH BOTTOM B - Bulk |
| AM29LV008BB-90ED | 制造商:Spansion 功能描述:Flash Memory IC |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。