- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄376777 > DM6806 (Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc.) DM5806 DATA MODULE DIGITAL I/O BOARD PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | DM6806 |
| 廠商: | Electronic Theatre Controls, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | DM5806 DATA MODULE DIGITAL I/O BOARD |
| 中文描述: | DM5806數(shù)據(jù)模塊數(shù)字I / O板 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 29/64頁 |
| 文件大小: | 270K |
| 代理商: | DM6806 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁當(dāng)前第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁
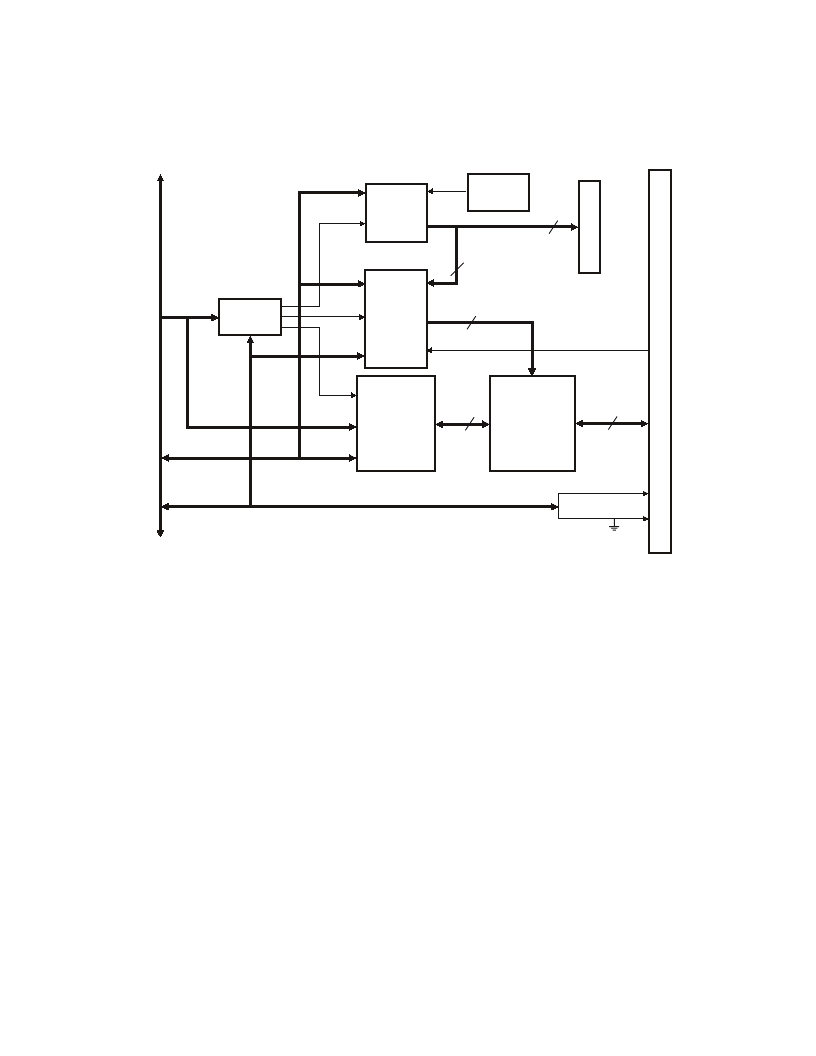
3-3
The DM5806 provides buffered digital I/O lines and three 16-bit timer/counters, as shown Figure 3-1. This
chapter describes the hardware which makes up the digital I/O circuitry, timer/counters, and hardware-selectable
interrupts.
Fig. 3-1 — DM806 Block Diagram
Digital I/O, 8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface
The 8255 programmable peripheral interface (PPI) can be easily configured to solve a wide range of digital
real-world problems. This high-performance TTL/CMOS compatible chip has 24 parallel programmable digital I/O
lines divided into two groups of 12 lines each:
Group A — Port A (8 lines) and Port C Upper (4 lines);
Group B — Port B (8 lines) and Port C Lower (4 lines).
Each group can be programmed for Mode 0 or Mode 1 operation.
Do not try to use Mode 2 operation!
The
DM5806 does not support Mode 2. When operating in Mode 1, the on-board buffers must be removed from the
Port C lines. This procedure is described in Chapter 1 in the S2 DIP switch discussion. The DM5806 operating
modes are:
Mode 0 — Basic input/output. Lets you use simple input and output operation for a port. Data is written to or
read from the specified port.
Mode 1 — Strobed input/output. Lets you transfer I/O data from Port A or Port B in conjunction with strobes or
handshaking signals.
These modes are detailed in the 8255 Data Sheet, reprinted from Intel in Appendix C.
The bidirectional buffers on the 8255’s I/O lines monitor the 8255 control word to automatically set their
direction. Hardware changes to the buffer circuitry is required only when using Mode 1, where the Port C buffers
must be removed as described in Chapter 1.
+5 VOLTS
DIGITAL
GROUND
24
ADDRESS
DECODE
BUFFER
AND
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
ADDRESS
DATA
CONTROL
I
P
EXTINT
BUFFERS
AND
PULL-UP/DOWN
RESISTORS
8255
PPI
24
4
8254
PIT
8 MHz
OSC
I
9
3
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| DM6380L | V.34 Integrated Data/ Fax/Voice/Speakerphone Modem Device Set |
| DM6381F | V.34 Integrated Data/ Fax/Voice/Speakerphone Modem Device Set |
| DM6382F | V.34 Integrated Data/ Fax/Voice/Speakerphone Modem Device Set |
| DM6383F | V.34 Integrated Data/ Fax/Voice/Speakerphone Modem Device Set |
| DM336P | V.34 Integrated Data/ Fax/Voice/Speakerphone Modem Device Set |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| DM6CD330J03 | 制造商:n/a 功能描述:DM6X033 S7B3A |
| DM6-M25 | 制造商:Mencom 功能描述: |
| DM6-MF-25 | 制造商:Mencom 功能描述: |
| DM6-MM-06 | 制造商:Mencom 功能描述: |
| DM6-MM-10 | 制造商:Mencom 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。