- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄358702 > DS89C430 Ultra-High-Speed Flash Microcontrollers PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | DS89C430 |
| 英文描述: | Ultra-High-Speed Flash Microcontrollers |
| 中文描述: | 超高速閃存微控制器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 27/48頁 |
| 文件大小: | 934K |
| 代理商: | DS89C430 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁當前第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁
DS89C430/DS89C440/DS89C450 Ultra-High-Speed Flash Microcontrollers
27 of 48
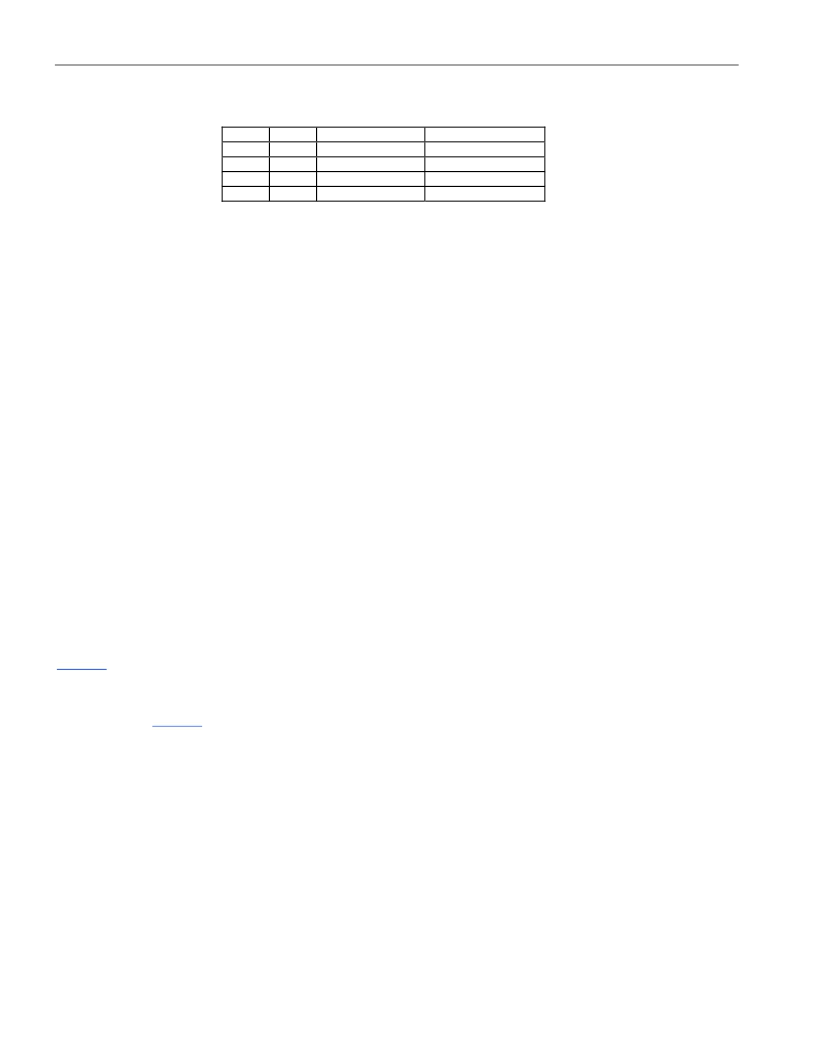
DPTR instruction decrements the DPTR1 contents by 1. With this feature, the user can configure the data pointers
to operate in four ways for the INC DPTR instruction:
ID1
ID0
SEL = 0
0
0
INC DPTR
0
1
DEC DPTR
1
0
INC DPTR
1
1
DEC DPTR
SEL = 1
INC DPTR1
INC DPTR1
DEC DPTR1
DEC DPTR1
SEL (DPS.0) bit always selects the active data pointer. The DS89C430 offers a programmable option that allows
any instructions related to data pointer to toggle the SEL bit automatically. This option is enabled by setting the
toggle-select-enable bit (TSL–DPS.5) to a logic 1. Once enabled, the SEL bit is automatically toggled
after
the
execution of one of the following five DPTR-related instructions:
INC DPTR
MOV DPTR #data16
MOVC A, @A+DPTR
MOVX A, @DPTR
MOVX @DPTR, A
The DS89C430 also offers a programmable option that automatically increases (or decreases) the contents of the
selected data pointer by 1
after
the execution of a DPTR-related instruction. The actual function (increment or
decrement) is dependent on the setting of the ID1 and ID0 bits. This option is enabled by setting the automatic
increment/decrement enable (AID–DPS.4) to a logic 1 and is affected by the following three instructions:
MOVC A, @A+DPTR
MOVX A, @DPTR
MOVX @DPTR, A
External Memory
The DS89C430 executes external memory cycles for code fetches and read/writes of external program and data
memory. A nonpage external memory cycle is four times slower than the internal memory cycles (i.e., an external
memory cycle contains four system clocks). However, a page mode external memory cycle can be completed in
one, two, or four system clocks for a page hit and two, four, or eight system clocks for a page miss, depending on
user selection. The DS89C430 also supports a second page mode operation with a different external bus structure
that provides for fast external code fetches but uses four system clock cycles for data memory access.
External Program Memory Interface (Nonpage Mode)
Figure 7
shows the timing relationship for internal and external code fetches when CD1 and CD0 are set to 10b,
assuming the microcontroller is in nonpage mode for external fetches. Note that an external program fetch takes
four system clocks, and an internal program fetch requires only one system clock.
As illustrated in
Figure 7
, ALE is deasserted when executing an internal memory fetch. The DS89C430 provides a
programmable user option to turn on ALE during internal program memory operation. ALE is automatically enabled
for code fetch externally, independent of the setting of this option.
PSEN
is only asserted for external code fetches, and is inactive during internal execution.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| DS89C440 | Ultra-High-Speed Flash Microcontrollers |
| DS89C450 | Ultra-High-Speed Flash Microcontrollers |
| DS89C21TMX | Transceiver |
| DSDK101 | Low-Cost Demo Kit Motherboard |
| E.FL-LP-040 | CABLE ; Connector type A:MFD-Titan; Connector type B:MFD-Titan; Length, lead:5m |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| DS89C430_07 | 制造商:DALLAS 制造商全稱:Dallas Semiconductor 功能描述:Ultra-High-Speed Flash Microcontrollers |
| DS89C430+ENG | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:MCU 8BIT CISC 16KB FLASH 5V 44TQFP - Trays |
| DS89C430+ENL | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:MICRO HS 44P TQFP 33MHZ IND PB-FREE - Trays |
| DS89C430+MNL | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:MCU 8BIT CISC 16KB FLASH 5V 40PDIP - Rail/Tube |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。