- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄169797 > EQ1101-9 1-OUTPUT 60 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | EQ1101-9 |
| 元件分類: | 電源模塊 |
| 英文描述: | 1-OUTPUT 60 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| 封裝: | METAL, CASE Q01, MODULE |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 6/25頁 |
| 文件大小: | 747K |
| 代理商: | EQ1101-9 |
Cassette Style
DC-DC Converters
Q Series
Edition 5/5.2000
14/25
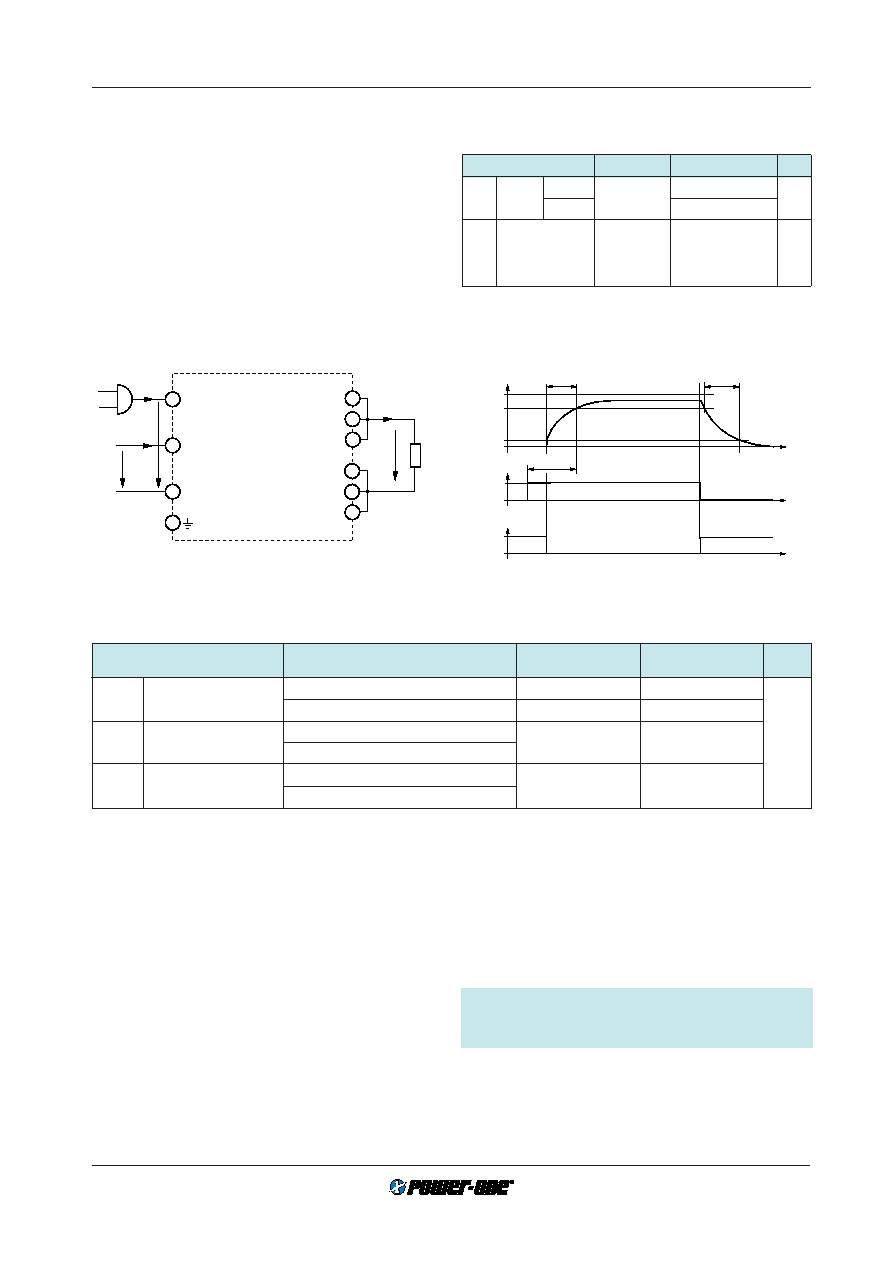
Auxilary Functions
i Inhibit for Remote On and Off
Note: If this function is not actively used, the inhibit pin 28
must be interconnected with the negative input pin 32 to en-
able the output(s). A non-connected pin 28 will be inter-
preted by the internal logic as an active inhibit signal and
therefore output(s) will remain disabled: Fail safe function.
An inhibit input enables (logic low, pull down) or disables
(logic high, pull up) the output if a logic signal e.g. TTL,
CMOS is applied. In systems consisting of several units,
this feature may be used, for example, to control the activa-
tion sequence of the converters by means of logic signals,
or to allow the unit's source for a proper start up before full
load is applied (e.g. in combination with LT units).
Table 6: Inhibit characteristics
Characteristics
Conditions
min typ max
Unit
Uinh Inhibit
Uo = on Ui min...Ui max
–100
0.8
V DC
voltage
Uo = off
TC min...TC max
2.4
100
Iinh
Inhibit current
Uinh = –50 V
–500
A
Uinh =0 V
–40
Uinh = 50 V
+500
Uinh = 100 V
+1000
i
Vi–
Vi+
Vo–
S–
Ui
Io
Uo
RL
Ii
Iinh
Uinh
Vo–
Vo+
S+
28
30
32
26
14
10
8
6
4
12
06091
Fig. 18
Definition of input and output parameters
0
tr
Ui
t
0.8
on
off
Uinh [V]
2.4
0.1
Uo/Uo normal
tf
td on
0.99
1.01
06092
Fig. 19
Output response as a function of input voltage (on/off
switching) or inhibit control
Output Response
The output response when enabling and disabling the out-
put by the inhibit input is shown in the following figure.
Table 7: Output response time with outputs resistively loaded and R-input and P option not used
BQ, CQ, GQ
DQ, EQ
Characteristics
Conditions
min
typ
max
min
typ
max
Unit
td on
Turn-on delay time
Ui = 0 → Ui min, RL = Uo nom/0.5 Io nom
5
850
ms
Ui = 0 → Ui nom, RL = Uo nom/Io nom
3.5
250
tr
Output voltage rise time
Ui = 0 → Ui nom, RL = Uo nom/Io nom
2.5
Ui inh = 2.4 → 0.8 V, RL = Uo nom/Io nom
tf
Output voltage fall time
Ui = Ui nom → 0, RL = Uo nom/Io nom
33
Ui inh = 0.8 → 2.4 V, RL = Uo nom /Io nom
Current Sharing (T Function)
The current sharing facility should be used where several
units are to be operated in parallel for high reliability n+1
redundant systems or in order to provide higher output
powers. Using this feature reduces the stress on the units
and further improves the reliability of the system.
Interconnection of the current sharing terminals T causes
the units to share the output current to the average of all
units. The current tolerance of each unit is approx.
±20% of
the sum of its nominal output currents
Io1 nom + Io2 nom.
In n+1 redundant systems, a failure of a single unit will not
lead to a system failure if the outputs are decoupled by di-
odes. See also
Sense Lines.
Since the voltage on the T pin is referenced to the sense pin
S–, the installer must ensure that the S– pins of all units are
at the same electrical potential, i.e. voltage drops
>50 mV
across the connection lines between these pins shall be
avoided.
BQ...GQ 2000 DC-DC converters with outputs connected
in series can also be paralleled with current sharing, if pins
Vo1– of all units are connected together. See
Sense Lines.
If the output voltages are programmed to a voltage other
than
Uo nom by means of the R pin or option P, the outputs
should be adjusted individually within a tolerance of
±1%.
The current sharing will be less accurate when operating
with dynamic loads.
Important: For applications using the hot plug-in capa-
bilities, dynamic output voltage changes during the plug-
in/plug-out cycles must be considered.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| BQ1001-7R | 1-OUTPUT 82 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| EQ2660-7P | 2-OUTPUT 106 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| CQ92M | epoxy molded silicon Triacs |
| CQ92N | epoxy molded silicon Triacs |
| CQY80N(G) | 1 CHANNEL TRANSISTOR OUTPUT OPTOCOUPLER |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| EQ1-11000 | 制造商:NEC 制造商全稱:NEC 功能描述:Same pin-layout as conventional relay, 70% less relay volume than conventional relay |
| EQ1-11000S | 制造商:NEC 制造商全稱:NEC 功能描述:Same pin-layout as conventional relay, 70% less relay volume than conventional relay |
| EQ1-11040 | 制造商:NEC 制造商全稱:NEC 功能描述:MOTOR AND LAMP CONTROL |
| EQ1-11040S | 制造商:NEC 制造商全稱:NEC 功能描述:MOTOR AND LAMP CONTROL |
| EQ1-11100 | 制造商:NEC 制造商全稱:NEC 功能描述:Same pin-layout as conventional relay, 70% less relay volume than conventional relay |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。