- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄43918 > LH1785-2RD1 (POWER-ONE INC) 1-OUTPUT AC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | LH1785-2RD1 |
| 廠商: | POWER-ONE INC |
| 元件分類: | 電源模塊 |
| 英文描述: | 1-OUTPUT AC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| 封裝: | ROHS COMPLIANT PACKAGE-32/11 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 20/21頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 984K |
| 代理商: | LH1785-2RD1 |
H Series Data Sheet
70 Watt AC-DC Converters
BCD20019 Rev AA
Page 8 of 21
www.power-one.com
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
40
60
70
80
I
o/Io nom
T
A [°C]
1.0
Forced cooling
05142a
T
C max
50
Convection cooling
LH2000
LH3000
LH1000
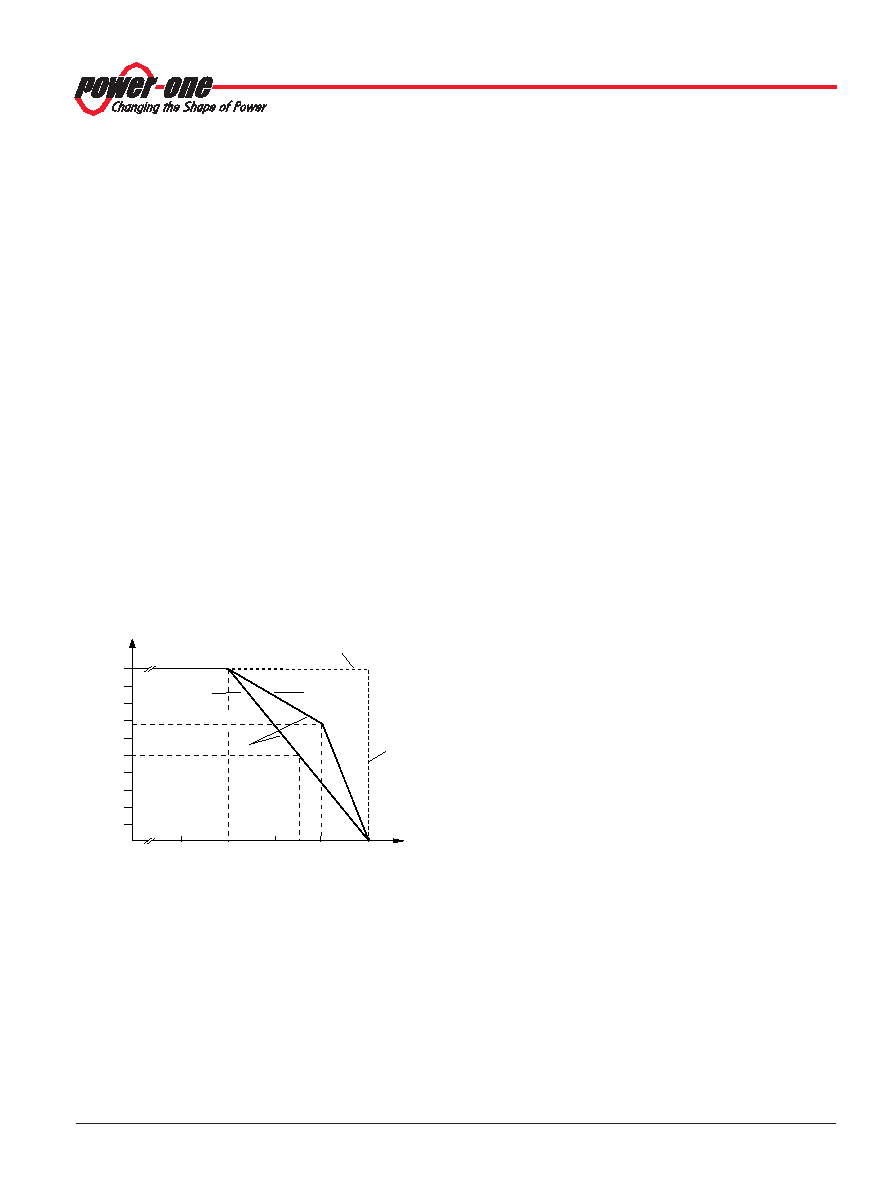
Fig. 9
Output current derating versus temperature
Thermal Considerations and Protection
If a converter is located in free, quasi-stationary air (convection
cooling) at the indicated maximum ambient temperature TA max
(see table Temperature specifications) and is operated at its
nominal input voltage and output power, the temperature
measured at the measuring point of case temperature TC (see
Mechanical Data
) will approach the indicated value TC max after
the warm-up phase. However, the relationship between TA and
TC depends heavily on the conditions of operation and
integration into a system. The thermal conditions are
influenced by input voltage, output current, airflow, and
temperature of surrounding components and surfaces. TA max
is therefore, contrary to TC max, an indicative value only.
Caution:
The installer must ensure that under all operating
conditions TC remains within the limits stated in the table
Temperature specifications.
Notes:
Sufficient forced cooling or an additional heat sink allow TA
to pass over 50 °C, if TC max is not exceeded.
At an ambient temperature TA of 65 °C with only convection
cooling, the maximum permissible current for each output is
approx. 50% of its nominal value; see fig. 9 .
A temperature sensor generates an internal inhibit signal
disabling the outputs, when the case temperature exceeds
TC max.
The outputs automatically recover, when the
temperature drops below this limit.
Parallel and Series Connection
Main outputs of equal nominal voltage can be connected in
parallel. It is important to assure that the main output of a
multiple-output converter is forced to supply a minimum
current of 10% of Io nom to enable correct operation of its own
auxiliary outputs.
In parallel operation, one or more of the main outputs may
operate continuously in current limitation, causing an increase
of the case temperature TC. Consequently, a reduction of the
max. ambient temperature by 10 K is recommended.
Both outputs of a double-output converter may be connected
in parallel without any restriction.
Note:
If output 2 of a double-output converter is not used, we
recommend to connect it in parallel with the main output.
Output 2 and output 3 of a triple-output converter may be
connected in parallel without any restriction.
Note:
If the output 2 or 3 of a triple-output converter is not used, we
recommend to connect it in parallel with the other auxiliary output.
Main or auxiliary outputs can be connected in series with any
other output of the same or another converter. In series
connection, the maximum output current is limited by the
lowest current limit. Output ripple and regulation values are
added. Connection wiring should be kept as short as possible.
If output terminals are connected together in order to establish
multi-voltage configurations, e.g., +5.1 V, ±12 V etc., the
common-ground connecting point should be as close as
possible to the connector of the converter in order to avoid
excessive output ripple voltages.
Auxiliary outputs of different converters should not be
connected in parallel!
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LH1601-2RD4 | 1-OUTPUT 72 W AC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| LH3040-2-D2 | 3-OUTPUT 44 W AC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| LH1782-2RD7 | 1-OUTPUT AC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| LH1501-2R-D7 | 1-OUTPUT AC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| LH1501-2RD6 | 1-OUTPUT 67.5 W AC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LH180M0180BPF-2220 | 制造商:Yageo Corporation 功能描述: |
| LH180M0270BPF-2520 | 制造商:Yageo Corporation 功能描述: |
| LH180M0820BPF-2540 | 制造商:Yageo Corporation 功能描述: |
| LH1842A | 制造商:Advanced Micro Devices 功能描述: |
| LH19/13K | 制造商:FLOWTECH 功能描述:7MMX14MM WHIP HOSE |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。