- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄358828 > LM2711MTX-ADJ (NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP) TFT Panel Module PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | LM2711MTX-ADJ |
| 廠商: | NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | TFT Panel Module |
| 中文描述: | 1.4 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 1500 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO20 |
| 封裝: | TSSOP-20 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 17/20頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 846K |
| 代理商: | LM2711MTX-ADJ |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)當(dāng)前第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)
Operation
(Continued)
performance of the buffers. If the capacitance presented by
the load is less than 5nF external components will be re-
quired as the load itself will not ensure stability. No external
compensation in this case will lead to oscillation of the buffer
and an increase in power consumption. A single 5nF or
greater capacitor on the output will ensure a stable buffer
with no oscillations. For applications requiring a higher slew
rate, a good choice for compensation is to add a 50
(Rox)
in series with a 1nF (Cox) capacitor from the output of the
buffer to ground. This allows for driving zero to infinite ca-
pacitance loads with no oscillations, minimal overshoot, and
a higher slew rate than using a large capacitor. The high
phase margin created by the external compensation will
guarantee stability and good performance for all conditions.
For noise sensitive applications greater output capacitance
may be desired. When the power supply for the buffers (Vs+)
is connected to the output of the switching regulator, the
output ripple of the regulator will produce ripple at the output
of the buffers.
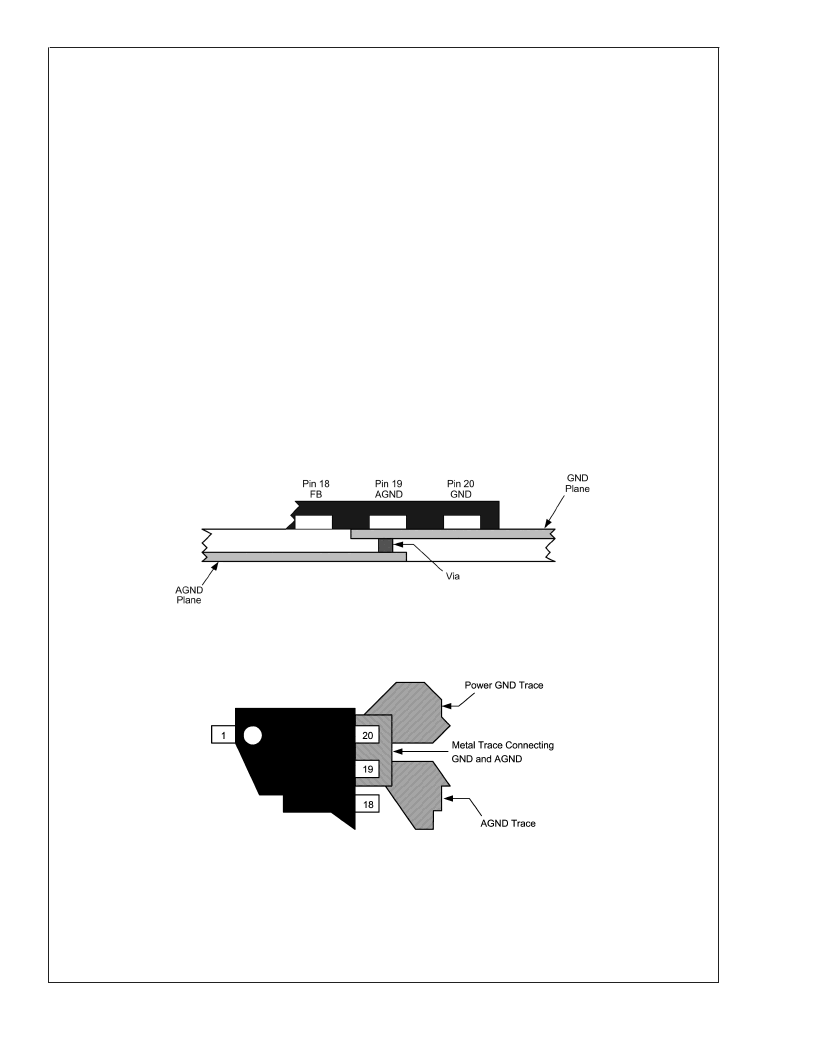
LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS
The LM2711 uses two separate ground connections, GND
for the driver and NMOS power device of the boost regulator
and AGND for the sensitive analog control circuitry of the
boost regulator and the V
COM
and Gamma buffers. The
AGND and GND pins should be tied directly together at the
package, see
Figure 3
and
Figure 4
. The feedback, softstart,
and compensation networks should be connected directly to
a dedicated analog ground plane and this ground plane must
connect to the AGND pin, as in
Figure 3
. If no analog ground
plane is available then the ground connections of the feed-
back, softstart, and compensation networks must tie directly
to the AGND pin, as show in
Figure 4
. Connecting these
networks to the GND pin can inject noise into the system and
effect performance. For 600kHz operation the FSLCT pin
should be tied to an analog ground plane or directly to the
AGND pin. For 1.25MHz operation the FSLCT pin should be
tied to the V
IN
pin.
The input bypass capacitor C
IN
must be placed close to the
IC. This will reduce copper trace resistance which effects
input voltage ripple of the IC. For additional input voltage
filtering, a 100nF bypass capacitor can be placed in parallel
with C
, close to the V
pin, to shunt any high frequency
noise to ground. The output capacitor, C
, should also be
placed close to the IC. Any copper trace connections for the
C
capacitor can increase the series resistance, which
directly effects output voltage ripple and efficiency. The feed-
back network, resistors R1 and R2, should be kept close to
the FB pin, and away from the inductor, to minimize copper
trace connections that can inject noise into the system.
Trace connections made to the inductor and schottky diode
should be minimized to reduce power dissipation and in-
crease overall efficiency.
20046852
FIGURE 3. Multi-Layer Layout
20046853
FIGURE 4. Single Layer Layout
L
www.national.com
17
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LM2711 | TFT Panel Module |
| LM2715MT-ADJ | TFT Panel Module |
| LM2715MTX-ADJ | TFT Panel Module |
| LM2715 | TFT Panel Module |
| LM2716MTX-ADJ | Dual (Step-up and Step-down) PWM DC/DC Converter |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LM2715 | 制造商:NSC 制造商全稱:National Semiconductor 功能描述:TFT Panel Module |
| LM2715_06 | 制造商:NSC 制造商全稱:National Semiconductor 功能描述:TFT Panel Module |
| LM27150 | 制造商:HTC 制造商全稱:HTC Korea TAEJIN Technology Co. 功能描述:1.5A Very L.D.O Voltage Regulator |
| LM27150R-1.5 | 制造商:HTC 制造商全稱:HTC Korea TAEJIN Technology Co. 功能描述:1.5A Very L.D.O Voltage Regulator |
| LM27150R-1.8 | 制造商:HTC 制造商全稱:HTC Korea TAEJIN Technology Co. 功能描述:1.5A Very L.D.O Voltage Regulator |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。