- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄8612 > LTC6406CUD#TRPBF (Linear Technology)IC DIFF AMP/DRIVER R-R 16-QFN PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | LTC6406CUD#TRPBF |
| 廠商: | Linear Technology |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 20/24頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 0K |
| 描述: | IC DIFF AMP/DRIVER R-R 16-QFN |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 2,500 |
| 類型: | ADC 驅(qū)動(dòng)器 |
| 應(yīng)用: | 數(shù)據(jù)采集 |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 封裝/外殼: | 16-WFQFN 裸露焊盤 |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 16-QFN-EP(3x3) |
| 包裝: | 帶卷 (TR) |
LTC6406
5
6406fc
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Note 1: Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. Exposure to any Absolute
Maximum Rating condition for extended periods may affect device
reliability and lifetime.
Note 2: Input pins (+IN, –IN, VOCM, SHDN and VTIP) are protected by
steering diodes to either supply. If the inputs should exceed either supply
voltage, the input current should be limited to less than 10mA. In addition,
the inputs +IN, –IN are protected by a pair of back-to-back diodes. If the
differential input voltage exceeds 1.4V, the input current should be limited
to less than 10mA.
Note 3: A heat sink may be required to keep the junction temperature
below the Absolute Maximum Rating when the output is shorted
indenitely. Long-term application of output currents in excess of the
absolute maximum ratings may impair the life of the device.
Note 4: The LTC6406C/LTC6406I are guaranteed functional over the
operating temperature range –40°C to 85°C.
Note 5: The LTC6406C is guaranteed to meet specied performance from
0°C to 70°C. The LTC6406C is designed, characterized, and expected
to meet specied performance from –40°C to 85°C but is not tested or
QA sampled at these temperatures. The LTC6406I is guaranteed to meet
specied performance from –40°C to 85°C.
Note 6: Input bias current is dened as the average of the input currents
owing into the inputs (–IN, and +IN). Input offset current is dened as the
difference between the input currents (IOS = IB+ – IB–).
Note 7: Input common mode range is tested using the test circuit of
Figure 1 by taking three measurements of differential gain with a ±1V DC
differential output with VICM = 0V; VICM = 1.25V; VICM = 3V, verifying that
the differential gain has not deviated from the VICM = 1.25V case by more
than 0.5%, and that the common mode offset (VOSCM) has not deviated
from the common mode offset at VICM = 1.25V by more than ±20mV.
The voltage range for the output common mode range is tested using the
test circuit of Figure 1 by applying a voltage on the VOCM pin and testing at
both VOCM = 1.25V and at the Electrical Characteristics table limits to verify
that the common mode offset (VOSCM) has not deviated by more than
±10mV from the VOCM = 1.25V case.
Note 8: Input CMRR is dened as the ratio of the change in the input
common mode voltage at the pins +IN or –IN to the change in differential
input referred voltage offset. Output CMRR is dened as the ratio of
the change in the voltage at the VOCM pin to the change in differential
input referred voltage offset. This specication is strongly dependent on
feedback ratio matching between the two outputs and their respective
inputs, and it is difcult to measure actual amplier performance (see the
Effects of Resistor Pair Mismatch in the Applications Information section
of this data sheet). For a better indicator of actual amplier performance
independent of feedback component matching, refer to the PSRR
specication.
Note 9: Differential power supply rejection (PSRR) is dened as the ratio
of the change in supply voltage to the change in differential input referred
voltage offset. Common mode power supply rejection (PSRRCM) is
dened as the ratio of the change in supply voltage to the change in the
common mode offset, VOUTCM – VOCM.
Note 10: Extended operation with the output shorted may cause the
junction temperature to exceed the 150°C limit.
Note 11: Because the LTC6406 is a feedback amplier with low output
impedance, a resistive load is not required when driving an ADC.
Therefore, typical output power can be very small in many applications. In
order to compare the LTC6406 with RF style ampliers that require 50
Ω
load, the output voltage swing is converted to dBm as if the outputs were
driving a 50
Ω load. For example, 2VP-P output swing is equal to 10dBm
using this convention.
Note 12: Includes offset/drift induced by feedback resistors mismatch. See
the Applications Information section for more details.
Note 13: QFN package only. Refer to data sheet curves for MSOP package
numbers.
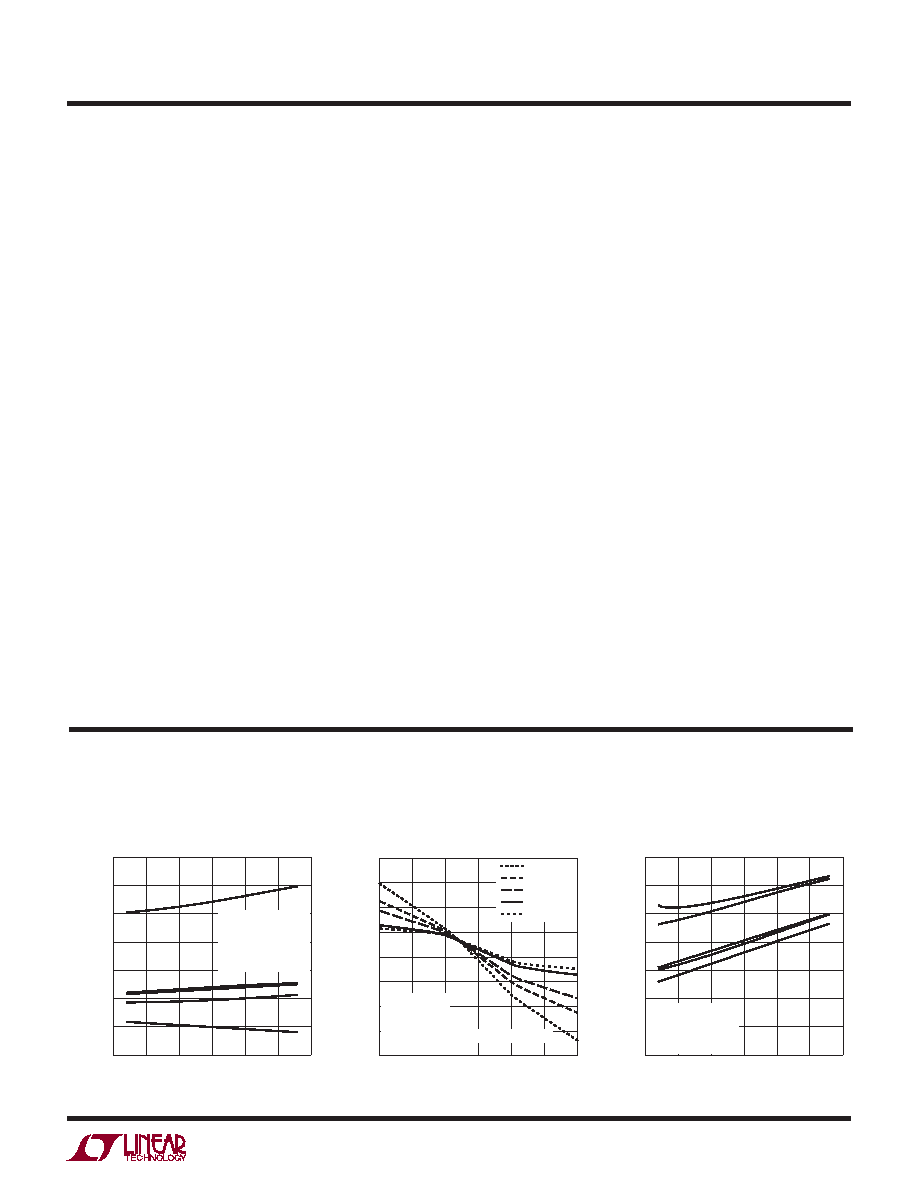
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Differential Input Referred Offset
Voltage vs Temperature
Differential Input Referred
Offset Voltage vs Input Common
Mode Voltage
Common Mode Offset Voltage
vs Temperature
TEMPERATURE (°C)
6406 G01
DIFFERENTIAL
V
OS
(mV)
VS = 3V
VOCM = 1.25V
VICM = 1.25V
RI = RF = 150Ω
FIVE TYPICAL UNITS
–50
50
100
–25
0
25
75
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–0.2
INPUT COMMON MODE VOLTAGE (V)
6406 G02
DIFFERENTIAL
V
OS
(mV)
VS = 3V
VOCM = 1.25V
RI = RF = 150Ω
0.1% FEEDBACK NETWORK RESISTORS
TYPICAL UNIT
0
2.0
3.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
–0.5
0
–1.0
–1.5
–2.0
TA = –40°C
TA = 0°C
TA = 25°C
TA = 70°C
TA = 85°C
TEMPERATURE (°C)
6406 G03
COMMON
MODE
OFFSET
VOL
TAGE
(mV)
VS = 3V
VOCM = 1.25V
VICM = 1.25V
FIVE TYPICAL UNITS
–50
50
100
–25
0
25
75
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| VE-J6M-MW-S | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 10V 100W |
| VE-242-IV-F1 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 15V 150W |
| AD421BR | IC DAC SRL 16BIT 16-SOIC |
| AD7548JPZ-REEL | IC DAC 12BIT LC2MOS 20PLCC |
| LTC6404CUD-4#PBF | IC AMP/DRIVER DIFF 16-QFN |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LTC6406IMS8E#PBF | 功能描述:IC AMP/DRIVER DIFF 8-MSOP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 線性 - 放大器 - 專用 系列:- 產(chǎn)品培訓(xùn)模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:60 系列:- 類型:可變?cè)鲆娣糯笃?應(yīng)用:CATV 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:20-WQFN 裸露焊盤 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:20-TQFN-EP(5x5) 包裝:托盤 |
| LTC6406IMS8E#TRPBF | 功能描述:IC AMP/DRIVER DIFF 8-MSOP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 線性 - 放大器 - 專用 系列:- 產(chǎn)品培訓(xùn)模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:60 系列:- 類型:可變?cè)鲆娣糯笃?應(yīng)用:CATV 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:20-WQFN 裸露焊盤 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:20-TQFN-EP(5x5) 包裝:托盤 |
| LTC6406IMS8E-PBF | 制造商:LINER 制造商全稱:Linear Technology 功能描述:3GHz, Low Noise, Rail-to-Rail Input Differential Amplifi er/Driver |
| LTC6406IMS8E-TRPBF | 制造商:LINER 制造商全稱:Linear Technology 功能描述:3GHz, Low Noise, Rail-to-Rail Input Differential Amplifi er/Driver |
| LTC6406IUD#PBF | 功能描述:IC DIFF AMP/DRIVER R-R 16-QFN RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 線性 - 放大器 - 專用 系列:- 產(chǎn)品培訓(xùn)模塊:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:60 系列:- 類型:可變?cè)鲆娣糯笃?應(yīng)用:CATV 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:20-WQFN 裸露焊盤 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:20-TQFN-EP(5x5) 包裝:托盤 |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。