- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄9860 > MAX13020ASA+T (Maxim Integrated Products)IC TRANSCEIVER LIN 8-SOIC PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MAX13020ASA+T |
| 廠商: | Maxim Integrated Products |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 4/16頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 0K |
| 描述: | IC TRANSCEIVER LIN 8-SOIC |
| 產(chǎn)品培訓(xùn)模塊: | Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 2,500 |
| 類型: | 收發(fā)器 |
| 驅(qū)動器/接收器數(shù): | 1/1 |
| 規(guī)程: | LIN |
| 電源電壓: | 5 V ~ 38 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 封裝/外殼: | 8-SOIC(0.154",3.90mm 寬) |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 8-SOIC |
| 包裝: | 帶卷 (TR) |
MAX13020/MAX13021
±60V Fault-Protected LIN Transceivers
12
Maxim Integrated
10A pullup. In applications where local wake-up capa-
bility is not required, connect NWAKE to BAT. For
improved EMI performance, connect NWAKE to BAT
through a 5k
resistance.
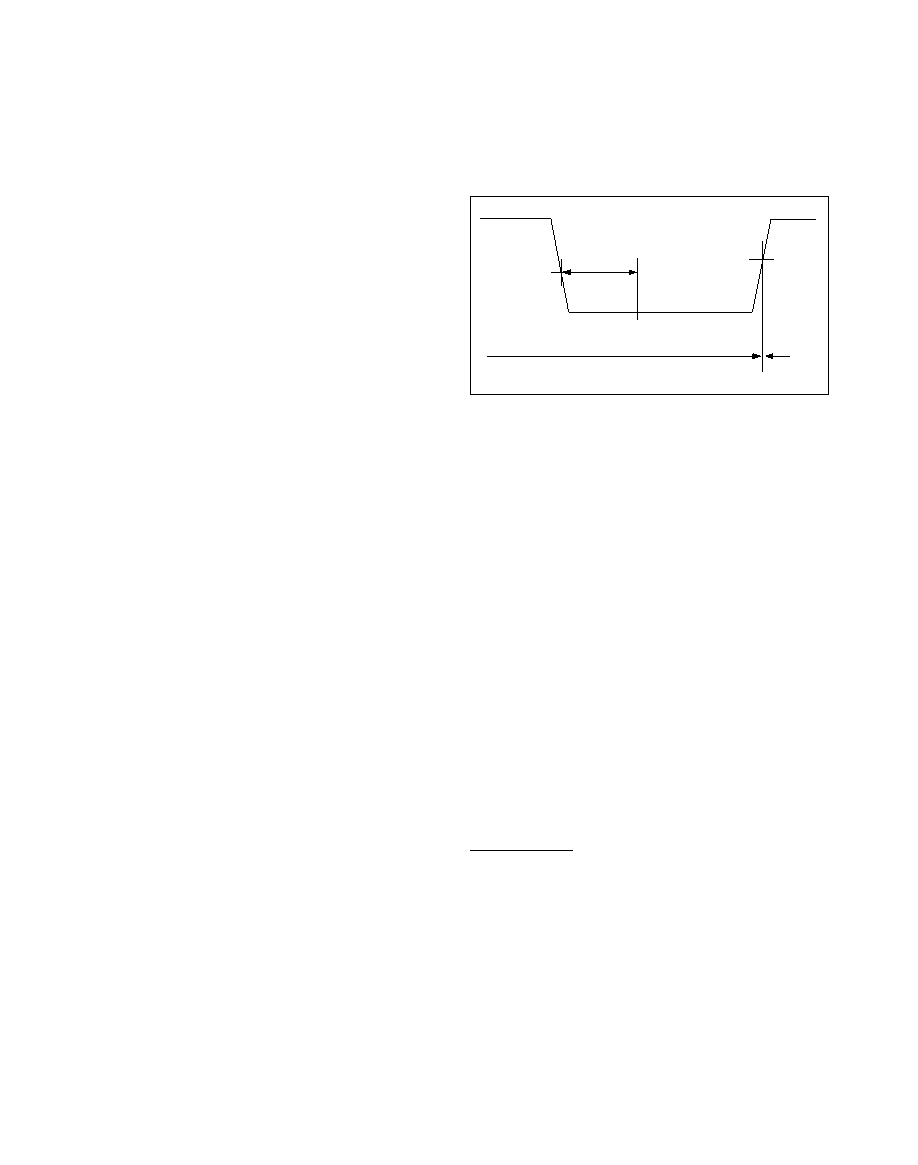
A remote wake-up event is generated when a reces-
sive-dominant-recessive sequence is detected on LIN.
The dominant state must be asserted longer than tBUS
to generate a remote wake-up (Figure 3).
Wake-Up Source Recognition
When a wake-up event is detected, the MAX13020/
MAX13021 enter standby mode and present the wake-up
interrupt on RXD as a logic-low. The wake-up source flag
is presented on TXD as a strong pulldown in the case of a
local wake-up. In the case of a remote wake-up, TXD is
pulled low by the internal 330k
resistor only. To read the
wake-up source flag, pull TXD high with an external
pullup resistor (see
Reading the Wake-Up Source Flag
section.) The wake-up interrupt and wake-up source flag
are cleared when the MAX13020/MAX13021 transition to
normal slope mode or low slope mode. The thermal-shut-
down circuit forces the driver outputs into high-imped-
ance state if the die temperature exceeds +160°C.
Normal operation resumes when the die temperature
cools to +140°C.
Fail-Safe Features
The MAX13020/MAX13021 include a number of fail-
safe features to handle fault conditions. Internal pull-
downs are provided on control inputs TXD and NSLP to
force the device into a known state in the event that
these inputs are disconnected.
LIN Short-Circuit Protection
The LIN transmitter is current-limited to prevent dam-
age from LIN-to-BAT shorts.
TXD Dominant Timeout
If TXD is shorted to GND or is otherwise held low, the
resulting dominant LIN state blocks traffic on the LIN
bus. In normal slope and low slope modes, the LIN
transmitter is disabled if TXD is held at logic-low for
longer than tTXD(DOM)(DIS). The transmitter is re-
enabled on the next rising edge on TXD.
Loss of Power
If BAT or GND are disconnected, interrupting power to
the MAX13020/MAX13021, LIN remains high imped-
ance to avoid loading the LIN bus. Additionally, RXD is
high impedance when BAT is disconnected, preventing
current flow from a connected microcontroller.
LIN Bus Dominant Management (MAX13021)
The MAX13021 provides LIN bus dominant manage-
ment protection to reduce current consumption during
a LIN-to-GND short condition. When the LIN-to-GND
short is cleared, and a recessive LIN state is detected,
the MAX13021 returns to standby or sleep mode.
ESD Protection
As with all Maxim devices, ESD-protection structures
are incorporated on all pins to protect against ESDs
encountered during handling and assembly. The LIN,
NWAKE, and BAT pins are protected up to ±4kV as
measured by the IEC61000-4-4 Contact Discharge
Model. LIN is protected to ±12kV Human Body Model.
Protection structures prevent damage caused by ESD
events in all operating modes and when the device is
unpowered.
ESD Test Conditions
ESD performance depends on a variety of conditions.
Contact Maxim for a reliability report documenting test
setup, methodology, and results.
Applications Information
Master LIN Nodes
Configure the MAX13020/MAX13021 as a master LIN
node by connecting a 1k
resistor from LIN to INH with
a blocking diode (see the
Typical Operating Circuit.)
INH is held at a logic-high level in normal slope, low
slope, standby, and fault (MAX13021) modes. INH is
high impedance in sleep mode and disable mode
(MAX13021) to reduce power consumption.
STANDBY
MODE
VLIN
LIN RECESSIVE
LIN DOMINANT
tBUS
0.4 x VBAT
0.6 x VBAT
SLEEP MODE
Figure 3. Remote Wake-Up Timing
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MS27497T16F8PB | CONN RCPT 8POS WALL MNT W/PINS |
| MS27656T11A98S | CONN RCPT 6POS WALL MNT W/SCKT |
| VI-JNH-MX-F2 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 52V 75W |
| MS27656E11A98S | CONN RCPT 6POS WALL MNT W/SCKT |
| VE-B74-MW-F1 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 48V 100W |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX13021ASA/V+ | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:+/-60V FAULT-PROTECTED LIN TRANSCEIVER - Rail/Tube 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:IC TXRX LIN 60V FAULT PRO 8-SOIC 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:60V+/- Fault Prot LIN Transceiver |
| MAX13021ASA/V+T | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:+/-60V FAULT-PROTECTED LIN TRANSCEIVER - Tape and Reel 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:IC TXRX LIN 60V FAULT PRO 8-SOIC 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:60V+/- Fault Prot LIN Transceiver |
| MAX13021ASA+ | 功能描述:LIN 收發(fā)器 60V Fault-Protect RoHS:否 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 工作電源電壓: 電源電流: 最大工作溫度: 封裝 / 箱體:SO-8 |
| MAX13021ASA+T | 功能描述:LIN 收發(fā)器 60V Fault-Protect RoHS:否 制造商:NXP Semiconductors 工作電源電壓: 電源電流: 最大工作溫度: 封裝 / 箱體:SO-8 |
| MAX1302AEUG+ | 功能描述:模數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換器 - ADC 16Bit, 8Ch, 4.096V Multi-In Serial ADC RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 通道數(shù)量:2 結(jié)構(gòu):Sigma-Delta 轉(zhuǎn)換速率:125 SPs to 8 KSPs 分辨率:24 bit 輸入類型:Differential 信噪比:107 dB 接口類型:SPI 工作電源電壓:1.7 V to 3.6 V, 2.7 V to 5.25 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:VQFN-32 |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。