- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371029 > MC33364D2 (MOTOROLA INC) CRITICAL CONDUCTION GREENLINEE SMPS CONTROLLER PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MC33364D2 |
| 廠商: | MOTOROLA INC |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | CRITICAL CONDUCTION GREENLINEE SMPS CONTROLLER |
| 中文描述: | SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 126 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO8 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, SO-8 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 6/14頁 |
| 文件大小: | 269K |
| 代理商: | MC33364D2 |
MC33364
6
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA
protected by two clamps. The upper 0.7 V clamp prevents
input overvoltage breakdown while the lower –0.7 V clamp
prevents substrate injection. An external resistor must be
used in series with the auxiliary winding to limit the current
through the clamps to 5.0 mA or less.
Current Sense Comparator and RS Latch
The Current Sense Comparator RS Latch configuration
used ensures that only a single pulse appears at the Drive
Output during a given cycle. The inductor current is
converted to a voltage by inserting a ground–referenced
sense resistor in series with the source of output switch. This
voltage is monitored by the Current Sense Input and
compared to the divided down feedback voltage. The internal
feedback voltage divider is limited to 1.5 V maximum.
Therefore the maximum peak switch current is:
Ipk(max)
1.5 V
RSense
The Current Sense Input to Drive Output propagation
delay is typically 232 nS.
Timer
A watchdog timer function was added to the IC to eliminate
the need for an external oscillator when used in stand alone
applications. The Timer provides a means to automatically
start or restart the preconverter if the Drive Output has been
off for more than 410 microseconds after the inductor current
reaches zero.
Undervoltage Lockout
The MC33364 has a 5.0 V internal reference brought out
to Pin 6 (D Suffix) or Pin 4 (D1 and D2 Suffixes) and capable
of sourcing 10 mA typically. It also contains an Under Voltage
Lockout (UVLO) circuit which suppresses the Gate output at
Pin 11 if the VCC supply voltage drops below 7.6 V typical.
Restart Delay
A restart delay function is provided to allow hiccup mode
fault protection in case of a short circuit condition and to
prevent the SMPS from repeatedly trying to restart after the
input line voltage has been removed. When power is first
applied, the VCC bypass capacitor is charged through a
constant current source. The Restart Delay turns off the high
voltage startup MOSFET when VCC reaches the startup
threshold level. The Restart Delay turns on the high voltage
MOSFET after VCC has dropped below 4.5 V.
If the SMPS output is short circuited, the transformer
winding, which provides the VCC voltage to the MC33364, will
be unable to sustain VCC. The restart delay prevents the high
voltage startup transistor within the IC from maintaining the
voltage on the VCC pin bootstrap capacitor. After VCC drops
below the UVLO threshold in the SMPS, the SMPS switching
transistors are held off for the time programmed by the restart
delay circuit. In this manner, the SMPS switching transistor is
operated at a very low duty cyle, preventing destruction. If
the short circuit fault is removed, the power supply system
will turn on by itself in a normal startup mode after the restart
delay has timed out
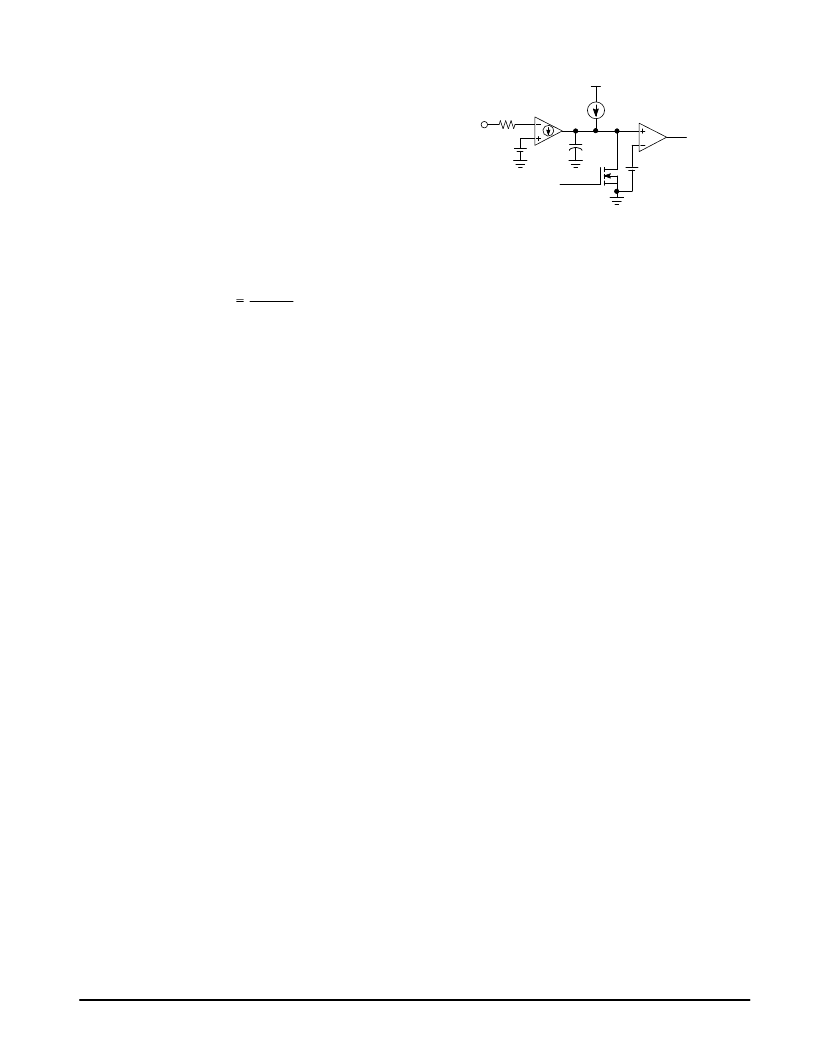
Figure 8. Frequency Clamp Circuit
5.0 V
Frequency
Clamp
Gate
Drive
Signal
FC Output
to PWM latch
4.0 k
10 pF
2.0 V
3.0
μ
A
0 = Disable
2.0 V
Output Switching Frequency Clamp
In normal operation, the MC33364 operates the flyback
transformer primary inductance in the critical mode. That is,
the inductor current ramps to a peak value, ramps down to
zero, then immediately begins ramping positive again. The
peak current is programmed by the current sense resistance
value. If the output load is reduced from full load to a standby
load or no load condition, the switching frequency can
increase to hundreds of kilohertz. Because regulatory
agency EMI limits for allowed conducted current decreases
as the switching frequency increases beyond 150 kHz, this
may be an undesireable operating condition. The Output
Switching Frequency Clamp remedies this situation to
minimize EMI generated in this operating region. The internal
frequency clamp circuit in the MC33364D1 and MC33364D
programs a minimum off time, forcing discontinuous mode
operation and limiting the operating frequency to less than
126 kHz. The MC33364D2 does NOT contain a frequency
clamp circuit. The Output Switching Frequency Clamp
function in the MC33364D can be disabled by connecting the
FC input, Pin 8, to ground. The clamp frequency can be set
externally by sinking or sourcing a current into the pin of up to
100 microamperes.
Output
The IC contains a CMOS output driver specifically
designed for direct drive of power MOSFETs. The Drive
Output is capable of up to
±
1500 mA peak current with a
typical rise and fall time of 50 nS with a 1.0 nF load. Additional
internal circuitry has been added to keep the Drive Output in
a sinking mode whenever the Undervoltage Lockout is
active. This characteristic eliminates the need for an external
gate pull–down resistor. The totem–pole output has been
optimized to minimize cross–conduction current during high
speed operation.
Design Example
Design an off–line Flyback converter according to the
following requirements:
Output Power:
Output:
Input voltage range: 90 Vac – 270 Vac, 50/60 Hz
12 W
6.0 V @ 2 Amperes
The operation for the circuit shown in Figure 9 is as
follows: the rectifier bridge D1–D4 and the capacitor C1
convert the ac line voltage to dc. This voltage supplies the
primary winding of the transformer T1 and the startup circuit
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC33389 | System Basis Chip with Low Speed Fault Tolerant CAN |
| MC33389ADH | System Basis Chip with Low Speed Fault Tolerant CAN |
| MC33389ADW | System Basis Chip with Low Speed Fault Tolerant CAN |
| MC33389CDH | System Basis Chip with Low Speed Fault Tolerant CAN |
| MC33389CDW | System Basis Chip with Low Speed Fault Tolerant CAN |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MC33364D2G | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 Variable Frequency SMPS RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時間: 下降時間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
| MC33364D2R2 | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 Variable Frequency RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時間: 下降時間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
| MC33364D2R2G | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 Variable Frequency SMPS RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時間: 下降時間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
| MC33364DG | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 Variable Frequency SMPS RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時間: 下降時間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
| MC33364DR2 | 功能描述:電流型 PWM 控制器 Variable Frequency RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 開關(guān)頻率:27 KHz 上升時間: 下降時間: 工作電源電壓:6 V to 15 V 工作電源電流:1.5 mA 輸出端數(shù)量:1 最大工作溫度:+ 105 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。