- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄45241 > MC68HC908GR4MFA (FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC) 8-BIT, FLASH, 8.2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP32 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MC68HC908GR4MFA |
| 廠商: | FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8.2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP32 |
| 封裝: | 7 X 7 MM, 1.40 MM HEIGHT, 0.80 MM PITCH, MS-026BBA, LQFP-32 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 125/286頁 |
| 文件大小: | 3708K |
| 代理商: | MC68HC908GR4MFA |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁當(dāng)前第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁第160頁第161頁第162頁第163頁第164頁第165頁第166頁第167頁第168頁第169頁第170頁第171頁第172頁第173頁第174頁第175頁第176頁第177頁第178頁第179頁第180頁第181頁第182頁第183頁第184頁第185頁第186頁第187頁第188頁第189頁第190頁第191頁第192頁第193頁第194頁第195頁第196頁第197頁第198頁第199頁第200頁第201頁第202頁第203頁第204頁第205頁第206頁第207頁第208頁第209頁第210頁第211頁第212頁第213頁第214頁第215頁第216頁第217頁第218頁第219頁第220頁第221頁第222頁第223頁第224頁第225頁第226頁第227頁第228頁第229頁第230頁第231頁第232頁第233頁第234頁第235頁第236頁第237頁第238頁第239頁第240頁第241頁第242頁第243頁第244頁第245頁第246頁第247頁第248頁第249頁第250頁第251頁第252頁第253頁第254頁第255頁第256頁第257頁第258頁第259頁第260頁第261頁第262頁第263頁第264頁第265頁第266頁第267頁第268頁第269頁第270頁第271頁第272頁第273頁第274頁第275頁第276頁第277頁第278頁第279頁第280頁第281頁第282頁第283頁第284頁第285頁第286頁
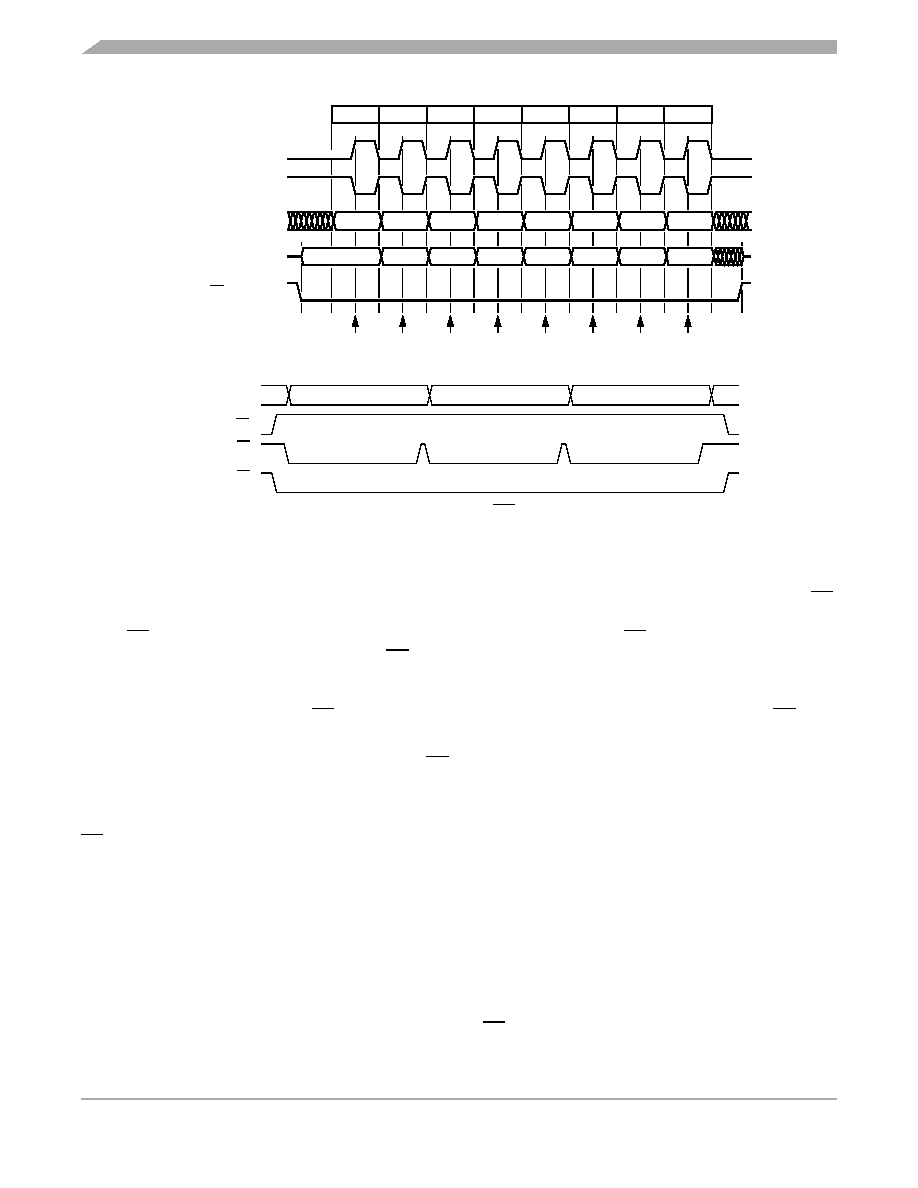
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
MC68HC908GR8 MC68HC908GR4 Data Sheet, Rev. 7
210
Freescale Semiconductor
Figure 20-4. Transmission Format (CPHA = 0)
Figure 20-5. CPHA/SS Timing
Two waveforms are shown for SPSCK: one for CPOL = 0 and another for CPOL = 1. The diagram may
be interpreted as a master or slave timing diagram since the serial clock (SPSCK), master in/slave out
(MISO), and master out/slave in (MOSI) pins are directly connected between the master and the slave.
The MISO signal is the output from the slave, and the MOSI signal is the output from the master. The SS
line is the slave select input to the slave. The slave SPI drives its MISO output only when its slave select
input (SS) is at 0, so that only the selected slave drives to the master. The SS pin of the master is not
shown but is assumed to be inactive. The SS pin of the master must be high or must be reconfigured as
general-purpose I/O not affecting the SPI. See 20.7.2 Mode Fault Error. When CPHA = 0, the first SPSCK
edge is the MSB capture strobe. Therefore, the slave must begin driving its data before the first SPSCK
edge, and a falling edge on the SS pin is used to start the slave data transmission. The slave’s SS pin
must be toggled back to high and then low again between each byte transmitted as shown in Figure 20-5.
When CPHA = 0 for a slave, the falling edge of SS indicates the beginning of the transmission. This
causes the SPI to leave its idle state and begin driving the MISO pin with the MSB of its data. Once the
transmission begins, no new data is allowed into the shift register from the transmit data register.
Therefore, the SPI data register of the slave must be loaded with transmit data before the falling edge of
SS. Any data written after the falling edge is stored in the transmit data register and transferred to the shift
register after the current transmission.
20.5.3 Transmission Format When CPHA = 1
Figure 20-6 shows an SPI transmission in which CPHA is logic 1. The figure should not be used as a
replacement for data sheet parametric information. Two waveforms are shown for SPSCK: one for
CPOL = 0 and another for CPOL = 1. The diagram may be interpreted as a master or slave timing
diagram since the serial clock (SPSCK), master in/slave out (MISO), and master out/slave in (MOSI) pins
are directly connected between the master and the slave. The MISO signal is the output from the slave,
and the MOSI signal is the output from the master. The SS line is the slave select input to the slave. The
BIT 6
BIT 5
BIT 4
BIT 3
BIT 2
BIT 1
LSB
MSB
BIT 6
BIT 5
BIT 4
BIT 3
BIT 2
BIT 1
LSB
MSB
123
4
5
6
7
8
SPSCK CYCLE #
FOR REFERENCE
SPSCK; CPOL = 0
SPSCK; CPOL =1
MOSI
FROM MASTER
MISO
FROM SLAVE
SS; TO SLAVE
CAPTURE STROBE
BYTE 1
BYTE 3
MISO/MOSI
BYTE 2
MASTER SS
SLAVE SS
CPHA = 0
SLAVE SS
CPHA = 1
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68HC908GR4VFA | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8.2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP32 |
| MC908GR8VFAR2 | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8.2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP32 |
| MC68HC908GR4VP | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8.2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP28 |
| MC68HC908GZ16CFA | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP48 |
| MC68HC908GZ16VFJ | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP32 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68HC908GR8ACFA | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk 制造商:Motorola Inc 功能描述: 制造商:MOTOROLA 功能描述: |
| MC68HC908GR8AMFA | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MC68HC908GR8AVFA | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MC68HC908GR8CB | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:8 BIT MCU, 7.5K FLASH - Bulk |
| MC68HC908GR8CD | 功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 8 Bit 8MHz RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 處理器系列:C8051F39x 數(shù)據(jù)總線寬度:8 bit 最大時(shí)鐘頻率:50 MHz 程序存儲器大小:16 KB 數(shù)據(jù) RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作電源電壓:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 105 C 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-20 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。