- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄45218 > MC68HSC05C8CFB (FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC) 8-BIT, MROM, 4.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MC68HSC05C8CFB |
| 廠商: | FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC |
| 元件分類(lèi): | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, MROM, 4.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 |
| 封裝: | QFP-44 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 56/116頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 781K |
| 代理商: | MC68HSC05C8CFB |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)當(dāng)前第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)
Timer
MC68HC05C8A MC68HCL05C8A MC68HSC05C8A Data Sheet, Rev. 5.1
44
Freescale Semiconductor
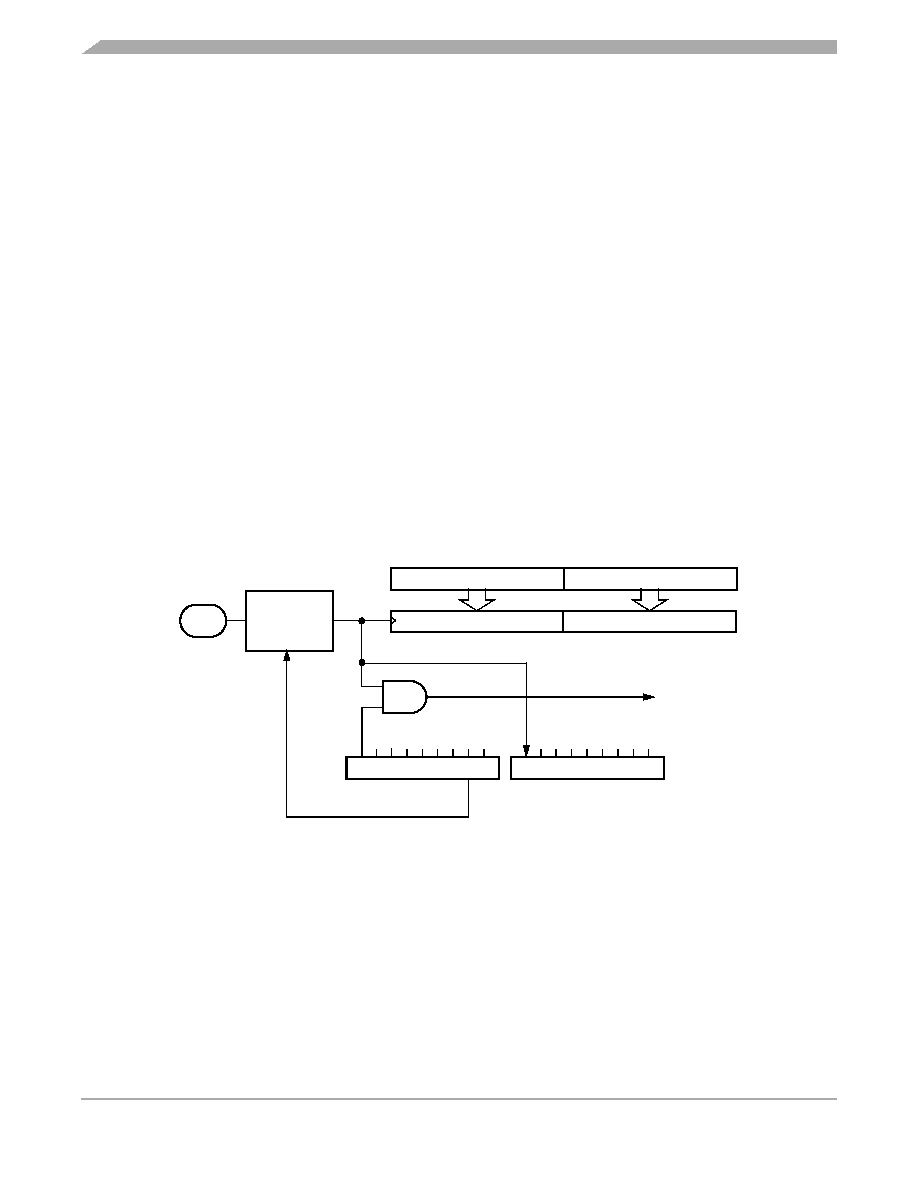
8.4 Input Capture Register
Two 8-bit registers, which make up the 16-bit input capture register, are read-only and are used to latch
the value of the free-running counter after the corresponding input capture edge detector senses a
defined transition. The level transition which triggers the counter transfer is defined by the corresponding
input edge bit (IEDG). Reset does not affect the contents of the input capture register except when exiting
stop mode.
The result obtained by an input capture will be one more than the value of the free-running counter on the
rising edge of the internal bus clock preceding the external transition. This delay is required for internal
synchronization. Resolution is one count of the free-running counter, which is four internal bus clock
cycles.
The free-running counter contents are transferred to the input capture register on each proper signal
transition regardless of whether the input capture flag (ICF) is set or clear. The input capture register
always contains the free-running counter value that corresponds to the most recent input capture.
After a read of the input capture register ($14) MSB, the counter transfer is inhibited until the LSB ($15)
is also read. This characteristic causes the time used in the input capture software routine and its
interaction with the main program to determine the minimum pulse period.
A read of the input capture register LSB ($15) does not inhibit the free-running counter transfer, since they
occur on opposite edges of the internal bus clock. Figure 8-3 shows the logic of the input capture function.
Figure 8-3. Input Capture Operation
INPUT CAPTURE REGISTER HIGH
INPUT CAPTURE REGISTER LOW
TIMER REGISTER HIGH
TCMP
EDGE
SELECT/DETECT
LOGIC
TIMER
INTERRUPT
REQUEST
TIMER REGISTER LOW
15
0
15
8 7
0
TIMER STATUS REGISTER
$0013
TIMER CONTROL REGISTER
$0012
ICI
E
OCIE
TO
IE
ICF
OCF
TO
F
87
$0018
$0019
$0014
$0015
IEDG
LATCH
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68HC05C8APE | 8-BIT, MROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP40 |
| MC68HC05C8AMB | 8-BIT, MROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP42 |
| MC68HCL05C8AFN | 8-BIT, MROM, MICROCONTROLLER, PQCC44 |
| MC68HSC05C8AFB | 8-BIT, MROM, 4.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 |
| MC68HC05C8AMFN | 8-BIT, MROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQCC44 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68HSC705C8ACFB | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:8 BIT MCU, 304 BYTES RAM - Bulk |
| MC68HSC705C8ACP | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述: 制造商:Freescale Semiconductor 功能描述: |
| MC68HSC705C8ACS | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MC68HSC705J1ACDW | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MC68HSC705J1ACP | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:8 BIT MCU, 64 BYTES RAM - Bulk |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。