- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄359155 > MCZ33291EG (飛思卡爾半導(dǎo)體(中國(guó))有限公司) Eight-Output Switch with Serial Peripheral Interface I/O PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MCZ33291EG |
| 廠商: | 飛思卡爾半導(dǎo)體(中國(guó))有限公司 |
| 英文描述: | Eight-Output Switch with Serial Peripheral Interface I/O |
| 中文描述: | 8輸出開關(guān)串行外設(shè)接口的I / O |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 18/26頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 379K |
| 代理商: | MCZ33291EG |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)當(dāng)前第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
Freescale Semiconductor
18
33291
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
FAULT LOGIC OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
The MCU can perform a parity check of the fault logic
operation by comparing the command 8-bit word to the status
8-bit word. Assume after system reset, the MCU first sends
an 8-bit command word to the 33291. This word is called
Command Word 1. Each output to be turned ON will have its
corresponding data bit low. Refer to the data transfer timing
illustration in
Figure 18
.
As Command Word 1 is being written into the Shift register
of the 33291, a status word is being simultaneously written
and received by the MCU. However, the word being received
by the MCU is the status of the previous write word to the
33291, Status Word 0. If the command word of the MCU is
written a second time (Command Word 2 = Command Word
1), the word received by the MCU, Status Word 2, is the
status of Command Word 1. The timing diagram illustrated in
Figure 18
depicts this operation. Status Word 2 is then
compared with Command Word 1. The MCU will Exclusive
OR Status Word 2 with Command Word 1 to determine if the
two words are identical. If the two words are identical, no
faults exist. The timing between the two write words must be
greater than 100
μ
s to receive proper drain status. The
system data bus integrity may be tested by writing two like
words to the 33291 within a few microseconds of each other.
INITIAL SYSTEM SETUP TIMING
The MCU can monitor two kinds of faults:
1. Communication errors on the data bus
2. Actual faults of the output loads
After initial system startup or reset, the MCU will write one
word to the 33291. If the word is repeated within
approximately five microseconds of the first word, the word
received by the MCU, at the end of the repeated word, serves
as a confirmation of data bus integrity (1). At startup, the
33291 will take 25
μ
s to 100
μ
s before a repeat of the first
word should be repeated at least 100
μ
s later to verify the
status of the outputs.
The SO of the 33291 will indicate any one of four faults.
The four possible faults are:
1. Overtemperature
2. Output OFF Open Fault
3. Short Fault (overcurrent)
4. V
PWR
Overvoltage Fault
With the exception of the Overvoltage Fault, all of these
faults are output specific. Overtemperature Detect, Output
OFF Open Detect, and Output Short Detect are dedicated to
each output separately such that the outputs are independent
in operation. A V
PWR
Overvoltage Detect is of a
global
nature,
causing all outputs to be turned OFF.
OVERTEMPERATURE FAULT
Patent pending Overtemperature Detect and shutdown
circuits are specifically incorporated for each individual
output. The shutdown following an Overtemperature
condition is independent of the system clock or any other
logic signal. Each independent output shuts down at 155°C
to 185°C. When an output shuts down due to an
Overtemperature Fault, no other outputs are affected. The
MCU recognizes the fault since the output was commanded
to be ON and the status word indicates it is OFF. A maximum
hysteresis of 20°C ensures an adequate time delay between
output turn OFF and recovery. This avoids a very rapid turn
ON and turn OFF of the device around the Overtemperature
threshold. When the temperature falls below the recovery
level for the Overtemperature Fault, the device will turn ON
only if the Command Word during the next write cycle
indicates the output should be turned ON.
OVERVOLTAGE FAULT
An Overvoltage condition on the V
PWR
pin causes the
33291 to shut down all outputs until the overvoltage condition
is removed and the device is re-programmed by the SPI. The
overvoltage threshold on the V
PWR
pin is specified as 28 V
to 36 V with 1.0 V typical hysteresis. Following the
overvoltage condition, the next write cycle sends the SO pin
the hexadecimal word $FF (all ones), indicating all outputs
are turned OFF. In this way, potentially dangerous timing
problems are avoided and the MCU reset routine ensures an
orderly startup of the loads. The 33291 does not detect an
overvoltage on the V
DD
pin. Other external circuitry, such as
the Freescale 33161 Universal Voltage Monitor, is necessary
to accomplish this function.
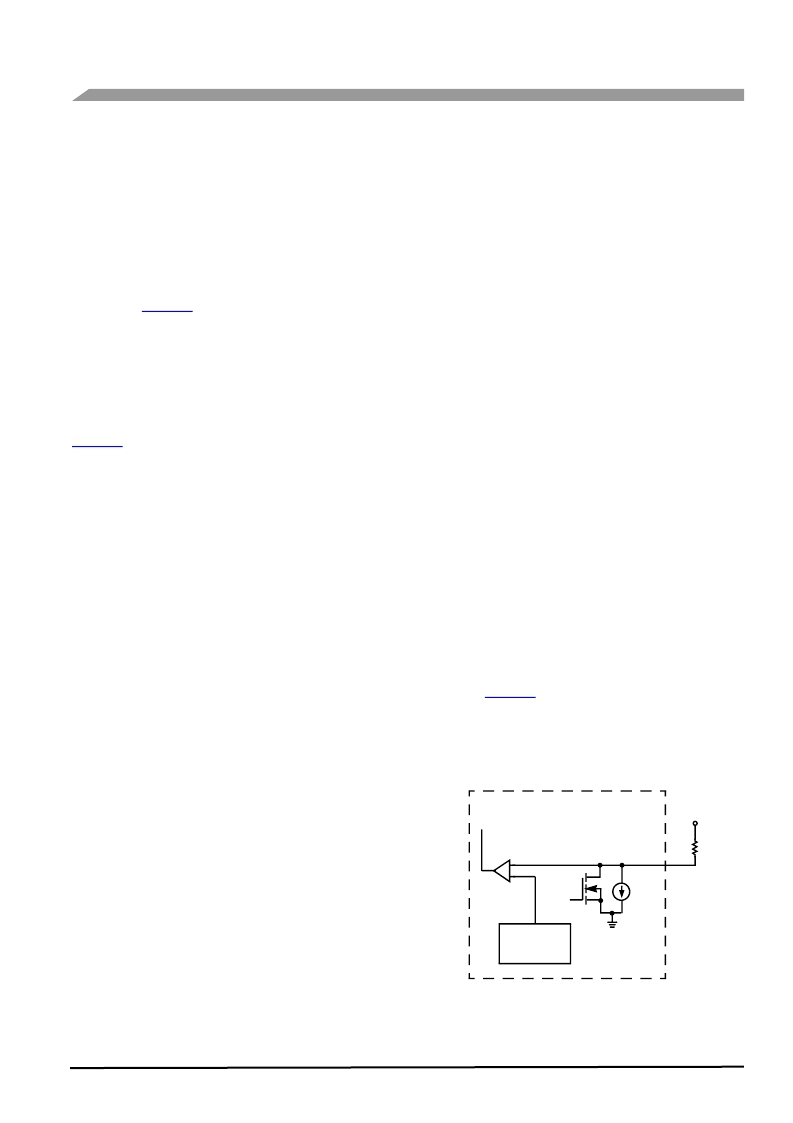
OUTPUT OFF OPEN LOAD FAULT
An Output OFF Open Load Fault is the detection and
reporting of an
open
load when the corresponding output is
disabled (input bit programmed to a logic high state). To
understand the operation of the Open Load Fault detect
circuit, see
Figure 19
. The Output OFF Open Load Fault is
detected by comparing the drain voltage of the specific
MOSFET output to an internally generated reference. Each
output has one dedicated comparator for this purpose.
Figure 19. Output OFF Open Load Fault
V
Thres
2.5 V to 3.5 V
+
Low = Fault
50
μ
A
Output
V
PWR
R
L
33291
MOSFET OFF
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MCZ33291LEG | Eight-Output Switch with Serial Peripheral Interface I/O |
| MCZ33390EF | Class B Serial Transceiver |
| MCZ33395EW | Three-Phase Gate Driver IC |
| MCZ33399EF | Local Interconnect Network (LIN) Physical Interface |
| MCZ33661EF | Local Area Network (LIN) Enhanced Physical Interface with Selectable Slew Rate |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MCZ33291EGR2 | 功能描述:電源開關(guān) IC - 配電 BASIC OCTAL SERIAL SW RoHS:否 制造商:Exar 輸出端數(shù)量:1 開啟電阻(最大值):85 mOhms 開啟時(shí)間(最大值):400 us 關(guān)閉時(shí)間(最大值):20 us 工作電源電壓:3.2 V to 6.5 V 電源電流(最大值): 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOT-23-5 |
| MCZ33291LEG | 功能描述:電源開關(guān) IC - 配電 BASIC OCTAL SER SW RoHS:否 制造商:Exar 輸出端數(shù)量:1 開啟電阻(最大值):85 mOhms 開啟時(shí)間(最大值):400 us 關(guān)閉時(shí)間(最大值):20 us 工作電源電壓:3.2 V to 6.5 V 電源電流(最大值): 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOT-23-5 |
| MCZ33291LEGR2 | 功能描述:電源開關(guān) IC - 配電 BASIC OCTAL SER SW RoHS:否 制造商:Exar 輸出端數(shù)量:1 開啟電阻(最大值):85 mOhms 開啟時(shí)間(最大值):400 us 關(guān)閉時(shí)間(最大值):20 us 工作電源電壓:3.2 V to 6.5 V 電源電流(最大值): 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOT-23-5 |
| MCZ33298EG | 功能描述:電源開關(guān) IC - 配電 OCTAL SERIAL SWITCH RoHS:否 制造商:Exar 輸出端數(shù)量:1 開啟電阻(最大值):85 mOhms 開啟時(shí)間(最大值):400 us 關(guān)閉時(shí)間(最大值):20 us 工作電源電壓:3.2 V to 6.5 V 電源電流(最大值): 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOT-23-5 |
| MCZ33298EG/R2 | 制造商:FREESCALE 制造商全稱:Freescale Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:Eight Output Switch with Serial Peripheral Interface I/O |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。