- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄377970 > ML4804CP (FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORP) Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | ML4804CP |
| 廠商: | FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORP |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo |
| 中文描述: | 1 A POWER FACTOR CONTROLLER WITH POST REGULATOR, 250 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDIP16 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, DIP-16 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 10/14頁 |
| 文件大小: | 145K |
| 代理商: | ML4804CP |
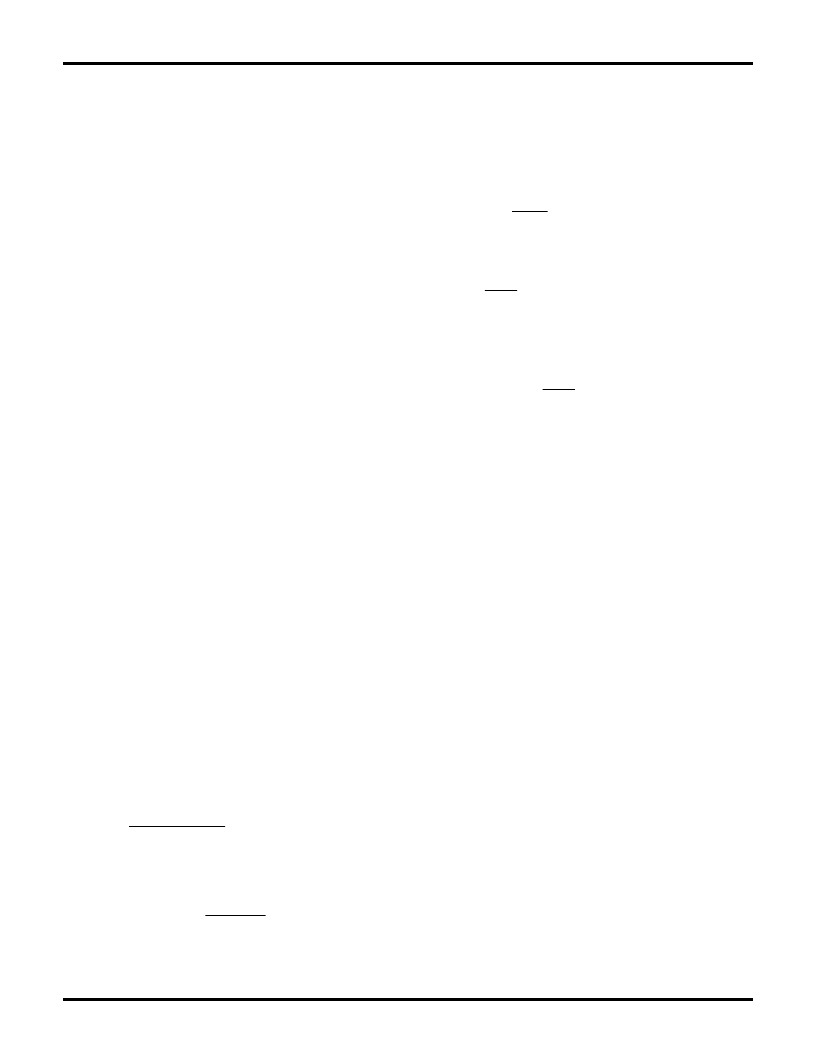
ML4804
10
REV. 1.0.2 3/9/2001
voltage loop error amplifier; stability and transient
response. Optimizing interaction between transient
response and stability requires that the error amplifier
’
s
open-loop crossover frequency should be 1/2 that of the
line frequency, or 23Hz for a 47Hz line (lowest
anticipated international power frequency). The gain vs.
input voltage of the ML4804
’
s voltage error amplifier has
a specially shaped nonlinearity such that under steady-
state operating conditions the transconductance of the
error amplifier is at a local minimum. Rapid perturbations
in line or load conditions will cause the input to the
voltage error amplifier (V
FB
) to deviate from its 2.5V
(nominal) value. If this happens, the transconductance of
the voltage error amplifier will increase significantly, as
shown in the Typical Performance Characteristics. This
raises the gain-bandwidth product of the voltage loop,
resulting in a much more rapid voltage loop response to
such perturbations than would occur with a conventional
linear gain characteristic.
The current amplifier compensation is similar to that of
the voltage error amplifier with the exception of the
choice of crossover frequency. The crossover frequency of
the current amplifier should be at least 10 times that of
the voltage amplifier, to prevent interaction with the
voltage loop. It should also be limited to less than 1/6th
that of the switching frequency, e.g. 16.7kHz for a
100kHz switching frequency.
There is a modest degree of gain contouring applied to the
transfer characteristic of the current error amplifier, to
increase its speed of response to current-loop
perturbations. However, the boost inductor will usually be
the dominant factor in overall current loop response.
Therefore, this contouring is significantly less marked than
that of the voltage error amplifier. This is illustrated in the
Typical Performance Characteristics.
For more information on compensating the current and
voltage control loops, see Application Notes 33 and 34.
Application Note 16 also contains valuable information
for the design of this class of PFC.
Oscillator (RAMP 1)
The oscillator frequency is determined by the values of R
T
and C
T
, which determine the ramp and off-time of the
oscillator output clock:
(2)
The deadtime of the oscillator is derived from the
following equation:
(3)
at V
REF
= 7.5V:
The deadtime of the oscillator may be determined using:
(4)
The deadtime is so small (t
RAMP
>> t
DEADTIME
) that the
operating frequency can typically be approximated by:
(5)
EXAMPLE:
For the application circuit shown in the data sheet, with
the oscillator running at:
Solving for R
T
x C
T
yields 1.96 x 10
-4
. Selecting standard
components values, C
T
= 390pF, and R
T
= 51.1k
.
The deadtime of the oscillator adds to the Maximum
PWM Duty Cycle (it is an input to the Duty Cycle
Limiter). With zero oscillator deadtime, the Maximum
PWM Duty Cycle is typically 45%. In many applications,
care should be taken that C
T
not be made so large as to
extend the Maximum Duty Cycle beyond 50%. This can
be accomplished by using a stable 390pF capacitor for C
T
.
PWM SECTION
Pulse Width Modulator
The PWM section of the ML4804 is straightforward, but
there are several points which should be noted. Foremost
among these is its inherent synchronization to the PFC
section of the device, from which it also derives its basic
timing. The PWM is capable of current-mode or voltage
mode operation. In current-mode applications, the PWM
ramp (RAMP 2) is usually derived directly from a current
sensing resistor or current transformer in the primary of the
output stage, and is thereby representative of the current
flowing in the converter
’
s output stage. DC I
LIMIT
, which
provides cycle-by-cycle current limiting, is typically
connected to RAMP 2 in such applications. For voltage-
mode operation or certain specialized applications,
RAMP 2 can be connected to a separate RC timing
network to generate a voltage ramp against which V
DC
will be compared. Under these conditions, the use of
voltage feedforward from the PFC buss can assist in line
regulation accuracy and response. As in current mode
operation, the DC I
LIMIT
input would is used for output
stage overcurrent protection.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
(Continued)
=
+
=
×
×
=
×
×
!
=
×
=
×
=
"#$
=
=
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ML4804CS | Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo |
| ML4804IP | Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo |
| ML4804IS | Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo |
| ML4804 | Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo(功率因數(shù)校正器和PWM控制器組合芯片) |
| ML4805 | Variable Feedforward PFC/PWM Controller Combo |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| ML4804CS | 制造商:MICRO-LINEAR 制造商全稱:MICRO-LINEAR 功能描述:Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo |
| ML4804IP | 制造商:MICRO-LINEAR 制造商全稱:MICRO-LINEAR 功能描述:Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo |
| ML4804IS | 制造商:MICRO-LINEAR 制造商全稱:MICRO-LINEAR 功能描述:Power Factor Correction and PWM Controller Combo |
| ML4805 | 制造商:MICRO-LINEAR 制造商全稱:MICRO-LINEAR 功能描述:Variable Feedforward PFC/PWM Controller Combo |
| ML4805CP | 功能描述:功率因數(shù)校正 IC DIP-18 RoHS:否 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor 開關(guān)頻率:300 KHz 最大功率耗散: 最大工作溫度:+ 125 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-8 封裝:Reel |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。