- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄69059 > PKU4515PIPLA (ERICSSON POWER MODULES AB) 1-OUTPUT 49.5 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | PKU4515PIPLA |
| 廠商: | ERICSSON POWER MODULES AB |
| 元件分類: | 電源模塊 |
| 英文描述: | 1-OUTPUT 49.5 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| 封裝: | ROHS COMPLIANT PACKAGE-8 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 26/38頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 1050K |
| 代理商: | PKU4515PIPLA |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)當(dāng)前第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)
Ericsson Internal
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
4 (6)
Prepared (also subject responsible if other)
No.
MPM/BK Gran Persson
3/1301-BMR 602 Uen
Approved
Checked
Date
Rev
Reference
MPM/BK (Natalie Johansson)
(MICRF)
2007-05-10
E
Thermal Consideration
General
The converters are designed to operate in different thermal
environments and sufficient cooling must be provided to
ensure reliable operation.
Cooling is achieved mainly by conduction, from the pins to
the host board, and convection, which is dependent on the
airflow across the converter. Increased airflow enhances the
cooling of the converter.
The Output Current Derating graph found in the Output
section for each model provides the available output current
vs. ambient air temperature and air velocity at Vin = 53 V.
The DC/DC converter is tested on a 254 x 254 mm,
35 μm (1 oz), 8-layer test board mounted vertically in a wind
tunnel with a cross-section of 305 x 305 mm.
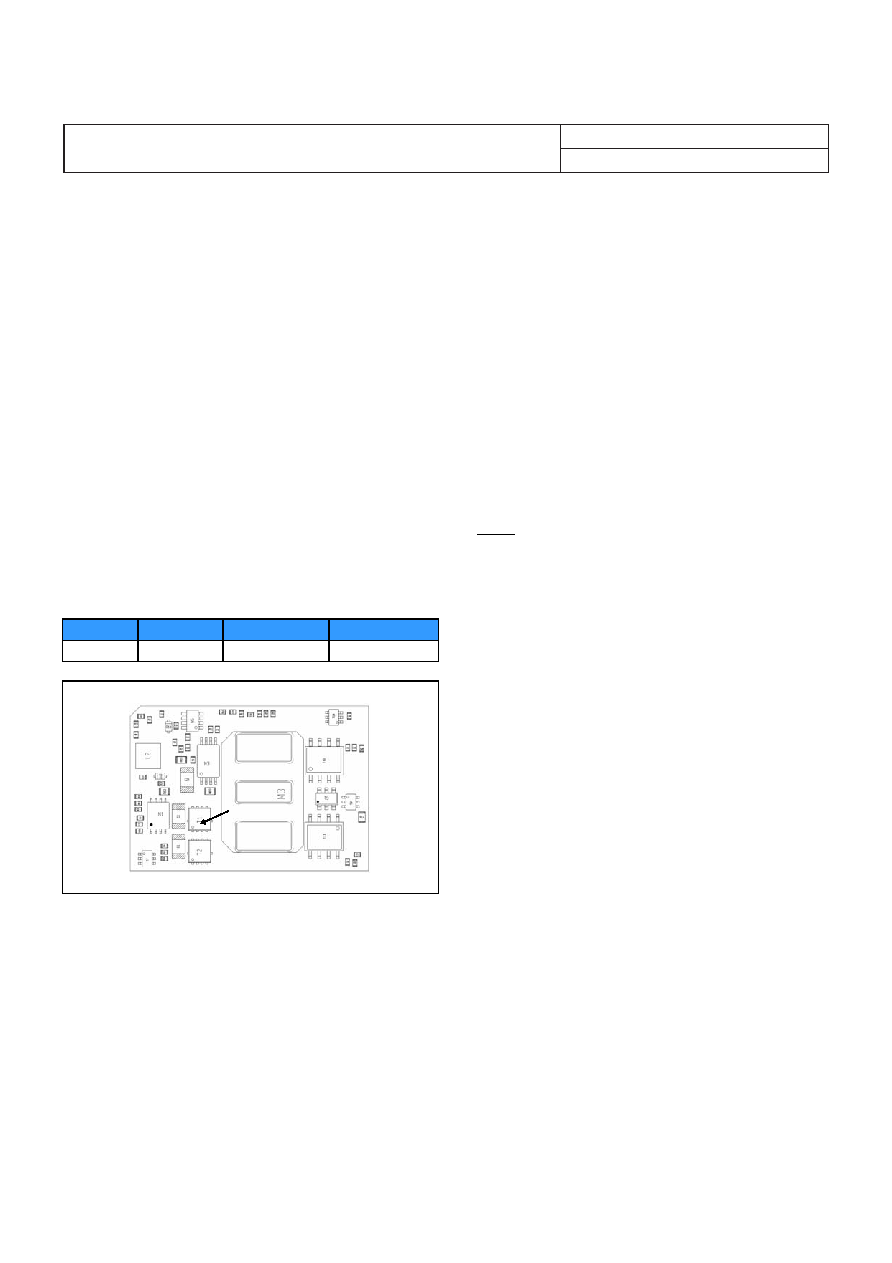
Proper cooling of the DC/DC converter can be verified by
measuring the temperature at positions P1. The temperature
at these positions should not exceed the max values provided
in the table below.
See Design Note 019 for further information.
Position
Device
Designation
Max value
P1
Mosfet
Tref
110C
P1
Definition of reference temperature (Tref)
The reference temperature is used to monitor the temperature
limits of the product. Temperatures above maximum Tref are
not allowed and may cause degradation or permanent
damage to the product. Tref is also used to define the
temperature range for normal operating conditions.
Tref is defined by the design and used to guarantee safety
margins, proper operation and high reliability of the module.
Ambient Temperature Calculation
By using the thermal resistance the maximum allowed
ambient temperature can be calculated.
1. The power loss is calculated by using the formula
((1/η) - 1) × output power = power losses (Pd).
η = efficiency of converter. For example 89.2 % = 0.892
2. Find the thermal resistance (R
th) in the Thermal Resistance
graph found in the Output section for each model.
Calculate the temperature increase (ΔT).
ΔT = Rt
h x Pd
3. Max allowed ambient temperature is:
Max T
ref - ΔT.
Example PKU 4510 (@ V
I 53 V &15 A) at 1 m/s:
1. ((
) -
1) × 49.5 W = 5.99 W
2. 5.99 W × 9.2°C/W = 55.1°C
3. 110 °C — 55.1°C = max ambient temperature is 54.9°C
The actual temperature will be dependent on several factors
such as the PCB size, number of layers and direction of
airflow.
1
0.892
E
PKU 4000 PI & SI series
DC/DC converters, Input 36-75 V, Output 25 A/50 W
EN/LZT 146 308 R2B May 2007
Ericsson Power Modules AB
Technical Specication
E
PKU 4000 PI & SI series
DC/DC converters, Input 36-75 V, Output 25 A/50 W
EN/LZT 146 308 R3A May 2007
Ericsson Power Modules AB
Technical Specication
32
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PKU4318LSIPLA | 1-OUTPUT 30 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| PKU4418GSIP | 1-OUTPUT 45 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| PKU4510SILA | 1-OUTPUT 49.5 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| PKU4318HPIPLA | 1-OUTPUT 37.5 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| PKU4513SILA | 1-OUTPUT 50 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PKU4515SI | 功能描述:DC/DC轉(zhuǎn)換器 50W 15V 3.3A 36-75Vin SMT RoHS:否 制造商:Murata 產(chǎn)品: 輸出功率: 輸入電壓范圍:3.6 V to 5.5 V 輸入電壓(標(biāo)稱): 輸出端數(shù)量:1 輸出電壓(通道 1):3.3 V 輸出電流(通道 1):600 mA 輸出電壓(通道 2): 輸出電流(通道 2): 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體尺寸: |
| PKU451OSI | 制造商:Ericsson 功能描述:- Trays |
| PKU4619PI | 功能描述:DC/DC轉(zhuǎn)換器 63W 2.5V 25A 36-75Vin RoHS:否 制造商:Murata 產(chǎn)品: 輸出功率: 輸入電壓范圍:3.6 V to 5.5 V 輸入電壓(標(biāo)稱): 輸出端數(shù)量:1 輸出電壓(通道 1):3.3 V 輸出電流(通道 1):600 mA 輸出電壓(通道 2): 輸出電流(通道 2): 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體尺寸: |
| PKU4710 PI | 制造商:Ericsson 功能描述: |
| PKU4710PI | 功能描述:DC/DC轉(zhuǎn)換器 66W 3.3V 20A 36-75Vin RoHS:否 制造商:Murata 產(chǎn)品: 輸出功率: 輸入電壓范圍:3.6 V to 5.5 V 輸入電壓(標(biāo)稱): 輸出端數(shù)量:1 輸出電壓(通道 1):3.3 V 輸出電流(通道 1):600 mA 輸出電壓(通道 2): 輸出電流(通道 2): 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體尺寸: |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。