- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371980 > RB2490-D06 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | RB2490-D06 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 3/4頁 |
| 文件大小: | 115K |
| 代理商: | RB2490-D06 |
Specifications are subject to change without notice (30.06.1999)
3
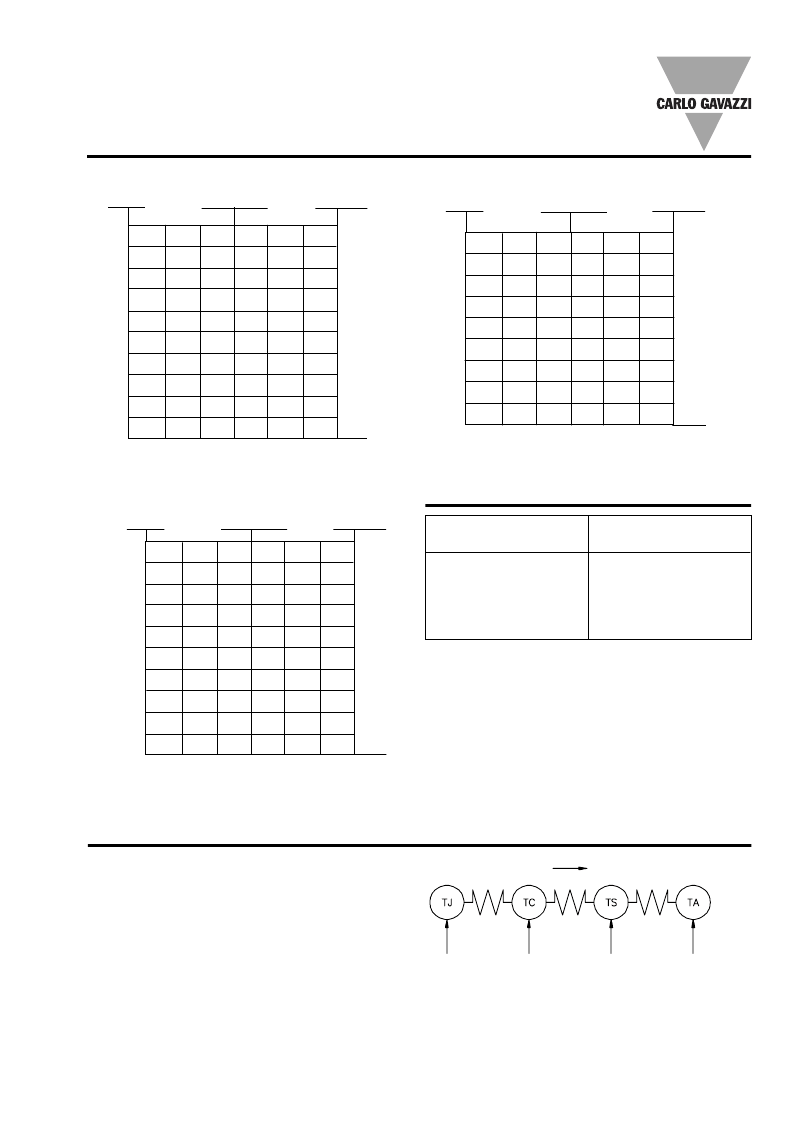
RA 60 50 -D 16, RA .. 90 -D .., RA .. 110 -D..
Heatsink Dimensions
(load current versus ambient temperature)
RA 60 50 -D 16
T
A
Ambient temp. [
°
C]
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
Power
dissipation [W]
Thermal resistance
[K/W]
Load
current [A]
0.92
0.76
0.60
0.45
0.29
-
63
1.2
0.99
0.80
0.62
0.44
0.26
55
1.5
1.3
1.1
0.85
0.63
0.42
47
1.9
1.6
1.4
1.1
0.89
0.63
40
2.4
2.1
1.8
1.5
1.2
0.91
33
3
2.7
2.3
1.9
1.5
1.1
26
3.9
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
20
5.5
4.8
4.1
3.4
2.7
2.1
15
8.6
7.5
6.4
5.4
4.3
3.2
9
17.9
20
15.6
30
13.4
40
11.2
50
8.9
60
6.7
70
4
RA .. 90 .. -D ..
T
A
Ambient temp. [
°
C]
0.63
0.53
0.42
0.32
-
-
97
0.81
0.69
0.57
0.45
0.33
-
84
1
0.89
0.75
0.61
0.47
0.33
71
1.3
1.2
1
0.83
0.66
0.49
59
1.7
1.5
1.3
1.1
0.85
0.64
47
2.2
1.9
1.7
1.4
1.1
0.83
36
3.1
2.7
2.3
1.9
1.5
1.2
26
4.8
4.2
3.6
3
2.4
1.8
17
10
20
8.8
30
7.5
40
6.3
50
5
3.8
70
8
60
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
Thermal resistance
[K/W]
Load
current [A]
Power
dissipation [W]
Applications
Heat flow
Heatsink
temperature
R
th
j-c
R
th
c-s
R
th
s-a
Junction
temperature
Case
temperature
Ambient
temperature
This relay is designed for use
in applications in which it is
exposed to high surge condi-
tions. Care must be taken to
ensure
proper
when the relay is to be used at
high sustained currents. Ade-
quate electrical connection
between relay terminals and
cable must be ensured.
heatsinking
Thermal characteristics
The thermal design of Solid
State Relays is very important.
Compare the value found in the load current versus tempera-
ture chart with the standard heatsink values and select the
heatsink with the next lower value.
Carlo Gavazzi Heatsink
(see Accessories)
No heatsink required
RHS 100 Assy
RHS 301 Assy
RHS 301 F Assy
Consult your distributor
Heatsink Selection
Thermal resistance
R
th s-a
> 12.5
K/W
3.0 K/W
0.8 K/W
0.25 K/W
< 0.25 K/W
R
th
c-s = case to heatsink
R
th
s-a = heatsink to ambient
Thermal resistance:
R
th
j-c = junction to case
RA.. 110-D ..
It is essential that the user
makes sure that cooling is ad-
equate and that the maximum
junction temperature of the
relay is not exceeded.
If the heatsink is placed in a
small closed room, control panel
or the like, the power dissipation
can cause the ambient tempe-
rature to rise. The heatsink is
to be calculated on the basis
of the ambient temperature and
the increase in temperature.
0.43
0.35
0.27
-
-
-
126
0.63
0.53
0.42
0.32
-
-
97
0.81
0.69
0.57
0.45
0.33
-
84
1
0.89
0.75
0.61
0.47
0.33
71
1.3
1.2
1
0.83
0.66
0.49
59
1.7
1.5
1.3
1.1
0.85
0.64
47
2.2
1.9
1.7
1.4
1.1
0.83
36
3.1
2.7
2.3
1.9
1.5
1.2
26
4.8
4.2
3.6
3
2.4
1.8
17
10
20
8.8
30
7.5
40
6.3
50
5
3.8
70
8
60
Thermal resistance
[K/W]
Load
current [A]
Power
dissipation [W]
T
A
Ambient temp. [
°
C]
110
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| RA4890HD10 | |
| RA4890HD12 | |
| RA4890LD10 | |
| RA4890LD12 | |
| RA2490HD06 | |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| RB24ED1100 | 制造商:E-Switch Inc 功能描述:SWITCH ROCKER NON ILLUMINATED 制造商:E-Switch Inc 功能描述:RB2 Series |
| RB24GC1100 | 功能描述:搖臂開關與扳鈕開關 ROCKER RoHS:否 制造商:C&K Components 觸點形式: 開關功能: 電流額定值:50 mA 電壓額定值 AC: 電壓額定值 DC:30 V 功率額定值: 端接類型: 執(zhí)行器:Paddle 顏色: 安裝風格:Panel 端子密封: 觸點電鍍: 照明:Not Illuminated 照明顏色: |
| RB24GC1100/ACC-F02-1 | 功能描述:搖臂開關與扳鈕開關 RoHS:否 制造商:C&K Components 觸點形式: 開關功能: 電流額定值:50 mA 電壓額定值 AC: 電壓額定值 DC:30 V 功率額定值: 端接類型: 執(zhí)行器:Paddle 顏色: 安裝風格:Panel 端子密封: 觸點電鍍: 照明:Not Illuminated 照明顏色: |
| RB24GC1200 | 功能描述:搖臂開關與扳鈕開關 ROCKER RoHS:否 制造商:C&K Components 觸點形式: 開關功能: 電流額定值:50 mA 電壓額定值 AC: 電壓額定值 DC:30 V 功率額定值: 端接類型: 執(zhí)行器:Paddle 顏色: 安裝風格:Panel 端子密封: 觸點電鍍: 照明:Not Illuminated 照明顏色: |
| RB24GD1100 | 功能描述:搖臂開關與扳鈕開關 20A 22mm x 20mm On-On RoHS:否 制造商:C&K Components 觸點形式: 開關功能: 電流額定值:50 mA 電壓額定值 AC: 電壓額定值 DC:30 V 功率額定值: 端接類型: 執(zhí)行器:Paddle 顏色: 安裝風格:Panel 端子密封: 觸點電鍍: 照明:Not Illuminated 照明顏色: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。