- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄271593 > SD-14595F1-382L (DATA DEVICE CORP) SYNCHRO OR RESOLVER TO DIGITAL CONVERTER, CDFP36 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | SD-14595F1-382L |
| 廠商: | DATA DEVICE CORP |
| 元件分類: | 位置變換器 |
| 英文描述: | SYNCHRO OR RESOLVER TO DIGITAL CONVERTER, CDFP36 |
| 封裝: | CERAMIC, FP-36 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 8/14頁 |
| 文件大小: | 416K |
| 代理商: | SD-14595F1-382L |
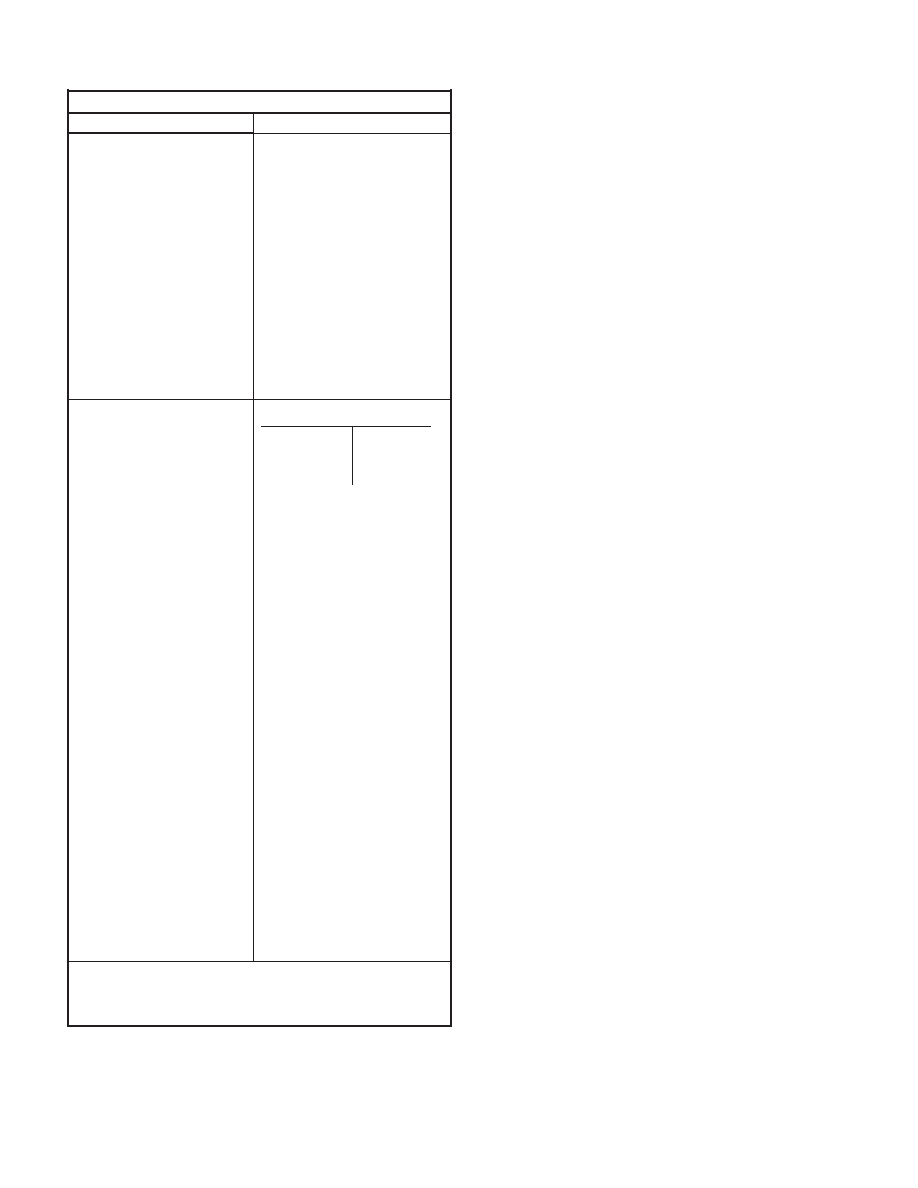
3
SynchroZIN(ZSO)
ResolverZIN
180
100 k
-
30 k
20 k
30 k
47 - 440 Hz
80 -138 V rms; 115 V rms
nominal resistive
600 k
min, resistive
500 V rms transformer isolated
+R (in phase with RH-RL) and -R
(in phase with RL- RH) derived
from op-amps. Short-Circuit proof.
3.0 V nominal riding on ground
reference V. Output Voltage level
tracks input level.
4 mA typ, 7 mA max from +15 V
supply.
47 - 440 Hz
10 -100 V rms L- L; 90 V rms
L- L nominal
148 k
min L- L balanced
resistive
±500 V rms, transformer isolated
Resolver output,
- sine (- S) + Cosine (+C) derived
from op-amps. Short circuit proof.
1.0 V rms nominal riding on
ground reference V. Output voltage
level tracks input level.
4 mA typ, 7 mA max from +15 V
supply.
360 - 1000 Hz
18 - 130 V
40 k
min
1200 V peak
360-1000 Hz
700 V peak
PARAMETER
VALUE
Notes:
(1) Pin Programmable.
(2) See TABLE 7.
(3) VEL polarity is negative volltage for positive angular rate
Minimum Input impedances
(Balanced)
90 V L-L
26 V L-L
11.8 V L-L
60 Hz TRANSFORMERS
Reference Transformer
Carrier Frequency Range
Input Voltage Range
Input Impedance
Input Common Mode Voltage
Output Description
Output Voltage
Power Required
Signal Transformer
Carrier Frequency Range
Input Voltage Range
Input Impedance
Input Common Mode Voltage
Output Description
Output Voltage
Power Required
TABLE 1. SD-14595/96/97 SPECIFICATIONS (CONTD)
THEORY OF OPERATION
The SD-14595/96/97 series are small, 36-pin DDIP synchro-to-
digital hybrid converters. As shown in the block diagram (FIG-
URE 1), the SD-14595/96/97 can be broken down into the fol-
lowing functional parts: Signal Input Option, Converter, Analog
Conditioner, Power Supply Conditioner, and Digital Interface.
CONVERTER OPERATION
As shown in FIGURE 1, the converter section of the SD-
14595/96/97 contains a high accuracy control transformer,
demodulator, error processor, voltage controlled oscillator
(VCO), up-down counter, and reference conditioner. The con-
verter produces a digital angle which tracks the analog input
angle to within the specified accuracy of the converter.The con-
trol transformer performs the following trigonometric computa-
tion:
sin(
θ - φ) = sinθ cosφ - cosθ sinφ
Where:
θ is angle theta representing the resolver shaft position.
φ is digital angle phi contained in the up/down counter.
The tracking process consists of continually adjusting
φ to make
(
θ - φ) = 0, so that φ will represent the shaft position θ.
The output of the demodulator is an analog dc level proportional
to sin(
θ - φ). The error processor receives its input from the
demodulator and integrates this sin(
θ - φ) error signal which then
drives the VCO. The VCO’s clock pulses are accumulated by the
up/down counter. The velocity voltage accuracy, linearity and off-
set are determined by the quality of the VCO. Functionally, the
up/down counter is an incremental integrator. Therefore, there
are two stages of integration which makes the converter a Type
II tracking servo.
In a Type II servo, the VCO always settles to a counting rate
which makes d
φ/dt equal to dθ/dt without lag. The output data will
always be fresh and available as long as the maximum tracking
rate of the converter is not exceeded.
The reference conditioner is a comparator that produces the
square wave reference voltage which drives the demodulator. It’s
single ended Input Z is 250k ohms/min, 500k ohms differential.
SPECIAL FUNCTIONS
REFERENCE SYNTHESIZER-QUADRATURE VOLTAGES.
The synthesized reference section of the SD-14595 eliminates
errors caused by quadrature voltage. Due to the inductive nature
of synchros and resolvers, their signals typically lead the refer-
ence signal (RH and RL) by about 6°. When an uncompensated
reference signal is used to demodulate the control transformer’s
output, quadrature voltages are not completely eliminated. In a
14-bit converter it is not necessary to compensate for the refer-
ence signal’s phase shift. A 6° phase shift will, however, cause
problems for the one minute accuracy converters. As shown in
FIGURE 1, the converter synthesizes its own cos(
ωt + α) refer-
TRANSFORMER
CHARACTERISTICS
(See ordering information for list
of Transformers.
Reference Transformers are
Optional for Both Solid-State
and Voltage Follower Input
Options.)
400 Hz TRANSFORMERS
Reference Transformer
Carrier Frequency Range
Voltage Range
Input Impedance
Breakdown Voltage to GND
Signal Transformer
Carrier Frequency Range
Breakdown Voltage to GND
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| SD-14595F1-382Y | SYNCHRO OR RESOLVER TO DIGITAL CONVERTER, CDFP36 |
| SD-14595F1-382Z | SYNCHRO OR RESOLVER TO DIGITAL CONVERTER, CDFP36 |
| SD-14595F1-384K | SYNCHRO OR RESOLVER TO DIGITAL CONVERTER, CDFP36 |
| SD-14595F1-384S | SYNCHRO OR RESOLVER TO DIGITAL CONVERTER, CDFP36 |
| SD-14595F1-384Z | SYNCHRO OR RESOLVER TO DIGITAL CONVERTER, CDFP36 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| SD-14595F2-102 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Synchro-to-Digital Converter |
| SD-14595F2-104 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Synchro-to-Digital Converter |
| SD-14595F2-105 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Synchro-to-Digital Converter |
| SD-14595F2-112 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Synchro-to-Digital Converter |
| SD-14595F2-114 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Synchro-to-Digital Converter |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。