- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄372185 > SP503EM Multiprotocol Transceiver PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | SP503EM |
| 英文描述: | Multiprotocol Transceiver |
| 中文描述: | 多協(xié)議收發(fā)器 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 10/29頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 641K |
| 代理商: | SP503EM |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)當(dāng)前第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)
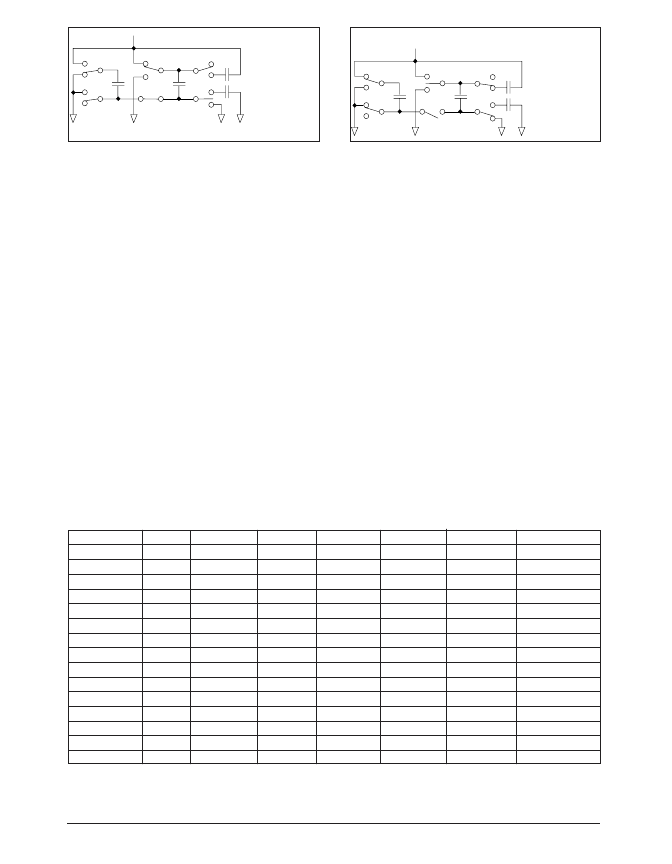
Date: 7/29/04
SP503 Multiprotocol Transceiver
10
Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
V
CC
= +5V
–5V
+5V
–5V
V
SS
Storage Capacitor
V
DD
Storage Capacitor
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
+
+
+
+
–
–
–
–
Figure 4. Charge Pump Phase 3.
V
CC
= +5V
+10V
V
SS
Storage Capacitor
V
DD
Storage Capacitor
C
1
C
2
C
3
C
4
+
+
+
+
–
–
–
–
Figure 5. Charge Pump Phase 4.
There are three basic types of driver circuits —
RS-232, RS-423, and RS-485. The RS-232 driv-
ers output a minimum of
±
5V level single–
ended signals (with 3k
and 2500pF loading),
and can operate up to 120kbps. The RS-232
drivers are used in RS-232 mode for all signals,
and also in V.35 mode where they are used as the
control line signals.
The RS-423 drivers output a minimum of
±
3.6V
level single–ended signals (with 450
loading)
and can operate up to 120kbps. Open circuit V
and V
measurements may exceed the
±
6V
limitation of RS-423. The RS-423 drivers are
used in RS-449 and EIA-530 modes as RL and
LL outputs.
The third type of driver supports RS-485, which
is a differential signal that can maintain
±
1.5V
differential output levels with a worst case load
of 54
. The signal levels and drive capability of
the RS-485 drivers allow the drivers to also
support RS-422 requirements of
±
2V differen-
tial output levels with 100
loads. The RS-422
drivers are used in RS-449 and EIA-530 modes
as clock, data, and some control line signals.
The RS-485–type drivers are also used in the
V.35 mode. V.35 levels require
±
0.55V signals
with a load of 100
. In order to meet the voltage
requirements of V.35, external series resistors
with source impedance termination resistors
must be implemented to voltage divide the driver
outputs from 0 to +5V to 0 to +0.55V.
Figure 6
shows the values of the resistor network and
how to connect them. The termination network
also achieves the 50
to 150
source imped-
ance for V.35. For applications that require
V.11 signals for clock and data instead of V.35
levels, omit the external termination networks.
All of the differential drivers, RS-485, RS-422,
and V.35 can operate up to 5Mbps.
Table 1. SP503 Drivers
Pin Label
Mode:
RS-232
V.35
RS-422
RS-485
RS-449
EIA-530
TDEC
3
–TDEC
0
SD(a)
0000
0010
1110
0100
0101
1100
1101
tri–state
RS-232
V.35–
RS-422–
RS-485–
RS-422–
RS-422–
SD(b)
tri–state
tri–state
V.35+
RS-422+
RS-485+
RS-422+
RS-422+
TR(a)
tri–state
RS-232
RS-232
RS-422–
RS-485–
RS-422–
RS-422–
TR(b)
tri–state
tri–state
tri–state
RS-422+
RS-485+
RS-422+
RS-422+
RS(a)
tri–state
RS-232
RS-232
RS-422–
RS-485–
RS-422–
RS-422–
RS(b)
tri–state
tri–state
tri–state
RS-422+
RS-485+
RS-422+
RS-422+
RL(a)
tri–state
RS-232
RS-232
RS-422–
RS-485–
RS-423
RS-423
RL(b)
tri–state
tri–state
tri–state
RS-422+
RS-485+
tri–state
tri–state
LL(a)
tri–state
RS-232
RS-232
RS-422–
RS-485–
RS-423
RS-423
LL(b)
tri–state
tri–state
tri–state
RS-422+
RS-485+
tri–state
tri–state
ST(a)
tri–state
RS-232
V.35–
RS-422–
RS-485–
RS-422–
RS-422–
ST(b)
tri–state
tri–state
V.35+
RS-422+
RS-485+
RS-422+
RS-422+
TT(a)
tri–state
RS-232
V.35–
RS-422–
RS-485–
RS-422–
RS-422–
TT(b)
tri–state
tri–state
V.35+
RS-422+
RS-485+
RS-422+
RS-422+
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| SP504 | WAN Multi-Mode Serial Transceiver |
| SP504AN | Application Note |
| SP504CF | Application Note |
| SP504EB | Evaluation Board Manual |
| SP504MCF | WAN Multi-Mode Serial Transceiver |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| SP503EM-L | 功能描述:總線收發(fā)器 Full Duplex RS-485 s RoHS:否 制造商:Fairchild Semiconductor 邏輯類(lèi)型:CMOS 邏輯系列:74VCX 每芯片的通道數(shù)量:16 輸入電平:CMOS 輸出電平:CMOS 輸出類(lèi)型:3-State 高電平輸出電流:- 24 mA 低電平輸出電流:24 mA 傳播延遲時(shí)間:6.2 ns 電源電壓-最大:2.7 V, 3.6 V 電源電壓-最小:1.65 V, 2.3 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-48 封裝:Reel |
| SP503P | 制造商:SII 制造商全稱(chēng):Seiko Instruments Inc 功能描述:LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAYS(STANDARD PRODUCTS) |
| SP504 | 制造商:SIPEX 制造商全稱(chēng):Sipex Corporation 功能描述:WAN Multi-Mode Serial Transceiver |
| SP504AN | 制造商:SIPEX 制造商全稱(chēng):Sipex Corporation 功能描述:Application Note |
| SP504CF | 制造商:SIPEX 制造商全稱(chēng):Sipex Corporation 功能描述:Application Note |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。