- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄372191 > SP6831EK Low Power Voltage Inverters With Shutdown PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | SP6831EK |
| 英文描述: | Low Power Voltage Inverters With Shutdown |
| 中文描述: | 低功率高壓變頻器具有關斷 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 10/16頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 208K |
| 代理商: | SP6831EK |
10
Rev. 9-22-00
SP6830/6831 Low Power Voltage Inverters With Shutdown Copyright 2000 Sipex Corporation
conversion loss during charge transfer between
the flying and output capacitors. These are the
three theoretical factors that may effect the power
efficiency of the SP6830/6831 devices in designs.
Any internal losses come from the IC's on board
circuitry. Losses in the IC can be induced by the
input voltage, the frequency of the oscillator, and
the ambient temperature. The most influential
internal loss in the IC may be found in the power-
on resistance of the internal MOSFET switches.
Any of the losses with the charge pump capacitors
will be induced by the capacitor's ESR. The
affects of the ESR losses and the output resistance
can be found in the following equation:
I
OUT
2
x R
OUT
= P
CAP
+ P
CONV
and
R
OUT
≈
4 x (2 x R
SWITCHES
+ ESR
C1
) +
ESR
C2
+
f
OSC
x C1
,
where I
it the output current, R
is the
circuit's output resistance, R
is the internal
resistance of the MOSFET switches, ESR
and
ESR
C2
are the ESR of their respective capacitors,
and f
OSC
is the oscillator frequency. This term
with f
is derived from an ideal switched-
capacitor circuit as seen in
Figure 19
.
Any losses due to the conversion process will
happen during the charge transfer between the
flying capacitor, C1, and the output capacitor,
C2, when there is a voltage difference between
them. P
CONV
can be determined by the following
equation:
P
CONV
= f
OSC
x [
1
/
2
x C1 x (V
IN
2
- V
OUT
2
) +
1
/
2
x C2 x (V
RIPPLE
2
- 2V
OUT
V
RIPPLE
) ].
Actual Efficiency
To determine the actual efficiency of the SP6830/
6831 device operation, a designer can use the
following equation:
Efficiency (actual) = P
OUT
P
IN
,
where
P
OUT
= V
OUT
x I
OUT
and
P
IN
= V
IN
x I
IN
where P
is the power output, V
is the
output voltage, I
is the output current, P
is
the power from the supply driving the SP6830/
6831 devices, V
is the supply input voltage, and
I
IN
is the supply input current.
Ideal Efficiency
The ideal efficiency is not the true power
efficiency because it does not involve the input
power which includes the input current losses in
the charge pump. The ideal efficiency can be
determined with the following equation:
Efficiency (ideal) = P
OUT
P
,
where
P
OUT(IDEAL)
= -V
IN
x-V
IN
R
L
,
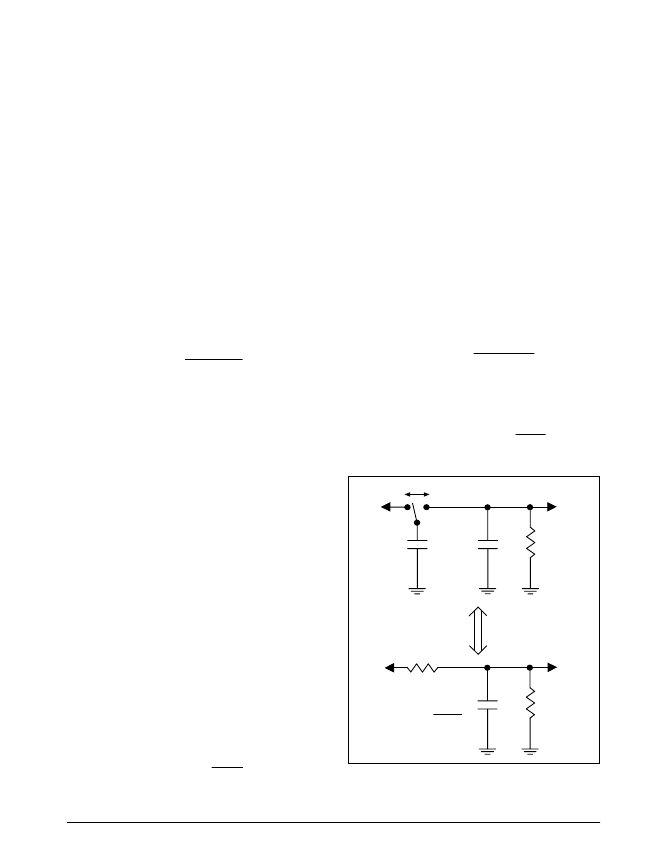
Figure 19. Equivalent Circuit for an Ideal Switched
Capacitor
V+
C2
R
L
V
OUT
C1
f
V+
C2
R
L
V
OUT
R
equivalent
=
1
f x C1
R
equivalent
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| SP6831 | Low Power Charge Pump Voltage Inverters With Shutdown(120kHz,低功耗電荷泵電壓反相器(帶關斷)) |
| SP6832 | High Speed, High Efficiency Voltage Inverter |
| SP6832EK | High Speed, High Efficiency Voltage Inverter |
| SP6850 | Green-Mode PWM Controller |
| SP6850AD8TG | Green-Mode PWM Controller |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| SP6831EK/TR | 制造商:SIPEX CORP 功能描述: 制造商:Exar Corporation 功能描述:Analog IC |
| SP6831TR | 制造商:SIPEX 制造商全稱:Sipex Corporation 功能描述:Low Power Voltage Inverters With Shutdown |
| SP6832 | 制造商:SIPEX 制造商全稱:Sipex Corporation 功能描述:High Speed, High Efficiency Voltage Inverter |
| SP6832EK | 制造商:Sipex 功能描述:Bulk |
| SP6832EK/TR | 制造商:SIPEX 制造商全稱:Sipex Corporation 功能描述:High Speed, High Efficiency Voltage Inverter |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。