- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98148 > STK17T88-RF45 PROGRAMMABLE TIMER, PDSO48 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | STK17T88-RF45 |
| 元件分類: | 時鐘/數(shù)據(jù)恢復(fù)及定時提取 |
| 英文描述: | PROGRAMMABLE TIMER, PDSO48 |
| 封裝: | 0.300 INCH, ROHS COMPLIANT, PLASTIC, SSOP-48 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 4/29頁 |
| 文件大小: | 535K |
| 代理商: | STK17T88-RF45 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁當(dāng)前第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁
12
Jan, 2008
Document Control #ML0024 Rev 2.0
STK17T88
nvSRAM OPERATION
nvSRAM
The STK17T88 nvSRAM is made up of two func-
tional components paired in the same physical cell.
These are the SRAM memory cell and a nonvolatile
QuantumTrap cell. The SRAM memory cell operates
like a standard fast static RAM. Data in the SRAM
can be transferred to the nonvolatile cell (the
STORE operation), or from the nonvolatile cell to
SRAM (the RECALL operation). This unique archi-
tecture allows all cells to be stored and recalled in
parallel. During the STORE and RECALL operations
SRAM READ and WRITE operations are inhibited.
The STK17T88 supports unlimited read and writes
like a typical SRAM. In addition, it provides unlimited
RECALL operations from the nonvolatile cells and
up to 200K STORE operations.
SRAM READ
The STK17T88 performs a READ cycle whenever E
and G are low while W and HSB are high. The
address specified on pins A0-14 determine which of
the 32,768 data bytes will be accessed. When the
READ is initiated by an address transition, the out-
puts will be valid after a delay of tAVQV (READ cycle
#1). If the READ is initiated by E and G, the outputs
will be valid at tELQV or at tGLQV, whichever is later
(READ cycle #2). The data outputs will repeatedly
respond to address changes within the tAVQV access
time without the need for transitions on any control
input pins, and will remain valid until another
address change or until E or G is brought high, or W
and HSB is brought low.
SRAM WRITE
A WRITE cycle is performed whenever E and W are
low and HSB is high. The address inputs must be sta-
ble prior to entering the WRITE cycle and must
remain stable until either E or W goes high at the
end of the cycle. The data on the common I/O pins
DQ0-7 will be written into memory if it is valid tDVWH
before the end of a W controlled WRITE or tDVEH
before the end of an E controlled WRITE.
It is recommended that G be kept high during the
entire WRITE cycle to avoid data bus contention on
common I/O lines. If G is left low, internal circuitry
will turn off the output buffers tWLQZ after W goes
low.
AutoStore OPERATION
The STK17T88 stores data to nvSRAM using one of
three storage operations. These three operations
are Hardware Store (activated by HSB), Software
Store (activated by an address sequence), and
AutoStore (on power down).
AutoStore operation, a unique feature of Simtek
QuanumTrap technology that is a standard feature
on the STK17T88.
During normal operation, the device will draw cur-
rent from VCC to charge a capacitor connected to
the VCAP pin. This stored charge will be used by the
chip to perform a single STORE operation. If the
voltage on the VCC pin drops below VSWITCH, the
part will automatically disconnect the VCAP pin from
VCC. A STORE operation will be initiated with power
provided by the VCAP capacitor.
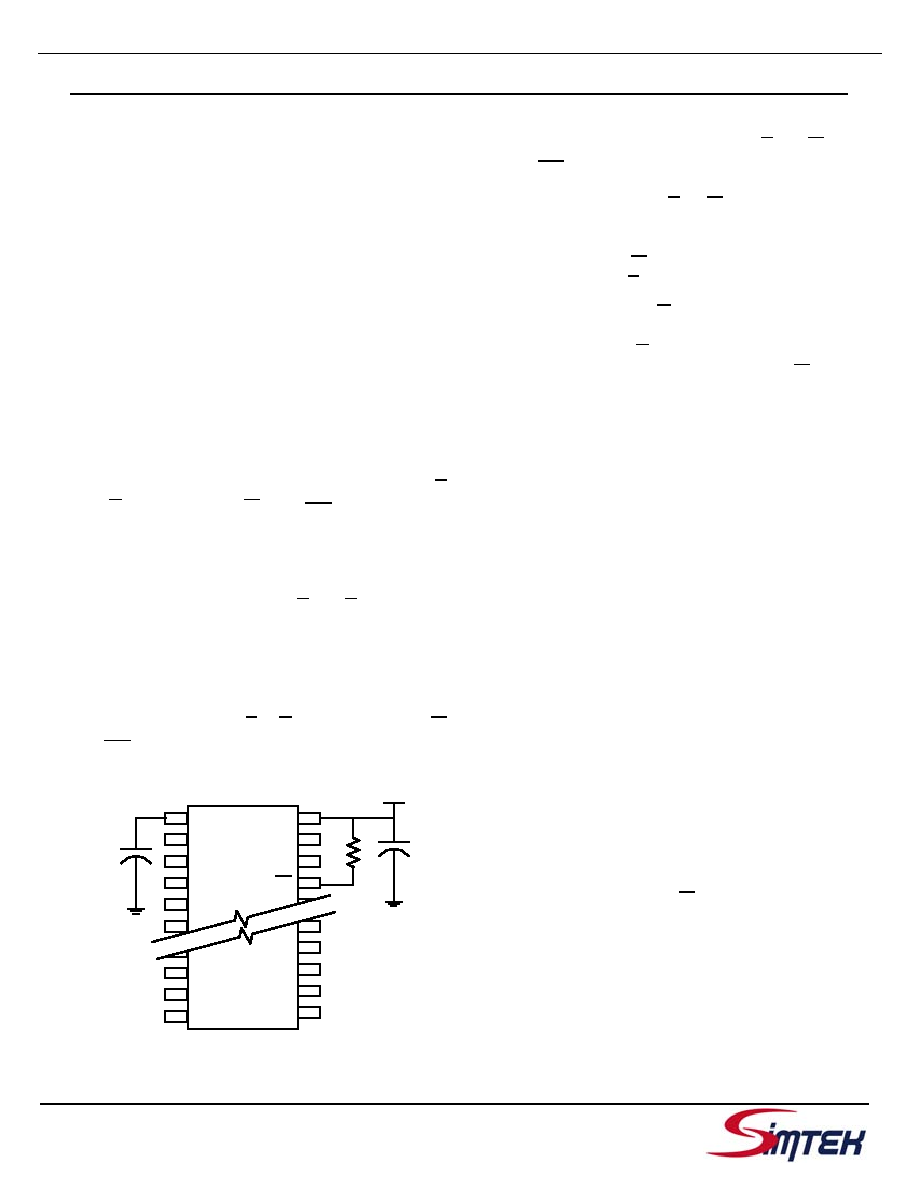
Figure 5 shows the proper connection of the storage
capacitor (VCAP) for automatic store operation.
Refer to the DC CHARACTERISTICS table for the
size of the capacitor. The voltage on the VCAP pin is
driven to 5V by a charge pump internal to the chip. A
pull up should be placed on W to hold it inactive dur-
ing power up.
To reduce unneeded nonvolatile stores, AutoStore
and Hardware Store operations will be ignored
unless at least one WRITE operation has taken
place since the most recent STORE or RECALL
cycle. Software initiated STORE cycles are per-
formed regardless of whether a WRITE operation
Figure 4: AutoStore Mode
VCC
V
CAP
10
k
O
h
m
0.1
F
VCC
VCAP
W
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| STK17T88-RF25ITR | PROGRAMMABLE TIMER, PDSO48 |
| STK17TA8-R25I | REAL TIME CLOCK, PDSO48 |
| STK17TA8-R35 | REAL TIME CLOCK, PDSO48 |
| STK17TA8-W25 | REAL TIME CLOCK, PDIP40 |
| STK17TA8-R45 | REAL TIME CLOCK, PDSO48 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| STK17T88-RF45I | 功能描述:NVRAM 32Kbx8+RTC 2.7-3.6V RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 數(shù)據(jù)總線寬度:8 bit 存儲容量:1024 Kbit 組織:128 K x 8 接口類型:Parallel 訪問時間:70 ns 電源電壓-最大:5.5 V 電源電壓-最小:4.5 V 工作電流:85 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 70 C 最小工作溫度:0 C 封裝 / 箱體:EDIP 封裝:Tube |
| STK17T88-RF45ITR | 功能描述:NVRAM 32Kbx8+RTC 2.7-3.6V RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 數(shù)據(jù)總線寬度:8 bit 存儲容量:1024 Kbit 組織:128 K x 8 接口類型:Parallel 訪問時間:70 ns 電源電壓-最大:5.5 V 電源電壓-最小:4.5 V 工作電流:85 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 70 C 最小工作溫度:0 C 封裝 / 箱體:EDIP 封裝:Tube |
| STK17T88-RF45TR | 功能描述:NVRAM 32Kbx8+RTC 2.7-3.6V RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 數(shù)據(jù)總線寬度:8 bit 存儲容量:1024 Kbit 組織:128 K x 8 接口類型:Parallel 訪問時間:70 ns 電源電壓-最大:5.5 V 電源電壓-最小:4.5 V 工作電流:85 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 70 C 最小工作溫度:0 C 封裝 / 箱體:EDIP 封裝:Tube |
| STK17TA8-RF25 | 功能描述:NVRAM 128Kbx8+RTC 2.7-3.6V RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 數(shù)據(jù)總線寬度:8 bit 存儲容量:1024 Kbit 組織:128 K x 8 接口類型:Parallel 訪問時間:70 ns 電源電壓-最大:5.5 V 電源電壓-最小:4.5 V 工作電流:85 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 70 C 最小工作溫度:0 C 封裝 / 箱體:EDIP 封裝:Tube |
| STK17TA8-RF25I | 功能描述:NVRAM 128Kbx8+RTC 2.7-3.6V RoHS:否 制造商:Maxim Integrated 數(shù)據(jù)總線寬度:8 bit 存儲容量:1024 Kbit 組織:128 K x 8 接口類型:Parallel 訪問時間:70 ns 電源電壓-最大:5.5 V 電源電壓-最小:4.5 V 工作電流:85 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 70 C 最小工作溫度:0 C 封裝 / 箱體:EDIP 封裝:Tube |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。