- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄361408 > TC7107IPL (TelCom Semiconductor, Inc.) PTB 41C 14#15,27#20 PIN/SKT RE PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | TC7107IPL |
| 廠商: | TelCom Semiconductor, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | PTB 41C 14#15,27#20 PIN/SKT RE |
| 中文描述: | 3-1/2位數(shù)的A / D轉(zhuǎn)換器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 13/19頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 296K |
| 代理商: | TC7107IPL |
3-195
TELCOM SEMICONDUCTOR, INC.
7
6
5
4
3
1
2
8
Analog Common (Pin 32)
The analog common pin is set at a voltage potential
approximately 3.0V below V
+
. The potential is guaranteed
to be between 2.7V and 3.35 V below V
+
. Analog common
is tied internally to the N channel FET capable of sinking
20mA. This FET will hold the common line at 3.0V should an
external load attempt to pull the common line toward V
+
.
Analog common source current is limited to 10
μ
A. Analog
common is therefore easily pulled to a more negative
voltage (i.e., below V
+
– 3.0V).
The TC7106A connects the internal V
+
to analog common during the auto-zero cycle. During the
reference-integrate phase, V
–
mon. If V
–
a common-mode voltage exists. This is rejected by the
converter's 86dB common-mode rejection ratio. In battery
operation, analog common and V
–
removing common-mode voltage concerns. In systems where
V
–
voltage, analog common should be connected to V
–
The analog common pin serves to set the analog section
reference or common point. The TC7106A is specifically
designed to operate from a battery or in any measurement
system where input signals are not referenced (float) with
respect to the TC7106A power source. The analog common
potential of V
+
– 3.0V gives a 6 V end of battery life voltage.
The common potential has a 0.001%/% voltage coefficient
and a 15
output impedance.
With sufficiently high total supply voltage (V
+
– V
–
> 7.0V) analog common is a very stable potential with
excellent temperature stability—typically 20ppm/
°
C. This
potential can be used to generate the reference voltage. An
external voltage reference will be unnecessary in most
cases because of the 50ppm/
°
C maximum temperature
coefficient. See Internal Voltage Reference discussion.
IN
and V
–
IN
inputs
IN
is connected to analog com-
IN
is not externally connected to analog common,
IN
are usually connected,
IN
is connected to the power supply ground or to a given
IN
.
Test (Pin 37)
The TEST pin potential is 5V less than V
+
. TEST may be
used as the negative power supply connection for external
CMOS logic. The TEST pin is tied to the internally generated
negative logic supply (Internal Logic Ground) through a
500
resistor in the TC7106A. The TEST pin load should be
no more than 1mA .
If TEST is pulled to V
+
all segments plus the minus sign
will be activated. Do not operate in this mode for more than
several minutes with the TC7106A. With TEST = V
+
the LCD
segments are impressed with a DC voltage which will
destroy the LCD.
The TEST pin will sink about 10mA when pulled to V
+
.
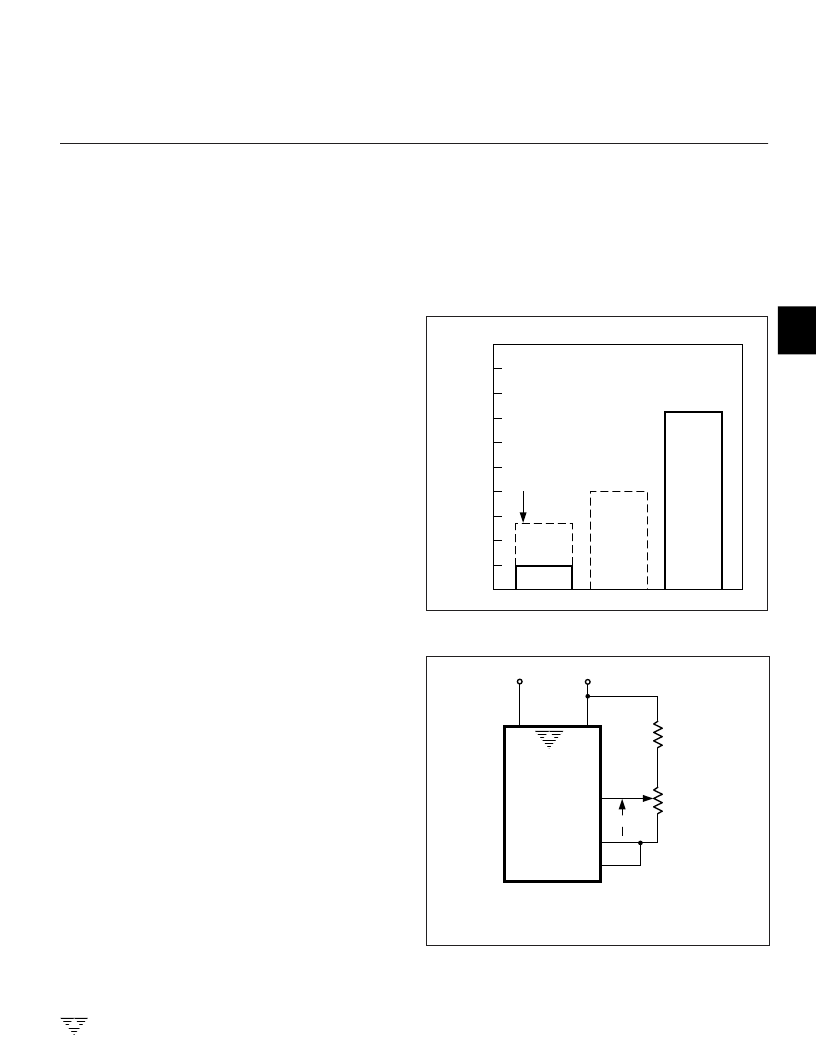
Internal Voltage Reference Stability
The analog common voltage temperature stability has
been significantly improved (Figure 10). The “A” version of
the industry standard circuits allow users to upgrade old
systems and design new systems without external voltage
references. External R and C values do not need to be
changed. Figure 11 shows analog common supplying the
necessary voltage reference for the TC7106A/TC7107A.
Figure 10. Analog Common Temperature Coefficient
Figure 11. Internal Voltage Reference Connection
TYPICAL
TYPICAL
NO
MAXIMUM
SPECIFIED
TYPICAL
NO MAXIMUM
SPECIFIED
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
T
ICL7136
NO MAXIMUM
SPECIFIED
TC
7106A
ICL7106
MAXIMUM
LIMIT
V–
ANALOG
COMMON
TC7106A
TC7107A
V+
32
35
36
24k
1k
V–
VREF
1
SET VREF = 1/2 VFULL SCALE
V+
TC7106
TC7106A
TC7107
TC7107A
3-1/2 DIGIT A/D CONVERTERS
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TC7107CKW | 3-1/2 DIGIT A/D CONVERTERS |
| TC7107ACKW | 3-1/2 DIGIT A/D CONVERTERS |
| TC7109CKW | 12-BIT UP-COMPATIBLE ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS |
| TC7109IJL | 12-BIT UP-COMPATIBLE ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS |
| TC7109 | 12-BIT UP-COMPATIBLE ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TC7107RCPL | 功能描述:LED顯示驅(qū)動器 w/LED Driver RoHS:否 制造商:Micrel 數(shù)位數(shù)量:5 片段數(shù)量: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:PLCC-44 工作電源電壓:4.75 V to 11 V 最大電源電流:10 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 最小工作溫度:- 40 C 封裝:Tube |
| TC7109 | 制造商:MICROCHIP 制造商全稱:Microchip Technology 功能描述:12-Bit レA-Compatible Analog-to-Digital Converters |
| TC7109_13 | 制造商:MICROCHIP 制造商全稱:Microchip Technology 功能描述:12-Bit ??-A-Compatible Analog-to-Digital Converters |
| TC7109A | 制造商:TELCOM 制造商全稱:TelCom Semiconductor, Inc 功能描述:12-BIT UP-COMPATIBLE ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS |
| TC7109ACKW | 功能描述:模數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換器 - ADC 13 Bit Fast Recovery RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 通道數(shù)量:2 結(jié)構(gòu):Sigma-Delta 轉(zhuǎn)換速率:125 SPs to 8 KSPs 分辨率:24 bit 輸入類型:Differential 信噪比:107 dB 接口類型:SPI 工作電源電壓:1.7 V to 3.6 V, 2.7 V to 5.25 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:VQFN-32 |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。