- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98227 > THS4601IDDARG3 (TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC) 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | THS4601IDDARG3 |
| 廠商: | TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 音頻/視頻放大 |
| 英文描述: | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 |
| 封裝: | GREEN, PLASTIC, SOP-8 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 4/34頁 |
| 文件大小: | 826K |
| 代理商: | THS4601IDDARG3 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁當前第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁
THS4601
SLOS388B OCTOBER 2001 REVISED JUNE 2002
12
www.ti.com
APPLICATION INFORMATION
introduction
The THS4601 is a high-speed, FET-input operational amplifier. The combination of its high frequency
capabilities and its DC precision make it a design option for a wide variety of applications, including test and
measurement, optical monitoring, transimpedance gain circuits, and high-impedance buffers. The applications
section of the data sheet discusses these particular applications in addition to general information about the
device and its features.
transimpedance fundamentals
FET-input amplifiers are often used in transimpedance applications because of their extremely high input
impedance. A transimpedance block accepts a current as an input and converts this current to a voltage at the
output. The high-input impedance associated with FET-input amplifiers minimizes errors in this process caused
by the input bias currents, IIB, of the amplifier.
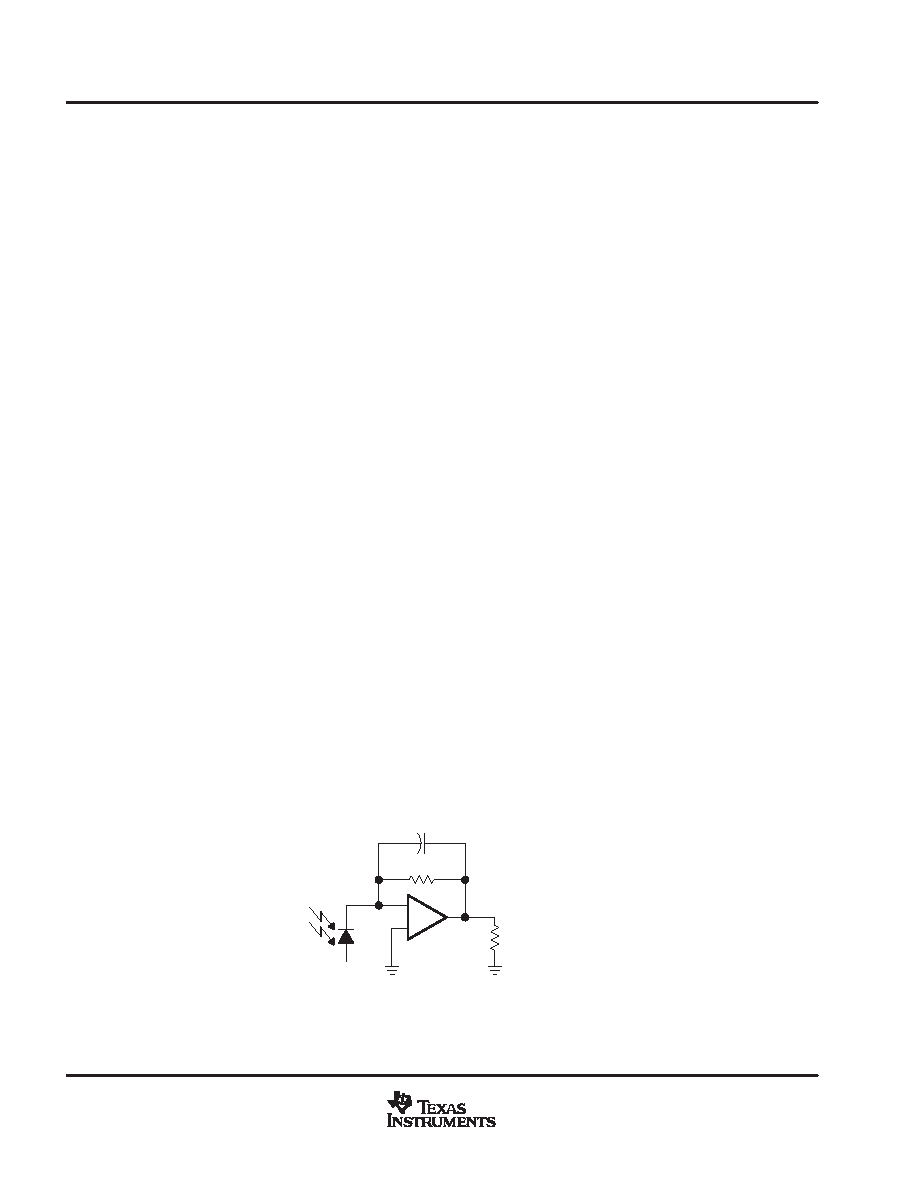
designing the transimpedance circuit
Typically, design of a transimpedance circuit is driven by the characteristics of the current source that provides
the input to the gain block. A photodiode is the most common example of a capacitive current source that would
interface with a transimpedance gain block. Continuing with the photodiode example, the system designer
traditionally chooses a photodiode based on two opposing criteria: speed and sensitivity. Faster photodiodes
cause a need for faster gain stages, and more sensitive photodiodes require higher gains in order to develop
appreciable signal levels at the output of the gain stage.
These parameters affect the design of the transimpedance circuit in a few ways. First, the speed of the
photodiode signal determines the required bandwidth of the gain circuit. However, the required gain, based on
the sensitivity of the photodiode, limits the bandwidth of the circuit. Additionally, the larger capacitance
associated with a more sensitive signal source also detracts from the achievable speed of the gain block. The
dynamic range of the input signal also places requirements on the amplifier’s dynamic range. Knowledge of the
source’s output current levels, coupled with a desired voltage swing on the output, dictates the value of the
feedback resistor, RF. The transfer function from input to output is VOUT = IINRF.
The large gain-bandwidth product of the THS4601 provides the capability for achieving both high trans-
impedance gain and wide bandwidth simultaneously. In addition, the high power supply rails provide the
potential for a very wide dynamic range at the output, allowing for the use of input sources which possess wide
dynamic range. The combination of these characteristics makes the THS4601 a design option for systems that
require transimpedance amplification of wideband, low-level input signals. A standard transimpedance circuit
is shown in Figure 26.
_
+
CF
λ
RL
RF
VBias
Figure 26. Wideband Photodiode Transimpedance Amplifier
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| THS4601IDG4 | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 |
| THS4601CDDAR | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 |
| THS4601CDDA | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 |
| THS4601CDR | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 |
| THS4601CD | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| THS4601IDG4 | 功能描述:高速運算放大器 Wideband FET-Input Op Amp RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 通道數(shù)量:1 電壓增益 dB:116 dB 輸入補償電壓:0.5 mV 轉換速度:55 V/us 工作電源電壓:36 V 電源電流:7.5 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-8 封裝:Tube |
| THS4601MUV | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:EVALUATION PART 10PIN CERAMIC FLATPACK - Rail/Tube |
| THS4631 | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:HIGH-VOLTAGE, HIGH SLEW RATE, WIDEBAND FET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER |
| THS4631D | 功能描述:高速運算放大器 High Speed FET-Input Op Amp RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 通道數(shù)量:1 電壓增益 dB:116 dB 輸入補償電壓:0.5 mV 轉換速度:55 V/us 工作電源電壓:36 V 電源電流:7.5 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-8 封裝:Tube |
| THS4631D | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:OP AMP 325MHZ 1000V/US 8SOI 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:IC HIGH SPEED OP-AMP ((NW)) |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。