- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98229 > THS7365IPWR (TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC) 6 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO20 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | THS7365IPWR |
| 廠商: | TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 音頻/視頻放大 |
| 英文描述: | 6 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO20 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, TSSOP-20 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 29/52頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1599K |
| 代理商: | THS7365IPWR |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁當(dāng)前第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁
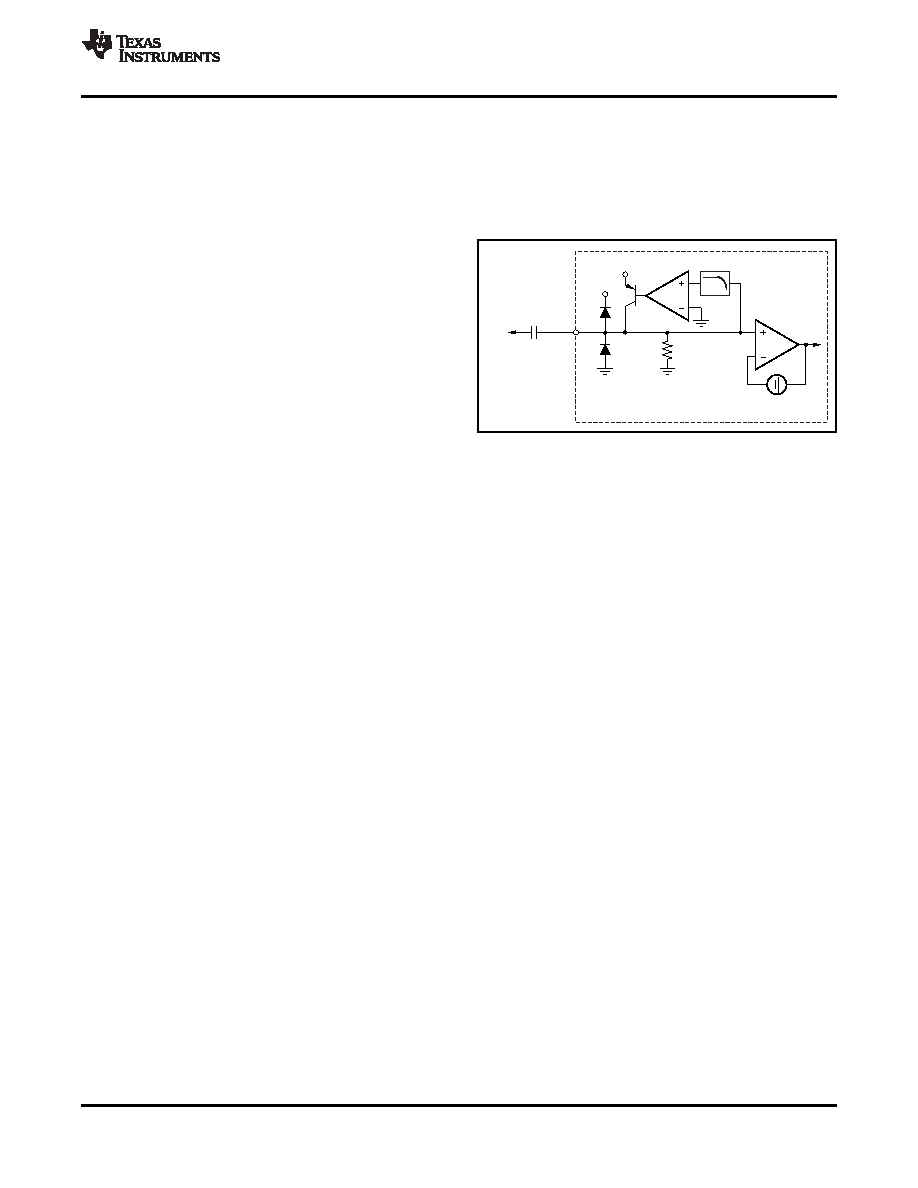
INPUT MODE OF OPERATION: AC SYNC TIP
Level
Shift
Internal
Circuitry
+V
S
800kW
Input
Pin
Input
0.1 mF
g
m
+V
S
STCLPF
www.ti.com.................................................................................................................................................................................................. SBOS467 – MARCH 2009
As a result of this delay, sync may have an apparent
CLAMP
voltage shift. The amount of shift depends on the
amount of droop in the signal as dictated by the input
Some video DACs or encoders are not referenced to
capacitor and the STC current flow. Because sync is
ground but rather to the positive power supply. The
used primarily for timing purposes with syncing
resulting video signals are generally at too great a
occurring on the edge of the sync signal, this shift is
voltage for a dc-coupled video buffer to function
transparent in most systems.
properly. To account for this scenario, the THS7365
incorporates a sync-tip clamp circuit. This function
requires a capacitor (nominally 0.1
F) to be in series
with the input. Although the term sync-tip-clamp is
used throughout this document, it should be noted
that the THS7365 would probably be better termed as
a dc restoration circuit based on how this function is
performed. This circuit is an active clamp circuit and
not a passive diode clamp function.
The input to the THS7365 has an internal control loop
that sets the lowest input applied voltage to clamp at
ground (0 V). By setting the reference at 0 V, the
THS7365 allows a dc-coupled input to also function.
Figure 118. Equivalent AC Sync-Tip-Clamp Input
Therefore, the sync-tip-clamp (STC) is considered
Circuit
transparent because it does not operate unless the
input signal goes below ground. The signal then goes
through the same 150-mV level shifter, resulting in an
While this feature may not fully eliminate overshoot
output voltage low level of 300 mV. If the input signal
issues on the input signal, in cases of extreme
tries to go below 0 V, the THS7365 internal control
overshoot and/or ringing, the STC system should help
loop sources up to 6 mA of current to increase the
minimize improper clamping levels. As an additional
input voltage level on the THS7365 input side of the
method to help minimize this issue, an external
coupling capacitor. As soon as the voltage goes
capacitor (for example, 10 pF to 47 pF) to ground in
above the 0-V level, the loop stops sourcing current
parallel with the external termination resistors can
and becomes very high impedance.
help filter overshoot problems.
One of the concerns about the sync-tip-clamp level is
It should be noted that this STC system is dynamic
how the clamp reacts to a sync edge that has
and does not rely upon timing in any way. It only
overshoot—common in VCR signals, noise, DAC
depends on the voltage that appears at the input pin
overshoot, or reflections found in poor printed circuit
at any given point in time. The STC filtering helps
board (PCB) layouts. Ideally, the STC should not
minimize
level
shift
problems
associated
with
react to the overshoot voltage of the input signal.
switching noises or very short spikes on the signal
Otherwise, this response could result in clipping on
line. This architecture helps ensure a very robust
the rest of the video signal because it may raise the
STC system.
bias voltage too much.
When the ac STC operation is used, there must also
To help minimize this input signal overshoot problem,
be some finite amount of discharge bias current. As
the control loop in the THS7365 has an internal
previously described, if the input signal goes below
low-pass filter, as shown in Figure 118. This filter
the 0-V clamp level, the internal loop of the THS7365
reduces the response time of the STC circuit. This
sources current to increase the voltage appearing at
delay is a function of how far the voltage is below
the input pin. As the difference between the signal
ground, but in general it is approximately a 400-ns
level and the 0-V reference level increases, the
delay for the 9.5-MHz filters and approximately a
amount
of
source
current
increases
150-ns delay for the 36-MHz filters. The effect of this
proportionally—supplying up to 6 mA of current.
filter is to slow down the response of the control loop
Thus, the time to re-establish the proper STC voltage
so as not to clamp on the input overshoot voltage but
can be very fast. If the difference is very small, then
rather the flat portion of the sync signal.
the source current is also very small to account for
minor voltage droop.
Copyright 2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated
35
Product Folder Link(s): THS7365
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| THS7365IPW | 6 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO20 |
| THS7368IPWR | 6 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO20 |
| THS7368IPW | 6 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO20 |
| THS7372IPWR | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
| THS7372IPW | 4 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO14 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| THS7368 | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:6-Channel Video Amplifier with 3-SD and 3-SD/ED/HD/Full-HD Filters and 6-dB Gain |
| THS7368EVM | 功能描述:放大器 IC 開發(fā)工具 THS7368EVM Eval Mod RoHS:否 制造商:International Rectifier 產(chǎn)品:Demonstration Boards 類型:Power Amplifiers 工具用于評(píng)估:IR4302 工作電源電壓:13 V to 23 V |
| THS7368IPW | 功能描述:視頻放大器 6-Ch Video Amp RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 通道數(shù)量:4 電源類型: 工作電源電壓:3.3 V, 5 V 電源電流: 最小工作溫度: 最大工作溫度: 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 封裝:Reel |
| THS7368IPW | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:Video Amplifier IC 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:IC, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, HEX, 350MHZ TSSOP20 |
| THS7368IPWR | 功能描述:視頻放大器 6-Ch Video Amp RoHS:否 制造商:ON Semiconductor 通道數(shù)量:4 電源類型: 工作電源電壓:3.3 V, 5 V 電源電流: 最小工作溫度: 最大工作溫度: 封裝 / 箱體:TSSOP-14 封裝:Reel |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。