- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98230 > TK15450M (TOKO INC) 2 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | TK15450M |
| 廠商: | TOKO INC |
| 元件分類: | 音頻/視頻放大 |
| 英文描述: | 2 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO8 |
| 封裝: | SOP-8 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 4/15頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 389K |
| 代理商: | TK15450M |
TK15450M/L
GC3-H036
Page 12
12. APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
12-1. About Amplitude Restrictions
In certain applications, the output voltage is limited by
the input voltage.
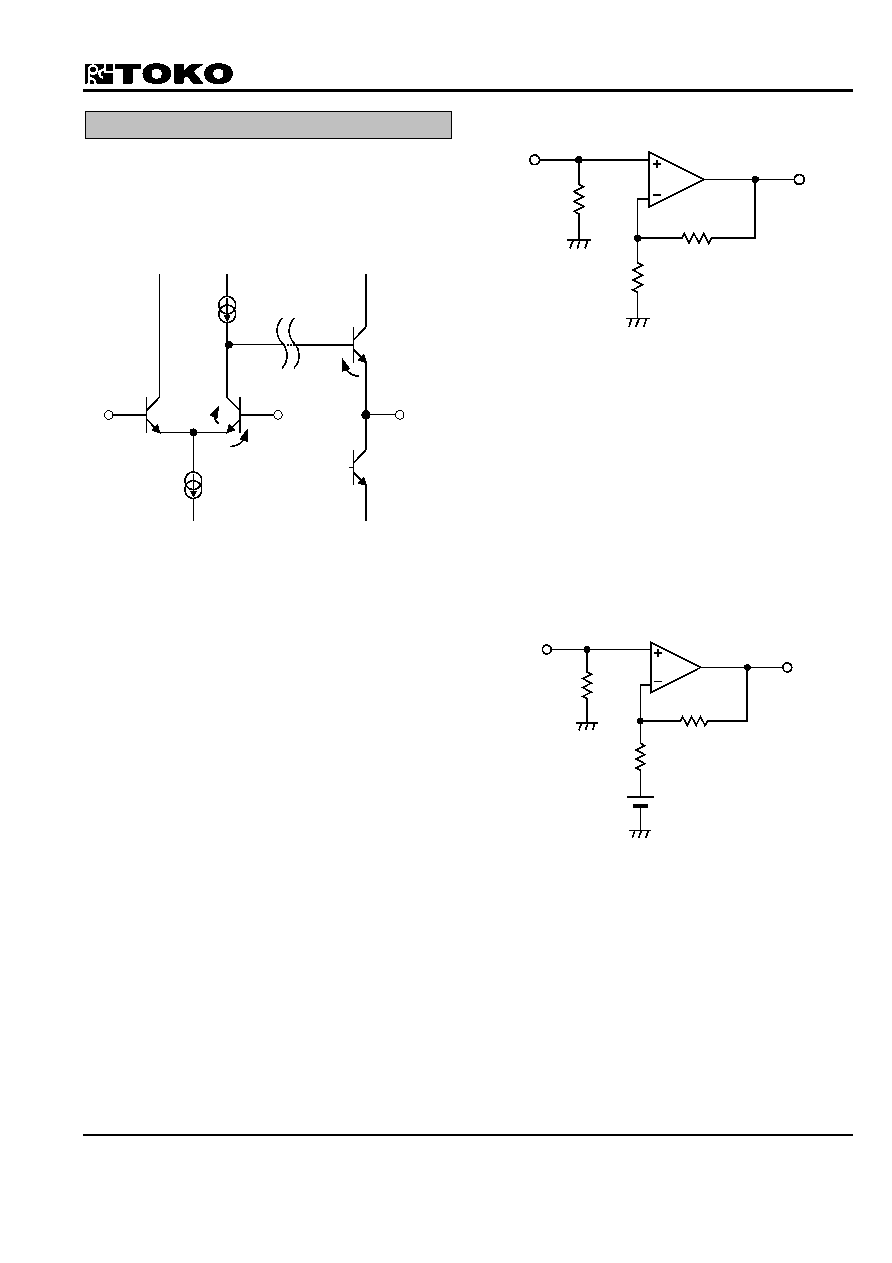
This is explained in the outline below using the internal
equivalent circuit shown in Figure 1.
Vin+
Vin-
VF
VCE
Vout
A
Figure 1: The internal equivalent circuit
From Figure 1, if the voltage V
A at A point is shown from
the input side and the output side respectively, the
expression is as follows:
CE
F
in
A
V
+
≥
(1)
F
out
A
V
+
=
(2)
Thus
CE
F
in
out
V
2V
V
≥
+
(3)
Substitution of V
F = 0.7V into (3) gives
CE
in
out
V
1.4V
V
≥
+
(4)
Depending on the relationship between Vout and Vin, it
may become impossible to secure the Saturation voltage
V
CE (about 0.3 V) of the inverting input transistor; as a
result, the linearity of the input and output voltage will
collapse.
An example of this application is shown in Figure 2 with
the measures explained below.
VCC/VEE =±5.0V, Vin=1.0Vp-p, GV=12dB
500
1.5k
75
Figure 2: Application example
In Figure 2, if -0.5V (the minimum value of input
amplitude) is given to the input, the output voltage will be
set to -2.0V. Substitution of Vin and Vout into (4) gives
)
V
3
.
0
(
V
0.1V
1.4V
V
CE
in
out
≤
=
+
(5)
This shows that the transistor of the inverting input is
operating in the saturation region; for this reason, it
becomes impossible to keep linearity of the input-to-
output voltage. As shown in Figure 3, there is a method
of providing V
REF as a preventive measure. It is possible
to raise the output voltage by setting up V
REF
appropriately, and avoid amplitude restrictions.
500
1.5k
75
VREF
Figure 3: Example of preventive measures
If the input voltage and V
REF are assumed to be -0.5V, the
output voltage also becomes -0.5V.
This result is substituted into expression (4)
)
V
3
.
0
(
V
1.4V
V
CE
in
out
≥
=
+
(6)
As a result, the saturation voltage of the inverting input
transistor is secured, and the amplitude limitation can be
avoided. However, it is necessary to pay attention to the
dynamic range, especially when using this IC with a low
power supply. This method may be used to control the
output bias voltage.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TK15465S | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO6 |
| TK15465S | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO6 |
| TK15467S | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO6 |
| TK15467S | 1 CHANNEL, VIDEO AMPLIFIER, PDSO6 |
| TK65020M | SWITCHING REGULATOR, 102 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO6 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TK15452V | 制造商:TOKO 制造商全稱:TOKO, Inc 功能描述:High speed triple video amplifier IC |
| TK15452VTL | 制造商:TOKO 制造商全稱:TOKO, Inc 功能描述:High speed triple video amplifier IC |
| TK15A | 制造商:TOPSTEK 制造商全稱:TOPSTEK 功能描述:Topstek Current Transducer |
| TK15A20D | 制造商:TOSHIBA 制造商全稱:Toshiba Semiconductor 功能描述:Switching Voltage Regulators |
| TK15A20D,S4X(S | 制造商:Toshiba America Electronic Components 功能描述:MOSFET N-ch 200V 15A 35W TO-220SIS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。