- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98272 > TPA3100D2RGZRG4 (TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC) 21.8 W, 2 CHANNEL, AUDIO AMPLIFIER, PQCC48 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | TPA3100D2RGZRG4 |
| 廠商: | TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 音頻/視頻放大 |
| 英文描述: | 21.8 W, 2 CHANNEL, AUDIO AMPLIFIER, PQCC48 |
| 封裝: | 7 X 7 MM, GREEN, PLASTIC, VQFN-48 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 22/41頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1191K |
| 代理商: | TPA3100D2RGZRG4 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁當前第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁
R
FILT
R
L
R
FILT
C
FILT
V
L=VIN
V
OUT
R
ANA
C
ANA
R
ANA
C
ANA
C
FILT
To APA
GND
AP AnalyzerInput
RCLow-PassFilters
Load
V
OUT
w
V
IN
wO
R
ANA + RFILT
R
ANA
1+j
(
)
=
f =
c
2 x f
max
C
=
FILT
1
2
xf
xR
p
c
FILT
www.ti.com
SLOS469F – OCTOBER 2005 – REVISED AUGUST 2010
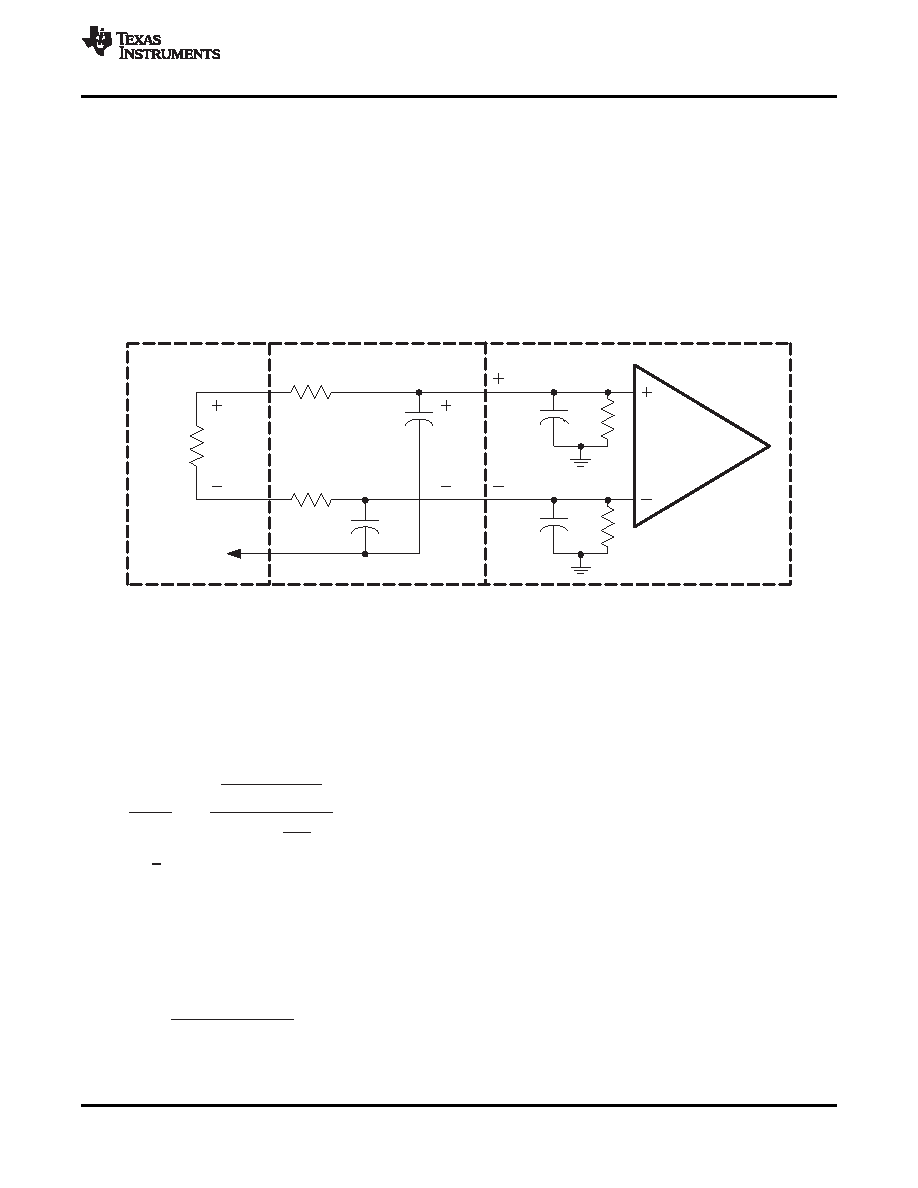
CLASS-D RC LOW-PASS FILTER
An RC filter is used to reduce the square-wave output when the analyzer inputs cannot process the pulse-width
modulated class-D output waveform. This filter has little effect on the measurement accuracy because the cutoff
frequency is set above the audio band. The high frequency of the square wave has negligible impact on
measurement accuracy because it is well above the audible frequency range, and the speaker cone cannot
respond at such a fast rate. The RC filter is not required when an LC low-pass filter is used, such as with the
class-D APAs that employ the traditional modulation scheme (TPA032D0x, TPA005Dxx).
The component values of the RC filter are selected using the equivalent output circuit as shown in Figure 37. RL
is the load impedance that the APA is driving for the test. The analyzer input impedance specifications should be
available and substituted for RANA and CANA. The filter components, RFILT and CFILT, can then be derived for the
system. The filter should be grounded to the APA near the output ground pins or at the power supply ground pin
to minimize ground loops.
Figure 37. Measurement Low-Pass Filter Derivation Circuit-Class-D APAs
The transfer function for this circuit is shown in Equation 5 where wO = REQCEQ, REQ = RFILT || RANA and
CEQ = (CFILT + CANA). The filter frequency should be set above fMAX, the highest frequency of the measurement
bandwidth, to avoid attenuating the audio signal. Equation 6 provides this cutoff frequency, fC. The value of RFILT
must be chosen large enough to minimize current that is shunted from the load, yet small enough to minimize the
attenuation of the analyzer-input voltage through the voltage divider formed by RFILT and RANA. A general rule is
that RFILT should be small (~100 ) for most measurements. This reduces the measurement error to less than
1% for RANA ≥ 10 k.
(5)
(6)
An exception occurs with the efficiency measurements, where RFILT must be increased by a factor of ten to
reduce the current shunted through the filter. CFILT must be decreased by a factor of ten to maintain the same
cutoff frequency. See Table 4 for the recommended filter component values.
Once fC is determined and RFILT is selected, the filter capacitance is calculated using Equation 7. When the
calculated value is not available, it is better to choose a smaller capacitance value to keep fC above the minimum
desired value calculated in Equation 7.
(7)
Copyright 2005–2010, Texas Instruments Incorporated
29
Product Folder Link(s): TPA3100D2
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TPA3100D2RGZTG4 | 21.8 W, 2 CHANNEL, AUDIO AMPLIFIER, PQCC48 |
| TPA3101D2RGZRG4 | 10 W, 2 CHANNEL, AUDIO AMPLIFIER, PQCC48 |
| TPA3101D2RGZR | 10 W, 2 CHANNEL, AUDIO AMPLIFIER, PQCC48 |
| TPA3101D2RGZTG4 | 10 W, 2 CHANNEL, AUDIO AMPLIFIER, PQCC48 |
| TPA3101D2RGZT | 10 W, 2 CHANNEL, AUDIO AMPLIFIER, PQCC48 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TPA3100D2RGZR-P | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:20-W STEREO CLASS-D AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER |
| TPA3100D2RGZT | 功能描述:音頻放大器 20 W Stereo Class-D Audio Amp RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 產(chǎn)品:General Purpose Audio Amplifiers 輸出類型:Digital 輸出功率: THD + 噪聲: 工作電源電壓:3.3 V 電源電流: 最大功率耗散: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TQFP-64 封裝:Reel |
| TPA3100D2RGZT | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:IC AMP AUDIO PWR 21.8W D 48VQFN |
| TPA3100D2RGZTG4 | 功能描述:音頻放大器 20 W Stereo Class-D Audio Amp RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 產(chǎn)品:General Purpose Audio Amplifiers 輸出類型:Digital 輸出功率: THD + 噪聲: 工作電源電壓:3.3 V 電源電流: 最大功率耗散: 最大工作溫度: 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:TQFP-64 封裝:Reel |
| TPA3101D2 | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:10-W STEREO CLASS-D AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。