- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄275683 > VM-702-FCE-BAAN-460M000000 (VECTRON INTERNATIONAL) CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR, CLOCK, 460 MHz, LVPECL OUTPUT PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | VM-702-FCE-BAAN-460M000000 |
| 廠商: | VECTRON INTERNATIONAL |
| 元件分類: | XO, clock |
| 英文描述: | CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR, CLOCK, 460 MHz, LVPECL OUTPUT |
| 封裝: | ROHS COMPLIANT, HERMETIC SEALED, PLASTIC PACKAGE-6 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 6/8頁 |
| 文件大小: | 291K |
| 代理商: | VM-702-FCE-BAAN-460M000000 |
Vectron International 267 Lowell Road, Hudson, NH 03051 Tel: 1-88-VECTRON-1 http://www.vectron.com
Environmental and IR Compliance
Table 5. Environmental Compliance
Parameter
Condition
Mechanical Shock
MIL-STD-883 Method 2002
Mechanical Vibration
MIL-STD-883 Method 2007
Temperature Cycle
MIL-STD-883 Method 1010
Solderability
MIL-STD-883 Method 2003
Fine and Gross Leak
MIL-STD-883 Method 1014
Resistance to Solvents
MIL-STD-202 Method 215
Moisture Sensitivity Level
MSL1
Page6
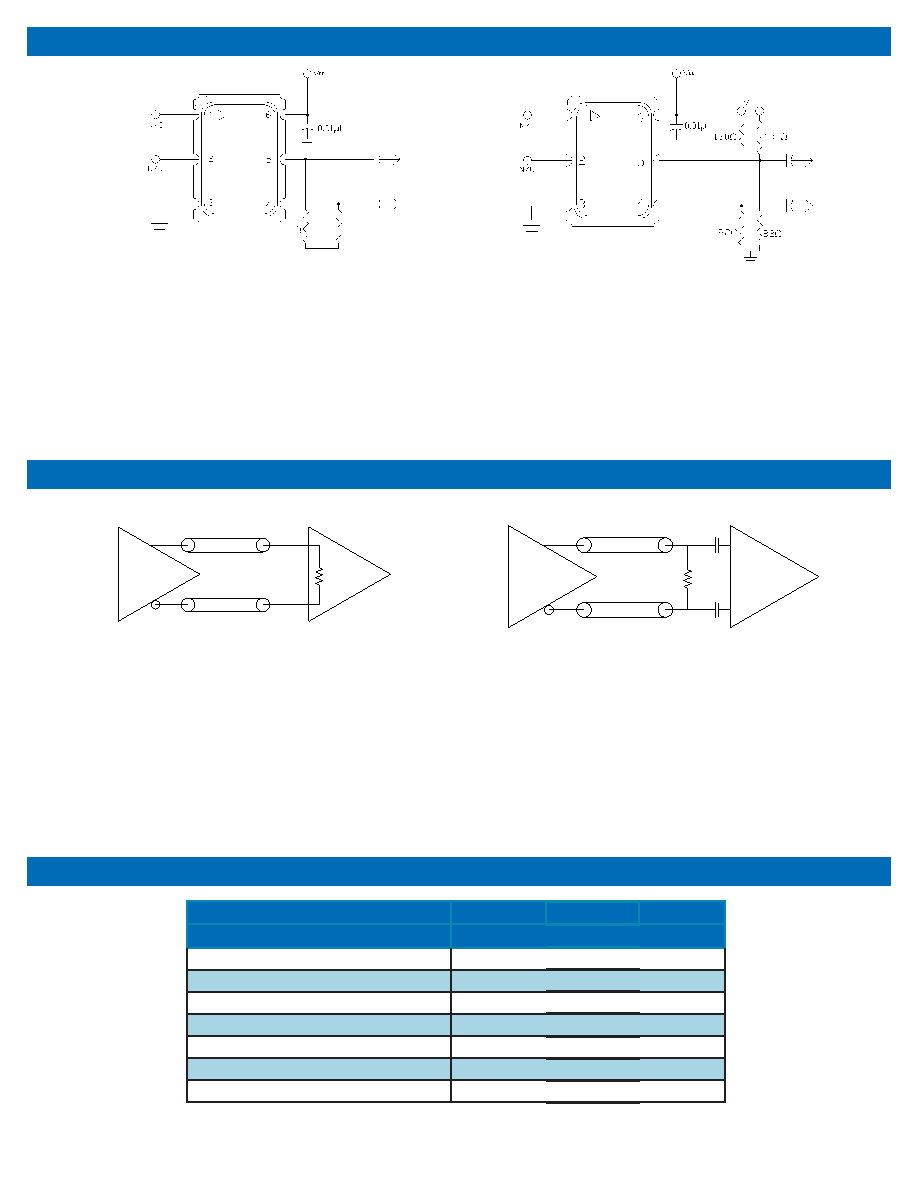
LVPECL Application Diagrams
The VM-702 incorporates a standard LVPECL output scheme, which are un-terminated emitters as shown in Figure 8. There are numerous application
notes on terminating and interfacing LVPECL logic and the two most common methods are a single resistor to ground, Figure 9, and a pull-up/pull-down
scheme as shown in Figure 10. An AC coupling capacitor is optional, depending on the application and the input logic requirements of the next stage.
Figure 11. Single Resistor Termination Scheme
Figure 12. Pull-Up Pull Down Termination
Resistor values are typically 140 ohms for 3.3V operation
and 82.5ohms for 2.5V operation.
Resistor values are typically for 3.3V operation
For 2.5V operation, the resistor to ground is 62
ohms and the resistor to supply is 250 ohms
100
LVDS
Driver
LVDS
Receiver
100
LVDS
Driver
Receiver
Figure 13. LVDS to LVDS Connection, Internal 100ohm
Figure 14. LVDS to LVDS Connection
External 100ohm and AC blocking caps
Some LVDS structures have an internal 100 ohm resistor on the
input and do not need additional components.
Some input structures may not have an internal 100 ohm
resistor on the input and will need an external 100ohm
resistor for impedance matching. Also, the input may have
an internal DC bias which may not be compatible with
LVDS levels, AC blocking capacitors can be used.
LVDS Application Diagrams
One of the most important considerations is terminating the Output and Complementary Outputs equally. An unused output should not be left un-termi-
nated, and if one of the two outputs is left open it will result in excessive jitter on both. PC board layout must take this and 50 ohm impedance matching
into account. Load matching and power supply noise are the main contributors to jitter related problems.
140Ω
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| VM-702-FCJ-FAAN-460M000000 | CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR, CLOCK, 460 MHz, LVPECL OUTPUT |
| VM-702-FDJ-FAAN-156M250000 | CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR, CLOCK, 156.25 MHz, LVDS OUTPUT |
| VM-802-FCE-KAAN-460M000000 | CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR, CLOCK, 460 MHz, LVPECL OUTPUT |
| VM-802-FDE-BAAN-156M250000 | CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR, CLOCK, 156.25 MHz, LVDS OUTPUT |
| VF150H-2-TG-FREQ | CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR, CLOCK, 0.2 MHz - 130 MHz, TTL OUTPUT |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| VM-702-FCE-KAAN | 制造商:VECTRON 制造商全稱:Vectron International, Inc 功能描述:MEMS based HCSL, LVDS, LVPECL Oscillator |
| VM-7063 | 制造商:BOTHHAND 制造商全稱:Bothhand USA, LP. 功能描述:VDSL MICRO FILTER |
| VM706-SM | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:SERVICE MANUAL |
| VM7200 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:2,4,6 OR 8-CHANNEL, 5-VOLT, THIN-FILM HEAD, READ/WRITE PREAMPLIFIER |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。