- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣(mài)IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄371212 > X25097P-2.7 5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E 2 PROM with IDLock TM Memory PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | X25097P-2.7 |
| 英文描述: | 5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E 2 PROM with IDLock TM Memory |
| 中文描述: | 5MHz的低功耗SPI串行e的2 IDLock商標(biāo)記憶胎膜早破 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 3/15頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 71K |
| 代理商: | X25097P-2.7 |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)當(dāng)前第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)
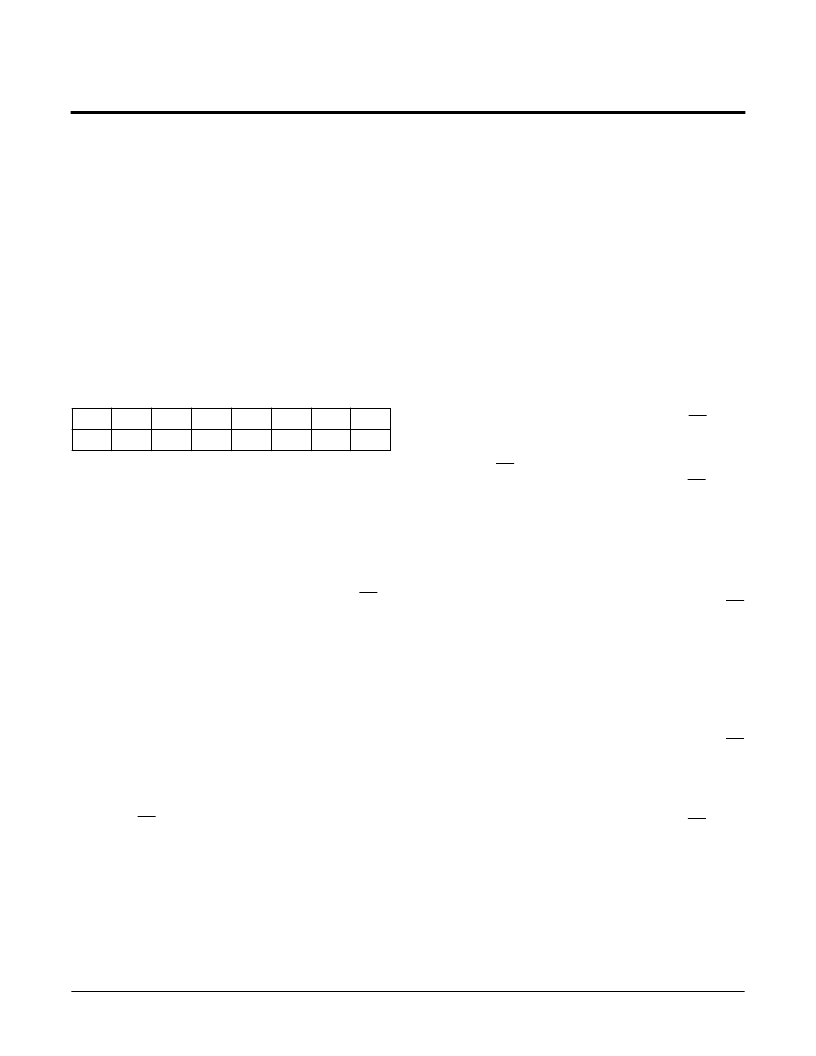
X25097
3
IDLock Memory
Xicor’s IDLock Memory provides a flexible mechanism to
store and lock system ID and parametric information.
There are seven distinct IDLock Memory areas within the
array which vary in size from one page to as much as half
of the entire array. These areas and associated address
ranges are IDLocked by writing the appropriate two byte
IDLock instruction to the device as described in Table 1
and Figure 7. Once an IDLock instruction has been com-
pleted, that IDLock setup is held in a nonvolatile Status
Register (Figure 1) until the next IDLock instruction is
issued. The sections of the memory array that are
IDLocked can be read but not written until IDLock Protec-
tion is removed or changed.
Figure 1. Status Register/IDLock Byte
Clock and Data Timing
Data input on the SI line is latched on the rising edge of
SCK. Data is output on the SO line by the falling edge of
SCK.
Read Sequence
When reading from the E
first pulled LOW to select the device. The 8-bit READ
instruction is transmitted to the X25097, followed by the
16-bit address, of which the last 10 bits are used (bits
[15:10] specified to be zeroes). After the READ opcode
and address are sent, the data stored in the memory at
the selected address is shifted out on the SO line. The
data stored in memory at the next address can be read
sequentially by continuing to provide clock pulses. The
address is automatically incremented to the next higher
address after each byte of data is shifted out. When the
highest address is reached (03FFh), the address counter
rolls over to address 0000h, allowing the read cycle to be
continued indefinitely. The read operation is terminated
by taking CS HIGH. Refer to the Read Operation
Sequence illustrated in Figure 2.
2
PROM memory array, CS is
Read Status Operation
If there is not a nonvolatile write in progress, the Read
Status instruction returns the ID Lock byte from the Sta-
tus Register which contains the ID Lock bits IDL2-IDL0
(Figure 1). The ID Lock bits define the ID Lock condition
(Figure 1/Table1). The other bits are reserved and will
return ’0’ when read. See Figure 3.
If a nonvolatile write is in progress, the Read Status
Instruction returns a HIGH on SO. When the nonvolatile
write cycle is completed, the status register data is read
out.
Clocking SCK is valid during a nonvolatile write in
progress, but is not necessary. If the SCK line is clocked,
the pointer to the status register is also clocked, even
though the SO pin shows the status of the nonvolatile
write operation (See Figure 3).
Write Sequence
Prior to any attempt to write data into the X25097, the
“Write Enable” latch must first be set by issuing the
WREN instruction (See Table 1 and Figure 4). CS is first
taken LOW. Then the WREN instruction is clocked into
the X25097. After all eight bits of the instruction are
transmitted, CS must then be taken HIGH. If the user
continues the write operation without taking CS HIGH
after issuing the WREN instruction, the write operation
will be ignored.
To write data to the E
issues the WRITE instruction, followed by the 16 bit
address and the data to be written. Only the last 10 bits of
the address are used and bits [15:10] are specified to be
zeroes. This is minimally a thirty-two clock operation. CS
must go LOW and remain LOW for the duration of the
operation. The host may continue to write up to 16 bytes
of data to the X25097. The only restriction is the 16 bytes
must reside on the same page. If the address counter
reaches the end of the page and the clock continues, the
counter will “roll over” to the first address of the page and
overwrite any data that may have been previously written.
2
PROM memory array, the user then
For a byte or page write operation to be completed, CS
can only be brought HIGH after bit 0 of the last data byte
to be written is clocked in. If it is brought HIGH at any
other time, the write operation will not be completed.
Refer to Figures 5 and 6 for detailed illustration of the
write sequences and time frames in which CS going
HIGH are valid.
7
0
6
0
5
0
4
0
3
0
2
1
0
IDL2 IDL1 IDL0
Note: Bits [7:3] specified to be “0’s”
7038 FRM T02.1
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| X25097PI | 5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E 2 PROM with IDLock TM Memory |
| X25097S | 5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E 2 PROM with IDLock TM Memory |
| X25097S-1.8 | 5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E 2 PROM with IDLock TM Memory |
| X25097S-2.7 | 5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E 2 PROM with IDLock TM Memory |
| X25097SI | 5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E 2 PROM with IDLock TM Memory |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| X25097PG | 制造商:ICMIC 制造商全稱(chēng):IC MICROSYSTEMS 功能描述:5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E2PROM with IDLockTM Memory |
| X25097PG-1.8 | 制造商:ICMIC 制造商全稱(chēng):IC MICROSYSTEMS 功能描述:5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E2PROM with IDLockTM Memory |
| X25097PG-2.7 | 制造商:ICMIC 制造商全稱(chēng):IC MICROSYSTEMS 功能描述:5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E2PROM with IDLockTM Memory |
| X25097PI | 制造商:ICMIC 制造商全稱(chēng):IC MICROSYSTEMS 功能描述:5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E2PROM with IDLockTM Memory |
| X25097PI-1.8 | 制造商:ICMIC 制造商全稱(chēng):IC MICROSYSTEMS 功能描述:5MHz Low Power SPI Serial E2PROM with IDLockTM Memory |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。