- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4274 > XC2S200-5FG456C (Xilinx Inc)IC FPGA 2.5V 1176 CLB'S 456-FBGA PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | XC2S200-5FG456C |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 37/99頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FPGA 2.5V 1176 CLB'S 456-FBGA |
| 標準包裝: | 60 |
| 系列: | Spartan®-II |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 1176 |
| 邏輯元件/單元數(shù): | 5292 |
| RAM 位總計: | 57344 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 284 |
| 門數(shù): | 200000 |
| 電源電壓: | 2.375 V ~ 2.625 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 85°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 456-BBGA |
| 供應商設備封裝: | 456-FBGA |
| 其它名稱: | 122-1233 XC2S200-5FG456C-ND |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁當前第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁
Spartan-II FPGA Family: Functional Description
DS001-2 (v2.8) June 13, 2008
Module 2 of 4
Product Specification
42
R
property. This property could have one of the following
seven values.
DRIVE=2
DRIVE=4
DRIVE=6
DRIVE=8
DRIVE=12 (Default)
DRIVE=16
DRIVE=24
Design Considerations
Reference Voltage (VREF) Pins
Low-voltage I/O standards with a differential amplifier input
buffer require an input reference voltage (VREF). Provide
the VREF as an external signal to the device.
The voltage reference signal is "banked" within the device
on a half-edge basis such that for all packages there are
page 39 for a representation of the I/O banks. Within each
bank approximately one of every six I/O pins is
automatically configured as a VREF input.
Within each VREF bank, any input buffers that require a
VREF signal must be of the same type. Output buffers of any
type and input buffers can be placed without requiring a
reference voltage within the same VREF bank.
Output Drive Source Voltage (VCCO) Pins
Many of the low voltage I/O standards supported by
Versatile I/Os require a different output drive source voltage
(VCCO). As a result each device can often have to support
multiple output drive source voltages.
The VCCO supplies are internally tied together for some
packages. The VQ100 and the PQ208 provide one
combined VCCO supply. The TQ144 and the CS144
packages provide four independent VCCO supplies. The
FG256 and the FG456 provide eight independent VCCO
supplies.
Output buffers within a given VCCO bank must share the
same output drive source voltage. Input buffers for LVTTL,
LVCMOS2, PCI33_3, and PCI 66_3 use the VCCO voltage
for Input VCCO voltage.
Transmission Line Effects
The delay of an electrical signal along a wire is dominated
by the rise and fall times when the signal travels a short
distance. Transmission line delays vary with inductance
and capacitance, but a well-designed board can experience
delays of approximately 180 ps per inch.
Transmission line effects, or reflections, typically start at
1.5" for fast (1.5 ns) rise and fall times. Poor (or
non-existent) termination or changes in the transmission
line impedance cause these reflections and can cause
additional delay in longer traces. As system speeds
continue to increase, the effect of I/O delays can become a
limiting factor and therefore transmission line termination
becomes increasingly more important.
Termination Techniques
A variety of termination techniques reduce the impact of
transmission line effects.
The following lists output termination techniques:
None
Series
Parallel (Shunt)
Series and Parallel (Series-Shunt)
Input termination techniques include the following:
None
Parallel (Shunt)
These termination techniques can be applied in any
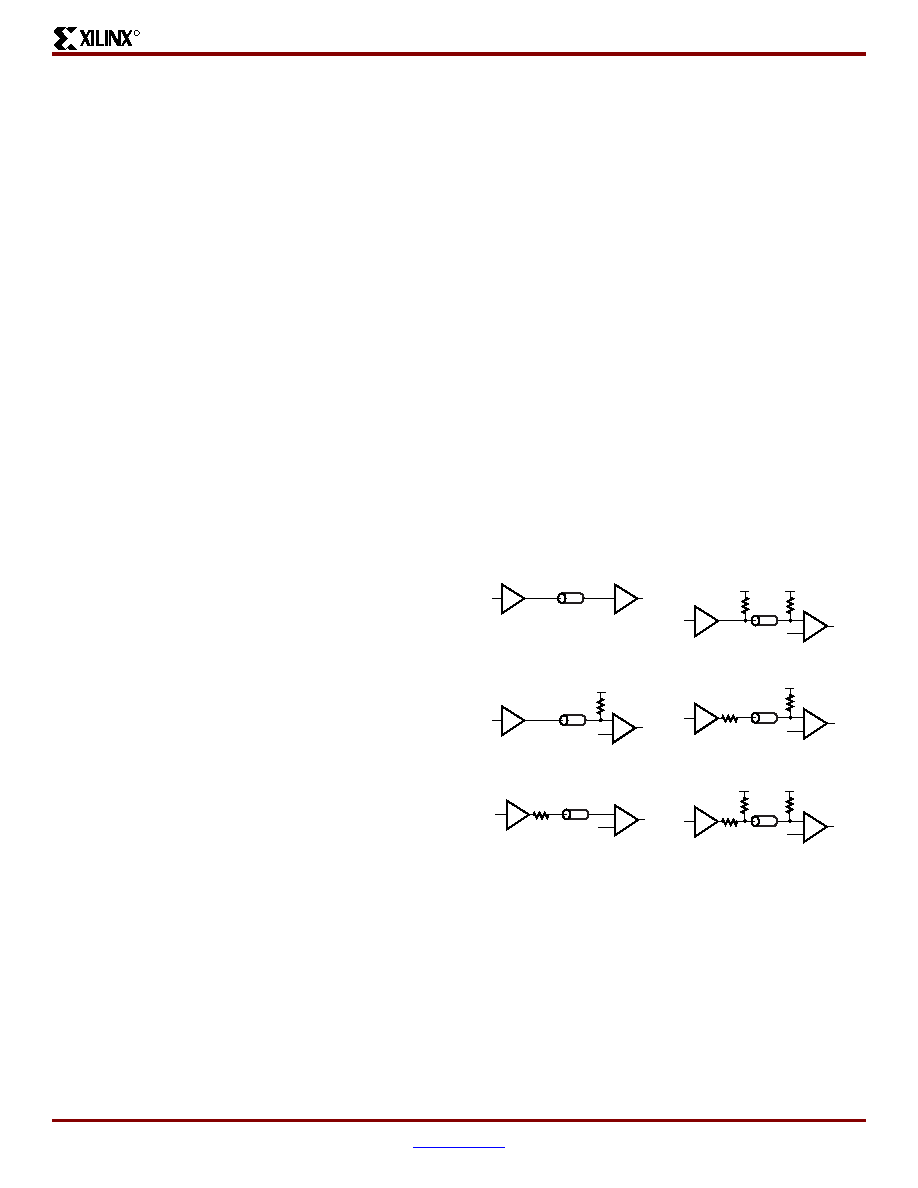
combination. A generic example of each combination of
termination methods appears in Figure 41.
Simultaneous Switching Guidelines
Ground bounce can occur with high-speed digital ICs when
multiple outputs change states simultaneously, causing
undesired transient behavior on an output, or in the internal
logic. This problem is also referred to as the Simultaneous
Switching Output (SSO) problem.
Ground bounce is primarily due to current changes in the
combined inductance of ground pins, bond wires, and
Figure 41: Overview of Standard Input and Output
Termination Methods
DS001_41_032300
Unterminated
Double Parallel Terminated
Series-Parallel Terminated Output
Driving a Parallel Terminated Input
Series Terminated Output Driving
a Parallel Terminated Input
Unterminated Output Driving
a Parallel Terminated Input
V
TT
V
REF
V
REF
V
REF
V
REF
V
TT
V
TT
V
TT
V
TT
V
TT
Series Terminated Output
V
REF
Z=50
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 93AA86CT-I/MNY | IC EEPROM SER 16K 1.8V 8TDFN |
| 93LC86A-E/SN | IC EEPROM 16KBIT 3MHZ 8SOIC |
| 93LC86B-E/SN | IC EEPROM 16KBIT 3MHZ 8SOIC |
| 24FC64-I/MC | IC EEPROM 64KBIT 1MHZ 8DFN |
| 24FC64T-I/MC | IC EEPROM 64KBIT 1MHZ 8DFN |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XC2S2005FG456C-ES | 制造商:Xilinx 功能描述: |
| XC2S200-5FG456I | 功能描述:IC FPGA 2.5V I-TEMP 456-FBGA RoHS:否 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 嵌入式 - FPGA(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) 系列:Spartan®-II 標準包裝:40 系列:Spartan® 6 LX LAB/CLB數(shù):3411 邏輯元件/單元數(shù):43661 RAM 位總計:2138112 輸入/輸出數(shù):358 門數(shù):- 電源電壓:1.14 V ~ 1.26 V 安裝類型:表面貼裝 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 100°C 封裝/外殼:676-BGA 供應商設備封裝:676-FBGA(27x27) |
| XC2S200-5FGG256C | 功能描述:IC SPARTAN-II FPGA 200K 256-FBGA RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 嵌入式 - FPGA(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) 系列:Spartan®-II 標準包裝:40 系列:Spartan® 6 LX LAB/CLB數(shù):3411 邏輯元件/單元數(shù):43661 RAM 位總計:2138112 輸入/輸出數(shù):358 門數(shù):- 電源電壓:1.14 V ~ 1.26 V 安裝類型:表面貼裝 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 100°C 封裝/外殼:676-BGA 供應商設備封裝:676-FBGA(27x27) |
| XC2S200-5FGG256I | 功能描述:IC SPARTAN-II FPGA 200K 256-FBGA RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 嵌入式 - FPGA(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) 系列:Spartan®-II 標準包裝:40 系列:Spartan® 6 LX LAB/CLB數(shù):3411 邏輯元件/單元數(shù):43661 RAM 位總計:2138112 輸入/輸出數(shù):358 門數(shù):- 電源電壓:1.14 V ~ 1.26 V 安裝類型:表面貼裝 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 100°C 封裝/外殼:676-BGA 供應商設備封裝:676-FBGA(27x27) |
| XC2S200-5FGG456C | 功能描述:IC SPARTAN-II FPGA 200K 456-FBGA RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 嵌入式 - FPGA(現(xiàn)場可編程門陣列) 系列:Spartan®-II 標準包裝:40 系列:Spartan® 6 LX LAB/CLB數(shù):3411 邏輯元件/單元數(shù):43661 RAM 位總計:2138112 輸入/輸出數(shù):358 門數(shù):- 電源電壓:1.14 V ~ 1.26 V 安裝類型:表面貼裝 工作溫度:-40°C ~ 100°C 封裝/外殼:676-BGA 供應商設備封裝:676-FBGA(27x27) |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。