- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄68792 > 5962-8760401GA (NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP) OP-AMP, 3000 uV OFFSET-MAX, MBCY8 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | 5962-8760401GA |
| 廠商: | NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORP |
| 元件分類: | 運算放大器 |
| 英文描述: | OP-AMP, 3000 uV OFFSET-MAX, MBCY8 |
| 封裝: | METAL CAN, 8 PIN |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 20/25頁 |
| 文件大小: | 762K |
| 代理商: | 5962-8760401GA |
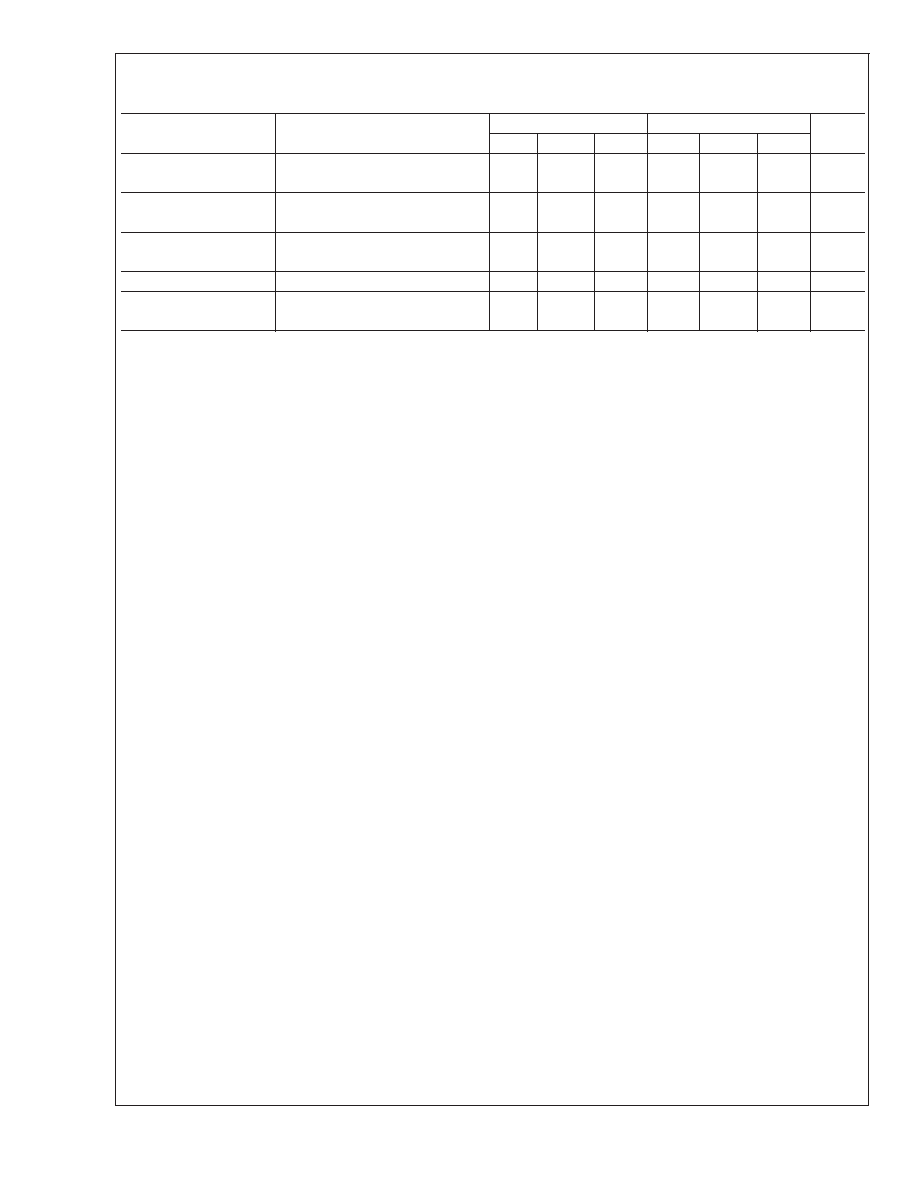
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
T
J=25C, TMIN≤TJ≤TMAX (Boldface type refers to limits over temperature range) (Note 5)
Parameter
Conditions
LM10BL
LM10CL
Units
Min
Typ
Max
Min
Typ
Max
Amplifier gain
0.2V
≤V
REF≤5.5V
30
70
20
70
V/mV
20
15
V/mV
Feedback sense voltage
195
200
205
190
200
210
mV
194
206
189
211
mV
Feedback current
20
50
22
75
nA
65
90
nA
Reference drift
0.002
0.003
%/C
Supply current
260
400
280
500
A
500
570
A
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is func-
tional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits.
Note 2: The Input voltage can exceed the supply voltages provided that the voltage from the input to any other terminal does not exceed the maximum differential
input voltage and excess dissipation is accounted for when VIN<V
.
Note 3: The maximum, operating-junction temperature is 150C for the LM10, 100C for the LM10B(L) and 85C for the LM10C(L). At elevated temperatures, devices
must be derated based on package thermal resistance.
Note 4: Internal thermal limiting prevents excessive heating that could result in sudden failure, but the IC can be subjected to accelerated stress with a shorted output
and worst-case conditions.
Note 5: These specifications apply for V
≤VCM≤V+0.85V (1.0V), 1.2V (1.3V) <VS≤VMAX,VREF=0.2V and 0≤IREF≤1.0 mA, unless otherwise specified: VMAX=40V
for the standard part and 6.5V for the low voltage part. Normal typeface indicates 25C limits. Boldface type indicates limits and altered test conditions for
full-temperature-range operation; this is 55C to 125C for the LM10, 25C to 85C for the LM10B(L) and 0C to 70C for the LM10C(L). The specifications do
not include the effects of thermal gradients (
τ1.20 ms), die heating (τ2.0.2s) or package heating. Gradient effects are small and tend to offset the electrical error
(see curves).
Note 6: For TJ>90C, IOS may exceed 1.5 nA for VCM=V
. With T
J=125C and V
≤VCM≤V+0.1V, IOS≤5 nA.
Note 7: This defines operation in floating applications such as the bootstrapped regulator or two-wire transmitter. Output is connected to the V+ terminal of the IC
and input common mode is referred to V (see typical applications). Effect of larger output-voltage swings with higher load resistance can be accounted for by adding
the positive-supply rejection error.
Note 8: Refer to RETS10X for LM10H military specifications.
Definition of Terms
Input offset voltage: That voltage which must be applied
between the input terminals to bias the unloaded output in
the linear region.
Input offset current: The difference in the currents at the in-
put terminals when the unloaded output is in the linear re-
gion.
Input bias current: The absolute value of the average of the
two input currents.
Input resistance: The ratio of the change in input voltage to
the change in input current on either input with the other
grounded.
Large signal voltage gain: The ratio of the specified output
voltage swing to the change in differential input voltage re-
quired to produce it.
Shunt gain: The ratio of the specified output voltage swing
to the change in differential input voltage required to produce
it with the output tied to the V+ terminal of the IC. The load
and power source are connected between the V
+ and V ter-
minals, and input common-mode is referred to the V
termi-
nal.
Common-mode rejection: The ratio of the input voltage
range to the change in offset voltage between the extremes.
Supply-voltage rejection: The ratio of the specified
supply-voltage change to the change in offset voltage be-
tween the extremes.
Line regulation: The average change in reference output
voltage over the specified supply voltage range.
Load regulation: The change in reference output voltage
from no load to that load specified.
Feedback sense voltage: The voltage, referred to V
,on
the reference feedback terminal while operating in regula-
tion.
Reference amplifier gain: The ratio of the specified refer-
ence output change to the change in feedback sense voltage
required to produce it.
Feedback current: The absolute value of the current at the
feedback terminal when operating in regulation.
Supply current: The current required from the power
source to operate the amplifier and reference with their out-
puts unloaded and operating in the linear range.
LM10
www.national.com
4
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| 5962-8760601GX | BUFFER AMPLIFIER, MBCY8 |
| 5962-8760601CX | BUFFER AMPLIFIER, CDIP14 |
| 5962-8760601CA | BUFFER AMPLIFIER, CDIP14 |
| 5962-8760601GA | BUFFER AMPLIFIER, MBCY8 |
| 5962-8764502EA | 0.2 A SWITCHING CONTROLLER, 500 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, CDIP16 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| 5962-87609012A | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:5962-87609012A, HEX INVERTER - Rail/Tube |
| 59628760901CA | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:54AC04DMQB |
| 5962-8760901CA | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:Inverter 6-Element CMOS 14-Pin CDIP Tube 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:INVERTER 6-ELEM CMOS 14CDIP - Rail/Tube 制造商:National Semiconductor 功能描述:Inverter 6-Element CMOS 14-Pin CDIP Tube |
| 59628760901DA | 制造商:TI 功能描述:* |
| 5962-8760901DA | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:Inverter 6-Element CMOS 14-Pin CFPAK Tube 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述:INVERTER 6-ELEM CMOS 14CFPAK - Rail/Tube 制造商:National Semiconductor 功能描述:Inverter 6-Element CMOS 14-Pin CFPAK Tube |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。