- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄375847 > FM25C020 (Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation) The CAT24FC02 is a 2-kb Serial CMOS EEPROM internally organized as 256 words of 8 bits each PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | FM25C020 |
| 廠商: | Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation |
| 元件分類: | DRAM |
| 英文描述: | The CAT24FC02 is a 2-kb Serial CMOS EEPROM internally organized as 256 words of 8 bits each |
| 中文描述: | 該CAT24FC02是一個(gè)2 KB的EEPROM的國內(nèi)256個(gè)8位每字舉辦的串行CMOS |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 9/11頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 105K |
| 代理商: | FM25C020 |
9
www.fairchildsemi.com
FM25C020U Rev. B
F
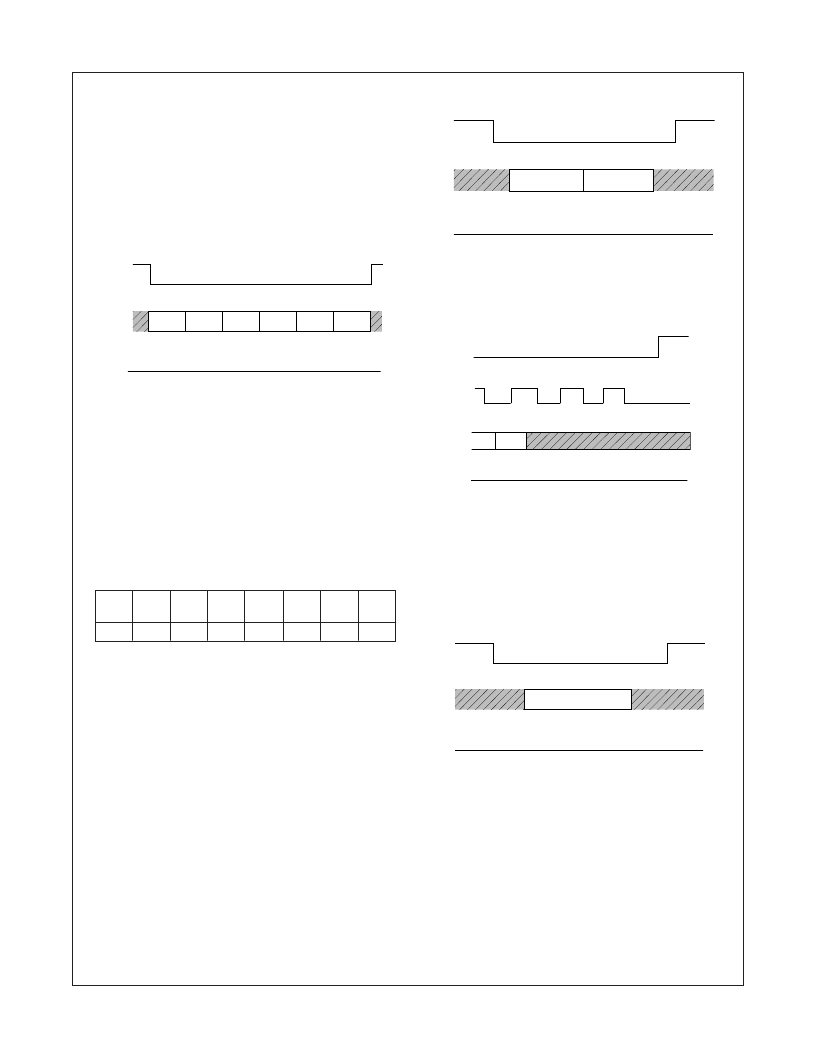
The FM25C020U is also capable of a 4 byte PAGE WRITE
operation. Page write is performed similar to byte write operation
described above. During a Page write operation, after the first byte
of data, additional bytes (up to 3 bytes) can be input, before
bringing the /CS pin high to start the programming. After receipt of
each byte of data, the EEPROM internally increments the two low
order address bits (A1-A0) by one. The high order address bits
(A7-A2) will remain constant. If the master should transmit more
than 4 bytes of data, the address counter (A1-A0) will
“
roll over
”
and the previously loaded data will be reloaded. See Figure11.
FIGURE 11. Page Write
/CS
SI
SO
Write
Op-Code
Byte
Addr
Data
(1)
Data
(2)
Data
(3)
Data
(4)
/CS
SI
SO
WRSR
Op-Code
SR Data
xxxxBP1BP0xx
FIGURE 12. Write Status Register
BP0
SCK
SI
SO
/CS
/CS
SI
SO
INVALID CODE
At the completion of a write cycle the EEPROM is automatically
returned to the write disabled state. Note that if the EEPROM is not
write enabled (WEN=0) before issuing the WRITE instruction, the
EEPROM will ignore the WRITE instruction and return to the
standby state when /CS is brought high.
WRITE STATUS REGISTER (WRSR):
The Write Status Register (WRSR) instruction provides write
access to the status register. This instruction is used to set Block
Write protection to a portion of the array as defined under Table
4. During a WRSR instruction only Bit3 (BP1) and Bit2 (BP0) can
be written with valid information while other bits are ignored.
Following is the format of WRSR data:
Status Register Write Data
Bit
7
X
Bit
6
X
Bit
5
X
Bit
4
X
Bit
3
BP1
Bit
2
BP0
Bit
1
X
Bit
0
X
X = Don
’
t Care
Note that the first four bits are don
’
t care bits followed by BP1 and
BP0 and two more don
’
t care bits.
WRSR instruction is enabled only when /WP pin is held high and
the EEPROM is write enabled previously (via WREN instruction).
WRSR command requires the following sequence. The /CS pin is
pulled low to select the EEPROM and then the WRSR opcode is
transmitted on the SI pin followed by the data to be programmed.
See Figure 12.
Programming will start after the /CS pin is forced back to a high
level. As in the WRITE instruction the LOW to HIGH transition of
the /CS pin must occur during the SCK low time immediately after
clocking in the last don
’
t care bit. See Figure 13.
FIGURE 13. Start WRSR Condition
At the completion of this instruction the EEPROM is automatically
returned to write disabled state.
INVALID OPCODE
If an invalid code is received, then no data is shifted into the
EEPROM, and the SO data output pin remains high impedance
state until a new /CS falling edge reinitializes the serial communi-
cation. See Figure14.
FIGURE 14. Invalid Op-Code
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| FM25C020U | 14=2X7 0.1" T/H MALE HDR SN |
| FM25C020UE | LOW PROFILE .025 SQ STRIPS |
| FM25C020UV | CONN-HDR,7P 1ROW,.1SP, TIN, LO PF |
| FM25C040 | The CAT24FC02 is a 2-kb Serial CMOS EEPROM internally organized as 256 words of 8 bits each |
| FM25C040U | LOW PROFILE .025 SQ STRIPS |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| FM25C020U | 制造商:FAIRCHILD 制造商全稱:Fairchild Semiconductor 功能描述:2K-Bit SPI⑩ Interface Serial CMOS EEPROM |
| FM25C020UE | 制造商:FAIRCHILD 制造商全稱:Fairchild Semiconductor 功能描述:2K-Bit SPI⑩ Interface Serial CMOS EEPROM |
| FM25C020UEM8 | 功能描述:電可擦除可編程只讀存儲器 SOIC-8 RoHS:否 制造商:Atmel 存儲容量:2 Kbit 組織:256 B x 8 數(shù)據(jù)保留:100 yr 最大時(shí)鐘頻率:1000 KHz 最大工作電流:6 uA 工作電源電壓:1.7 V to 5.5 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-8 |
| FM25C020UEM8X | 功能描述:電可擦除可編程只讀存儲器 DISC BY MFG 7/03 RoHS:否 制造商:Atmel 存儲容量:2 Kbit 組織:256 B x 8 數(shù)據(jù)保留:100 yr 最大時(shí)鐘頻率:1000 KHz 最大工作電流:6 uA 工作電源電壓:1.7 V to 5.5 V 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-8 |
| FM25C020UEMT8 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:SPI Serial EEPROM |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。