- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄10037 > IDT72805LB25PF (IDT, Integrated Device Technology Inc)IC FIFO SYNC DUAL 256X18 128TQFP PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | IDT72805LB25PF |
| 廠商: | IDT, Integrated Device Technology Inc |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 18/26頁 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FIFO SYNC DUAL 256X18 128TQFP |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 72 |
| 系列: | 7200 |
| 功能: | 同步 |
| 存儲(chǔ)容量: | 4.6K(256 x 18) |
| 數(shù)據(jù)速率: | 40MHz |
| 訪問時(shí)間: | 25ns |
| 電源電壓: | 4.5 V ~ 5.5 V |
| 工作溫度: | 0°C ~ 70°C |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 封裝/外殼: | 128-LQFP |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 128-TQFP(14x20) |
| 包裝: | 托盤 |
| 其它名稱: | 72805LB25PF |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁當(dāng)前第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁
25
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
IDT72805LB/72815LB/72825LB/72835LB/72845LB CMOS Dual SyncFIFOTM
256 x 18, 512 x 18, 1,024 x 18, 2,048 x 18 and 4,096 x 18
JANUARY 13, 2009
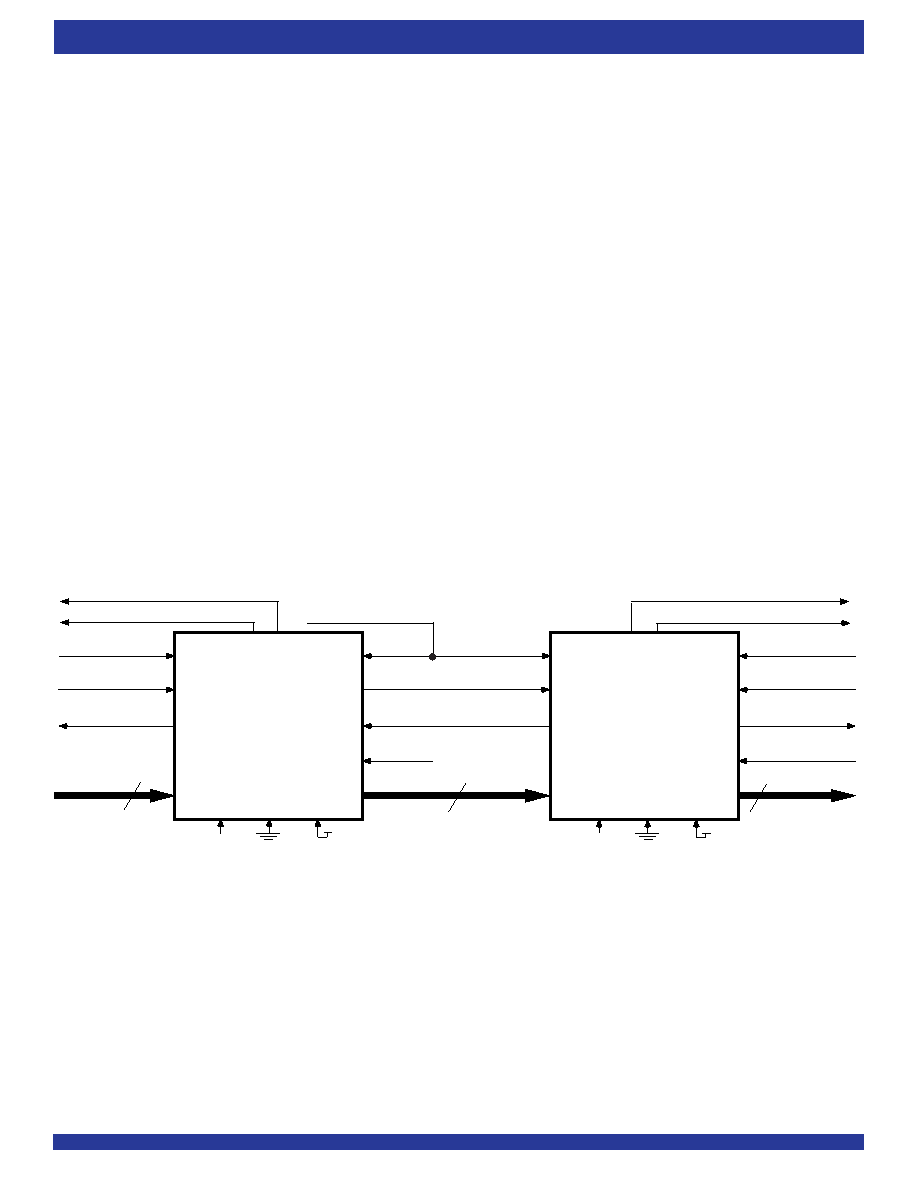
Figure 31. Block Diagram of 512 x 18, 1,024 x 18, 2,048 x 18, 4,096 x 18, 8,192 x 18 Synchronous
FIFO Memory With Programmable Flags used in Depth Expansion Configuration
Dn
INPUT READY
WRITE ENABLE
WRITE CLOCK
WEN
WCLK
IR
DATA IN
RCLK
READ CLOCK
RCLK
REN
OE
OUTPUT ENABLE
OUTPUT READY
Qn
Dn
IR
GND
WEN
WCLK
OR
REN
OE
Qn
READ ENABLE
OR
DATA OUT
TRANSFER CLOCK
3139 drw 31
n
RXI
HF
72805
72815
72825
72835
72845
WXI
FL
VCC
GND
(0,1)
72805
72815
72825
72835
72845
RXI
WXI
FL
VCC
GND
(0,1)
PAF
HF
PAE
DEPTH EXPANSION CONFIGURATION (FWFT MODE)
In FWFT mode, the FIFOs can be connected in series (the data outputs
of one FIFO connected to the data inputs of the next) with no external logic
necessary. The resulting configuration provides a total depth equivalent to
the sum of the depths associated with each single FIFO. Figure 31 shows
a depth expansion using one IDT72805LB/72815LB/72825LB/72835LB/
72845LB devices.
Care should be taken to select FWFT mode during Master Reset for all
FIFOs in the depth expansion configuration. The first word written to an
empty configuration will pass from one FIFO to the next (“ripple down”) until
it finally appears at the outputs of the last FIFO in the chain–no read
operation is necessary but the RCLK of each FIFO must be free-running.
Each time the data word appears at the outputs of one FIFO, that device’s
OR line goes LOW, enabling a write to the next FIFO in line.
For an empty expansion configuration, the amount of time it takes for
OR
of the last FIFO in the chain to go LOW (i.e. valid data to appear on the last
FIFO’s outputs) after a word has been written to the first FIFO is the sum of
the delays for each individual FIFO:
(N – 1)*(4*transfer clock) + 3*TRCLK
where N is the number of FIFOs in the expansion and TRCLK is the RCLK
period. Note that extra cycles should be added for the possibility that the
tSKEW1 specification is not met between WCLK and transfer clock, or RCLK
and transfer clock, for the
OR flag.
The “ripple down” delay is only noticeable for the first word written to an
empty depth expansion configuration. There will be no delay evident for
subsequent words written to the configuration.
The first free location created by reading from a full depth expansion
configuration will “bubble up” from the last FIFO to the previous one until it
finally moves into the first FIFO of the chain. Each time a free location is
created in one FIFO of the chain, that FIFO’s
IR line goes LOW, enabling
the preceding FIFO to write a word to fill it.
For a full expansion configuration, the amount of time it takes for
IR of the
first FIFO in the chain to go LOW after a word has been read from the last
FIFO is the sum of the delays for each individual FIFO:
(N – 1)*(3*transfer clock) + 2 TWCLK
where N is the number of FIFOs in the expansion and TWCLK is the WCLK
period. Note that extra cycles should be added for the possibility that the
tSKEW1 specification is not met between RCLK and transfer clock, or WCLK
and transfer clock, for the
IR flag.
The Transfer Clock line should be tied to either WCLK or RCLK,
whichever is faster. Both these actions result in data moving, as quickly as
possible, to the end of the chain and free locations to the beginning of the
chain.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| VI-BNW-IV-F2 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 5.5V 150W |
| VI-BNT-IV-F2 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 6.5V 150W |
| LTC1335CSW | IC TXRX RS232/485/EIA562 24-SOIC |
| VI-BNT-IV-F1 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 6.5V 150W |
| VI-B74-MY-S | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 48V 50W |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| IDT72805LB25PF8 | 功能描述:IC FIFO SYNC DUAL 256X18 128TQFP RoHS:否 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 邏輯 - FIFO 系列:7200 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:80 系列:7200 功能:同步 存儲(chǔ)容量:18.4K(1K x 18) 數(shù)據(jù)速率:- 訪問時(shí)間:10ns 電源電壓:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 工作溫度:0°C ~ 70°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:64-LQFP 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:64-TQFP(10x10) 包裝:托盤 其它名稱:72225LB10TF |
| IDT7280L12PA | 功能描述:IC MEM FIFO 256X9 12NS 56-TSSOP RoHS:否 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 邏輯 - FIFO 系列:7200 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:80 系列:7200 功能:同步 存儲(chǔ)容量:18.4K(1K x 18) 數(shù)據(jù)速率:- 訪問時(shí)間:10ns 電源電壓:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 工作溫度:0°C ~ 70°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:64-LQFP 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:64-TQFP(10x10) 包裝:托盤 其它名稱:72225LB10TF |
| IDT7280L12PA8 | 功能描述:IC MEM FIFO 256X9 12NS 56-TSSOP RoHS:否 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 邏輯 - FIFO 系列:7200 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:80 系列:7200 功能:同步 存儲(chǔ)容量:18.4K(1K x 18) 數(shù)據(jù)速率:- 訪問時(shí)間:10ns 電源電壓:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 工作溫度:0°C ~ 70°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:64-LQFP 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:64-TQFP(10x10) 包裝:托盤 其它名稱:72225LB10TF |
| IDT7280L12PAG | 功能描述:IC MEM FIFO 256X9 12NS 56-TSSOP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 邏輯 - FIFO 系列:7200 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:80 系列:7200 功能:同步 存儲(chǔ)容量:18.4K(1K x 18) 數(shù)據(jù)速率:- 訪問時(shí)間:10ns 電源電壓:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 工作溫度:0°C ~ 70°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:64-LQFP 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:64-TQFP(10x10) 包裝:托盤 其它名稱:72225LB10TF |
| IDT7280L12PAG8 | 功能描述:IC MEM FIFO 256X9 12NS 56-TSSOP RoHS:是 類別:集成電路 (IC) >> 邏輯 - FIFO 系列:7200 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝:80 系列:7200 功能:同步 存儲(chǔ)容量:18.4K(1K x 18) 數(shù)據(jù)速率:- 訪問時(shí)間:10ns 電源電壓:4.5 V ~ 5.5 V 工作溫度:0°C ~ 70°C 安裝類型:表面貼裝 封裝/外殼:64-LQFP 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝:64-TQFP(10x10) 包裝:托盤 其它名稱:72225LB10TF |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。