- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄43902 > LC016CL (LINEAGE POWER LLC) 2-OUTPUT 16 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | LC016CL |
| 廠商: | LINEAGE POWER LLC |
| 元件分類: | 電源模塊 |
| 英文描述: | 2-OUTPUT 16 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| 封裝: | MODULE-9 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 15/16頁 |
| 文件大小: | 389K |
| 代理商: | LC016CL |
8
LC016 Dual-Output Series Power Modules:
Advance Data Sheet
18 Vdc to 36 Vdc Inputs; 16 W
April 2008
Lineage Power
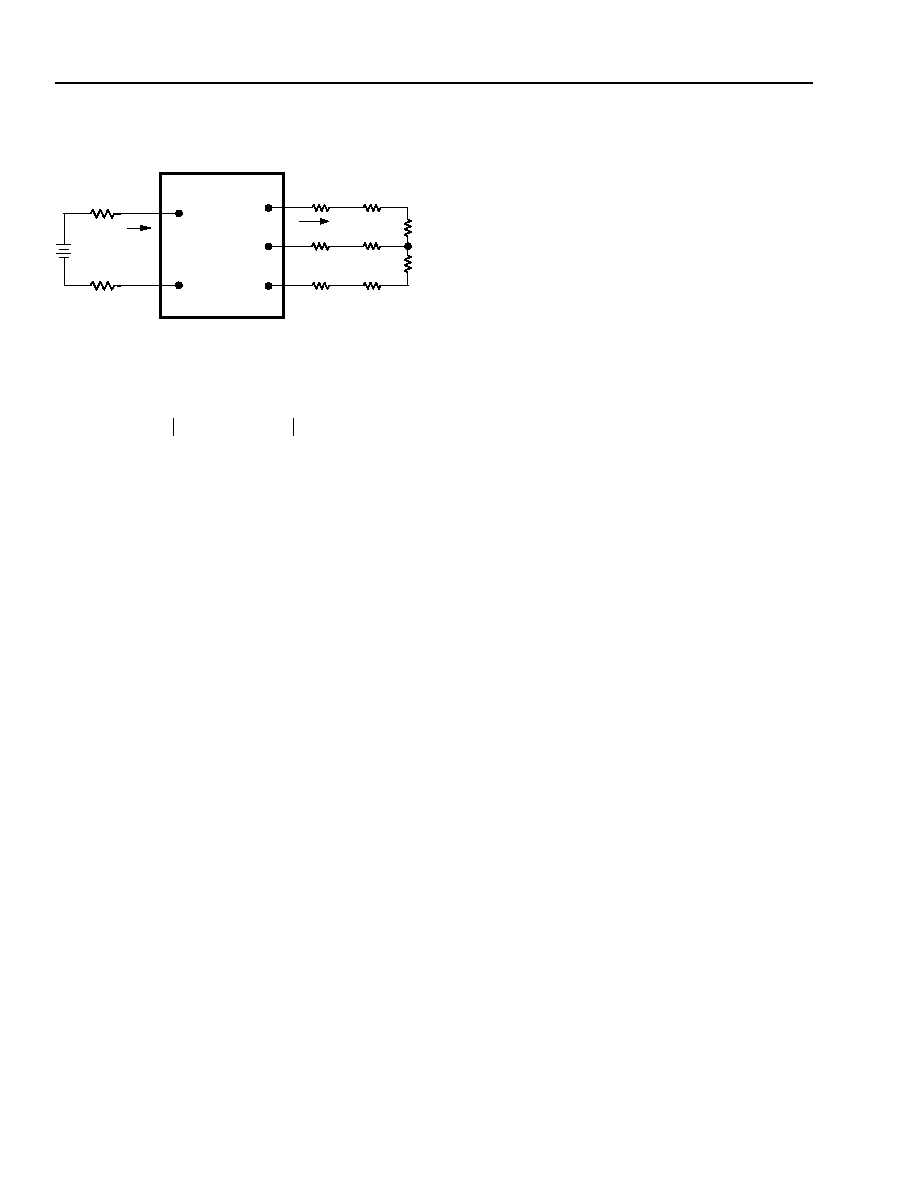
Test Configurations (continued)
8-863.a(C)
Note: All measurements are taken at the module terminals. When
socketing, place Kelvin connections at module terminals to
avoid measurement errors due to socket contact resistance.
Figure 9. Output Voltage and Efficiency Measure-
ment Test Setup
Design Considerations
Input Source Impedance
The power modules should be connected to low
ac-impedance input sources. Highly inductive source
impedances can affect the stability of the power mod-
ules. For the test configuration in Figure 7, a 33 F
electrolytic capacitor (ESR < 0.7 at 100 kHz)
mounted close to the power module helps ensure sta-
bility of the unit. For other highly inductive source
impedances, consult the factory for further application
guidelines.
Metal Case Connection
For standard units, the case is connected internally to
VI(–). For units with the case ground pin option, the
case is not connected internally allowing the user flexi-
bility in grounding.
Safety Considerations
For safety-agency approval of the system in which the
power module is used, the power module must be
installed in compliance with the spacing and separation
requirements of the end-use safety agency standard,
i.e., UL-1950, CSA 22.2-950, EN60950.
For the converter output to be considered meeting the
requirements of safety extra low voltage (SELV), the
input must meet SELV requirements.
If the input meets extra low voltage (ELV) require-
ments, then the converter’s output is considered ELV.
The input to these units are to be provided with a maxi-
mum 5 A normal-blow fuse in the ungrounded lead.
Feature Descriptions
Output Overvoltage Clamp
The output overvoltage clamp consists of control
circuitry, independent of the primary regulation loop,
that monitors the voltage on the output terminals. The
control loop of the shutdown has a higher voltage set
point than the primary loop (see Feature Specifications
table).
In a fault condition, the overvoltage clamp ensures that
the output voltage does not exceed VO, clamp, max. This
provides a redundant voltage-control that reduces the
risk of output overvoltage.
Current Limit
To provide protection in a fault (output overload) condi-
tion, the unit is equipped with internal current-limiting
circuitry and can endure current limiting for an unlim-
ited duration. At the point of current-limit inception, the
unit shifts from voltage control to current control. If the
output voltage is pulled very low during a severe fault,
the current-limit circuit can exhibit either foldback or tai-
lout characteristics (output-current decrease or
increase). The unit operate normally once the output
current is brought back into its specified range.
VI(+)
II
IO
SUPPLY
CONTACT
RESISTANCE
CONTACT AND
DISTRIBUTION LOSSES
LOAD
VI(-)
VO1
VO2
COM
LOAD
η
VOJ
COM
–
[]IOJ
J1
=
2
∑
VI
+
() VI –
()
–
[]II
---------------------------------------------------x 100
=
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LC016BK | 2-OUTPUT 16 W DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| LC020A8 | DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| LC020B8 | DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| LC020F3 | DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
| LC020F | DC-DC REG PWR SUPPLY MODULE |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LC016CL1 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:DC-to-DC Voltage Converter |
| LC016CL3 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Analog IC |
| LC016CL7 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Analog IC |
| LC016CL8 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:Analog IC |
| LC01-6T | 制造商:Semtech Corporation 功能描述:TVS DIODE, 1.5KW, 6V, SO-16W, Diode Type:(Not Available), Clamping Voltage Vc Ma |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。