- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄44122 > LK4301-7ER (POWER-ONE INC) 1-OUTPUT 150 W AC-DC PWR FACTOR CORR MODULE PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | LK4301-7ER |
| 廠商: | POWER-ONE INC |
| 元件分類: | 電源模塊 |
| 英文描述: | 1-OUTPUT 150 W AC-DC PWR FACTOR CORR MODULE |
| 封裝: | HEAT SINK, METAL, CASE K02 |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 5/28頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 627K |
| 代理商: | LK4301-7ER |
第1頁(yè)第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)當(dāng)前第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)
BCD20001-G Rev AB
Page 13 of 28
www.power-one.com
K Series with PFC Data Sheet
150 – 280 Watt AC-DC Converters
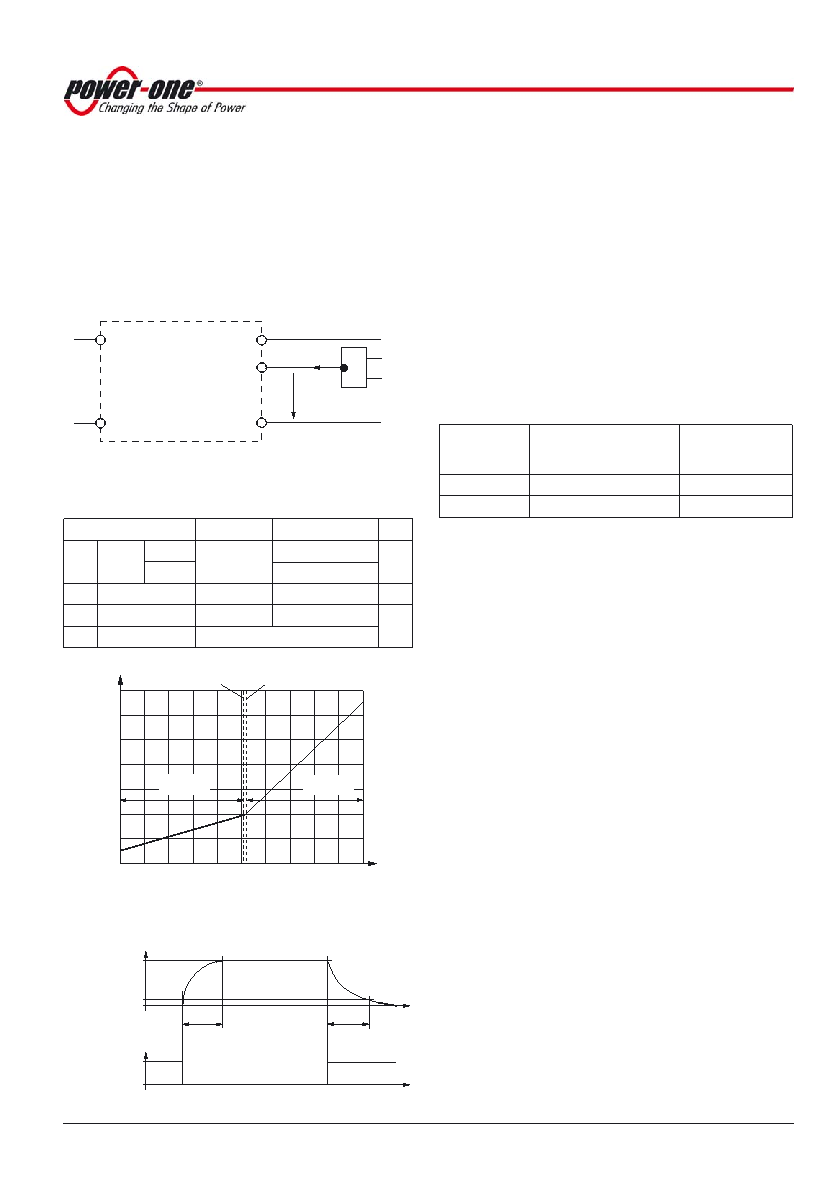
Auxiliary Functions
Inhibit for Remote On/Off
The outputs may be enabled or disabled by means of a
logic signal (TTL, CMOS, etc.) applied between the inhibit
input i and pin 18 (S– or Vo1–). In systems with several
converters, this feature can be used to control the
activation sequence of the converters. If the inhibit function
is not required, connect the inhibit pin 18 to pin 14.
Note: If pin 18 is not connected, the output is disabled.
Vi+
Vi–
Vo–
i
Vo+
Iinh
Vinh
06031
Fig. 18
Definition of Vinh and Iinh.
Table 8: Inhibit characteristics
Characteristic
Conditions
min
typ
max Unit
Vinh Inhibit
Vo = on
Vi min – Vi max
– 50
0.8
V
voltage
Vo = off
2.4
50
I inh
Inhibit current
Vinh = 0
– 400
A
t r
Rise time
30
ms
t f
Fall time
depending on Io
Fig. 20
Output response as a function of inhibit control
Fig. 19
Typical inhibit current I inh versus inhibit voltage Vinh
1.6
0.8
0
–0.8
–50
Vinh [V]
Iinh [mA]
–30
0
–10
10
30
50
2.0
1.2
0.4
–0.4
Vinh = 0.8 V
Vo = on
Vo = off
Vinh = 2.4 V
06032
0
t
0
Inhibit
1
0.1
1
Vo/Vo nom
tr
tf
06001
Sense Lines (Single-Output Models)
Important:
Sense
lines
must
always
be
connected!
Incorrectly
connected
sense
lines
may
activate
the
overvoltage protection resulting in a permanent short-circuit
of the output.
This feature allows for compensation of voltage drops
across the connector contacts and if necessary, across the
load lines. We recommend connecting the sense lines
directly at the female connector.
To ensure correct operation, both sense lines (S+, S–)
should be connected to their respective power outputs
(Vo1+ and Vo1–), and the voltage difference between any
sense line and its respective power output (as measured
on the connector) should not exceed the following values:
Table 9: Maximum voltage compensation allowed using
sense lines
Output
Total voltage difference
Voltage difference
voltage
between sense lines and
between
their respective outputs
Vo– and S–
5.1 V
<0.5 V
<0.25 V
12 V, 15 V, 24 V
<1.0 V
<0.25 V
Note: If the output voltages are increased above Vo nom via
R-input control, option P setting, remote sensing or option T,
the output currents must be reduced accordingly, so that
Po nom is not exceeded.
Programmable Output Voltage (R-Function)
As a standard feature, the converters offer an adjustable
output
voltage,
identified
by
letter
R
in
the
type
designation. The control input R (pin 16) accepts either a
control voltage Vext or a resistor Rext to adjust the desired
output voltage. When R is not connected, the output
voltage is set to Vo nom.
a) Adjustment by means of an external control voltage Vext
between pin 16 (R) and pin 14:
The control voltage range is 0 – 2.75 VDC and allows an
output voltage adjustment in the range of approximately
0 – 110% Vo nom.
Vo
Vext
≈ –––––– 2.5 V
Vo nom
b) Adjustment by means of an external resistor:
Depending upon the value of the required output voltage
the resistor shall be connected
either: Between pin 16 and pin 14 (Vo
< Vo nom) to
achieve an output voltage adjustment range of approxi-
mately 0 – 100% Vo nom.
or: Between pin 16 and pin 12 (Vo > Vo nom) to achieve an
output voltage adjustment range of 100 – 110% Vo nom.
Warning:
– Vext shall never exceed 2.75 VDC.
– The value of R'ext shall never be less than the lowest
value as indicated in table R'ext (for V0
> V0 nom) to
avoid damage to the converter!
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LK4301-9PD5TB1 | 1-OUTPUT 150 W AC-DC PWR FACTOR CORR MODULE |
| LK5660-7ERD5TB1 | 2-OUTPUT 150 W AC-DC PWR FACTOR CORR MODULE |
| LK4501-9RD1TB1 | 1-OUTPUT 150 W AC-DC PWR FACTOR CORR MODULE |
| LK4601-7ERD3TB1 | 1-OUTPUT 150 W AC-DC PWR FACTOR CORR MODULE |
| LK5660-7ERD2TB1 | 2-OUTPUT 150 W AC-DC PWR FACTOR CORR MODULE |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| LK4301-7R | 功能描述:線性和開關(guān)式電源 Euro-Cassette 144W (12V) RoHS:否 制造商:TDK-Lambda 產(chǎn)品:Switching Supplies 開放式框架/封閉式:Enclosed 輸出功率額定值:800 W 輸入電壓:85 VAC to 265 VAC 輸出端數(shù)量:1 輸出電壓(通道 1):20 V 輸出電流(通道 1):40 A 商用/醫(yī)用: 輸出電壓(通道 2): 輸出電流(通道 2): 安裝風(fēng)格:Rack 長(zhǎng)度: 寬度: 高度: |
| LK4301-9ER | 制造商:Power-One 功能描述:AC/DC PS SGL-OUT 12V 12A 280W 15PIN - Bulk |
| LK4303-9ERD4T | 制造商:Power-One 功能描述:- Bulk |
| LK4402 | 制造商:CLINCH NUT 功能描述: |
| LK-440-2 | 制造商:PennEngineering (PEM) 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。