- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370830 > M30201F6 (Mitsubishi Electric Corporation) SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | M30201F6 |
| 廠商: | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
| 英文描述: | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| 中文描述: | 單片16位CMOS微機 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 130/159頁 |
| 文件大小: | 2319K |
| 代理商: | M30201F6 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁當前第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁第145頁第146頁第147頁第148頁第149頁第150頁第151頁第152頁第153頁第154頁第155頁第156頁第157頁第158頁第159頁
Unde
CPU Rewrite Mode
Peimnay
STE instruction) in the second bus cycle, the flash memory control circuit executes the program op-
eration. The program operation requires approximately 20
μ
s. Wait for 20
μ
s or more before the user
go to the next processing.
During program operation, the watchdog timer remains idle, with the value “7FFF
16
” set in it.
deeopmen
Mitsubishi microcomputers
M30201 Group
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
130
Command
Program verify
Read
Program
03B6
16
First bus cycle
Second bus cycle
00
16
40
16
C0
16
Write
Write
Write
Program
address
Write
Read
Erase verify
A0
16
Write
Verify
address
Verify
data
Read
Erase
20
16
Write
03B6
16
20
16
Write
Verify
address
Reset
FF
16
Write
Mode
Address
Mode
Address
Data
(D
0
to D
7
)
Data
(D
0
to D
7
)
03B6
16
03B6
16
03B6
16
03B6
16
03B6
16
Program
data
Verify
data
FF
16
Write
03B6
16
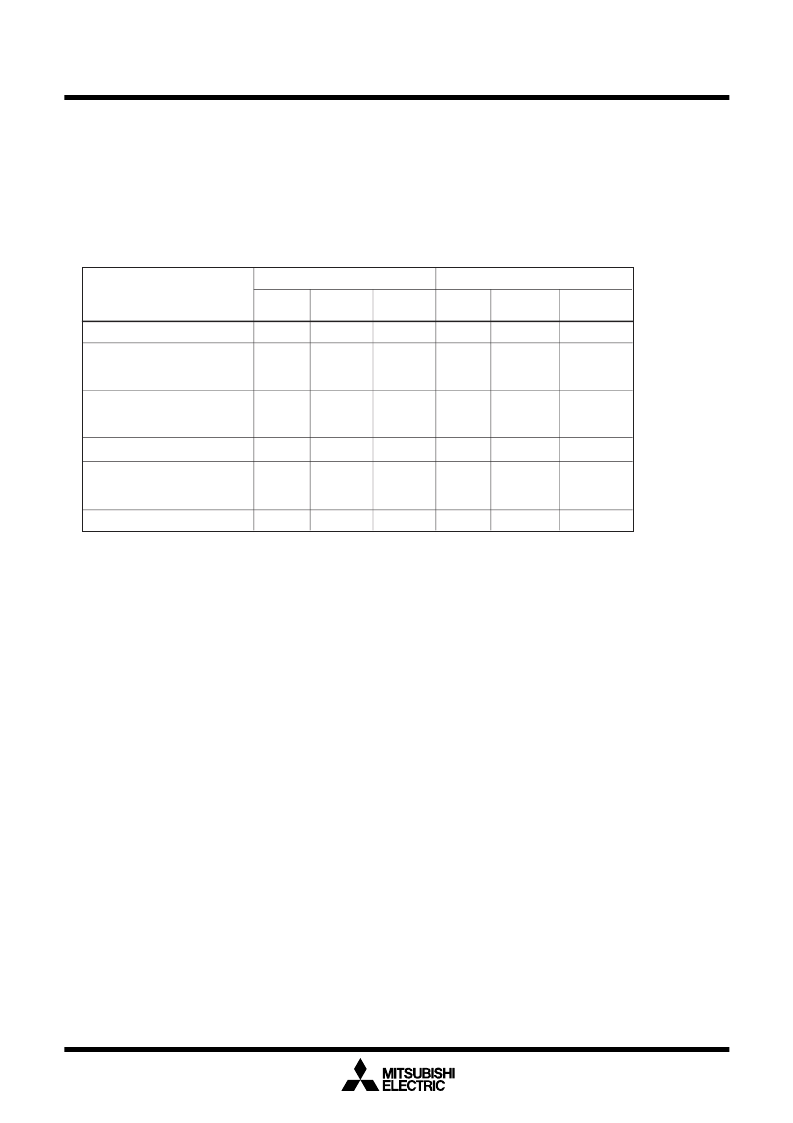
Software Commands
Table BB-1 lists the software commands available with the M30201 (flash memory version).
When CPU rewrite mode is enabled, write software commands to the flash command register to specify
the operation to erase or program.
The content of each software command is explained below.
Table BB-1. List of Software Commands (CPU Rewrite Mode)
Read Command (00
16
)
The read mode is entered by writing the command code “00
16
” to the flash command register in the
first bus cycle. When an address to be read is input in one of the bus cycles that follow, the content of
the specified address is read out at the data bus (D
0
–D
7
), 8 bits at a time.
The read mode is retained intact until another command is written.
After reset and after the reset command is executed, the read mode is set.
Program Command (40
16
)
The program mode is entered by writing the command code “40
16
” to the flash command register in
the first bus cycle. When the user execute an instruction to write byte data to the desired address (e.g.,
Note 1: The write operation is not completed immediately by writing a program command once. The
user must always execute a program-verify command after each program command executed. And if
verification fails, the user need to execute the program command repeatedly until the verification
passes. See Figure 1.BB.3 for an example of a programming flowchart.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M30201F6FP | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30201F6SP | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30201F6TSP | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30201M2 | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30201M2T | SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M30201F6FP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30201F6SP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30201F6TFP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M30201F6TFP#U1 | 制造商:Renesas Electronics Corporation 功能描述: |
| M30201F6TSP | 制造商:MITSUBISHI 制造商全稱:Mitsubishi Electric Semiconductor 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。