- 您現在的位置:買賣IC網 > PDF目錄45048 > M38C89EFFP 8-BIT, OTPROM, 4 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 PDF資料下載
參數資料
| 型號: | M38C89EFFP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 4 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| 封裝: | 20 X 20 MM, 0.50 MM PITCH, PLASTIC, LQFP-144 |
| 文件頁數: | 16/55頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 981K |
| 代理商: | M38C89EFFP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁當前第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁
22
SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
MITSUBISHI MICROCOMPUTERS
38C8 Group
Timer Y
Timer Y is a 16-bit timer that can be selected in one of four modes.
(1) Timer Mode
The timer counts f(XIN)/16 (or f(XCIN)/16 in low-speed mode).
(2) Period Measurement Mode
CNTR1 interrupt request is generated at rising/falling edge of CNTR1
pin input signal. Simultaneously, the value in timer Y latch is reloaded
in timer Y and timer Y continues counting down. Except for the above-
mentioned, the operation in period measurement mode is the same
as in timer mode.
The timer value just before the reloading at rising/falling of CNTR1
pin input signal is retained until the timer Y is read once after the
reload.
The rising/falling timing of CNTR1 pin input signal is found by CNTR1
interrupt. When using a timer in this mode, set the port shared with
the CNTR1 pin to input.
(3) Event Counter Mode
The timer counts signals input through the CNTR1 pin.
Except for this, the operation in event counter mode is the same as
in timer mode. When using a timer in this mode, set the port shared
with the CNTR1 pin to input.
(4) Pulse Width HL Continuously Measurement
Mode
CNTR1 interrupt request is generated at both rising and falling edges
of CNTR1 pin input signal. Except for this, the operation in pulse
width HL continuously measurement mode is the same as in period
measurement mode. When using a timer in this mode, set the port
shared with the CNTR1 pin to input.
sNotes on CNTR1 interrupt active edge selection
CNTR1 interrupt active edge depends on the CNTR1 active edge
switch bit. However, in the pulse width HL continuously measure-
ment mode, CNTR1 interrupt request is generated at both rising and
falling edges of CNTR1 pin input signal regardless of the setting of
CNTR1 active edge switch bit.
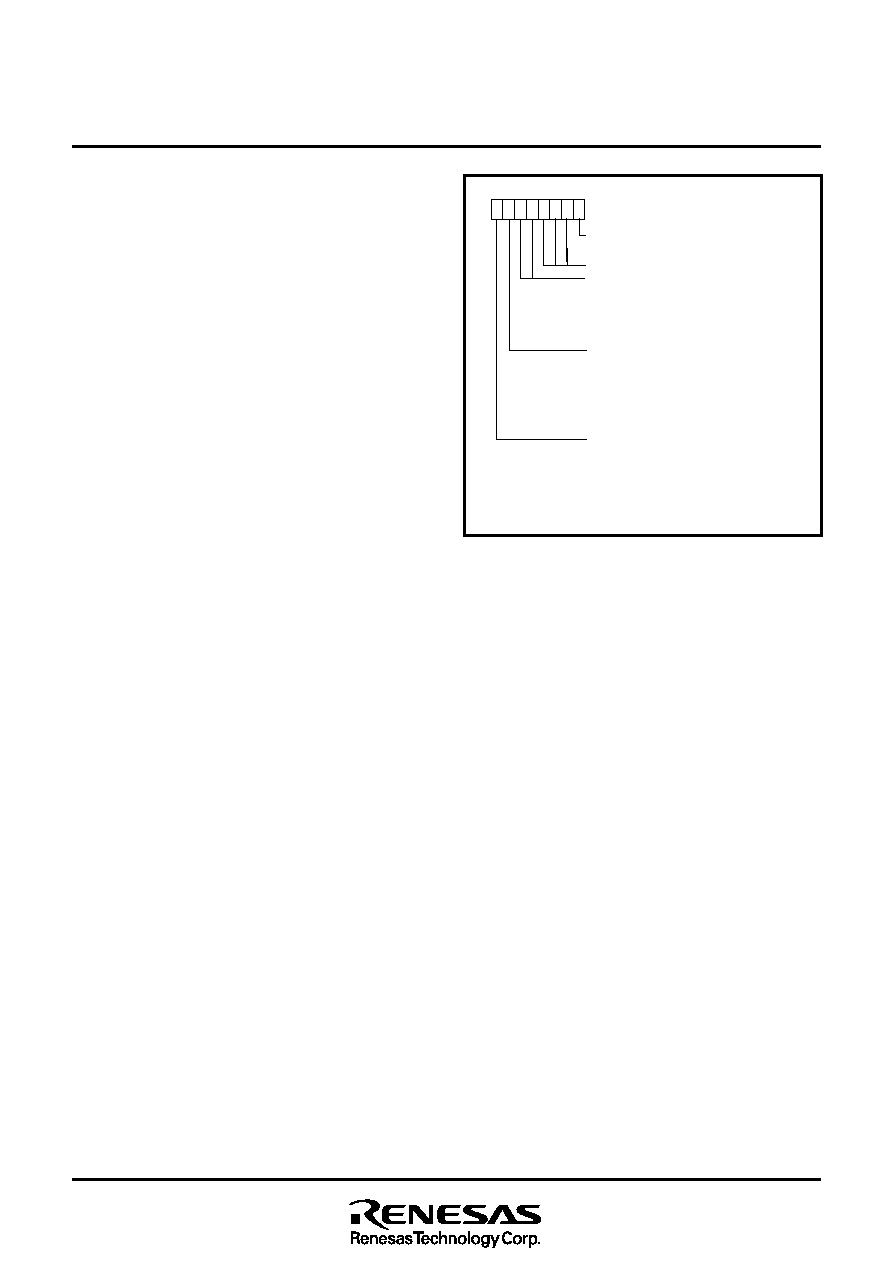
Fig. 18 Structure of timer Y mode register
Timer Y mode register
(TYM : address 002816)
b7
b0
Timer X count source selection bit
0 : f(XIN)/16 (f(XCIN)/16 in low-speed mode)
1 : f(XIN)
Not used (return “0” when read)
Timer Y operating mode bits
b5 b4
0
0 : Timer mode
0
1 : Period measurement mode
1
0 : Event counter mode
1
1 : Pulse width HL continuously
measurement mode
CNTR1 active edge switch bit
0 : Count at rising edge in event counter mode
Measure the falling edge to falling edge
period in period measurement mode
Interrupt falling edge active
1 : Count at falling edge in event counter mode
Measure the rising edge period in period
measurement mode
Interrupt rising edge active
Timer Y stop control bit
0 : Count start
1 : Count stop
Internal clock
φ in low-speed mode is XCIN divided by 2.
When the timer X operating mode bits are “00” or “11”, the timer X count source is
f(XCIN)/16. When the timer X operating mode bits are “01”, the timer X count source
is f(XCIN).
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M38C89MF-XXXFP | 8-BIT, MROM, 4 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| M38C89EFFP | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 4 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| M38D24G6HP | 8-BIT, FLASH, 6.25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
| M38D24G4FP | 8-BIT, FLASH, 6.25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
| M38D24G4-XXXHP | 8-BIT, FLASH, 6.25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
相關代理商/技術參數 |
參數描述 |
|---|---|
| M38D20F1XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38D20F1XXXHP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38D20F2XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38D20F2XXXHP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
| M38D20F3XXXFP | 制造商:RENESAS 制造商全稱:Renesas Technology Corp 功能描述:SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。