- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買(mǎi)賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄8621 > MAX3654ETE+ (Maxim Integrated Products)IC AMP TRANSIMPEDANCE 16-TQFN PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | MAX3654ETE+ |
| 廠商: | Maxim Integrated Products |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 6/8頁(yè) |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC AMP TRANSIMPEDANCE 16-TQFN |
| 產(chǎn)品培訓(xùn)模塊: | Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 75 |
| 類型: | 轉(zhuǎn)阻放大器 |
| 應(yīng)用: | CATV |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 封裝/外殼: | 16-WQFN 裸露焊盤(pán) |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 16-TQFN-EP(4x4) |
| 包裝: | 管件 |
Detailed Description
The MAX3654 is a broadband, high-linearity, low-noise
transimpedance amplifier. The transimpedance (gain)
can be adjusted between 43.5dB
and 62dB using
the voltage at an external control input (VAGC). When
connected as shown in the Typical Application Circuit,
optical input levels from -6dBm to +2dBm will produce
a minimum output of 14dBmV/channel, and 4dB tilt
compensation. Gain deviation over frequency from
47MHz to 870MHz is less than ±0.75dB.
Low-Noise Variable Gain Amplifier
The input stage is a low-noise analog transimpedance
amplifier (TIA) connected differentially to the analog
photodiode. Desired performance can be achieved
with a photodiode having capacitance (CPD) up to 1pF.
VAGC and Hysteresis Control
The gain-control pin VAGC sets overall TIA gain imple-
mented as three switchable gain stages, each with a
continuously variable gain control, as shown in Figure 3.
This produces a continuously variable gain ranging
from 62dB
(at VAGC = 0.175V) to 43.5dB at
(VAGC=1.4V). A set of comparators examines the
VAGC input to select a gain stage. As the voltage at
VAGC crosses the two locations in the gain vs. VAGC
curve, where the gain stage changes (350mV and
700mV), there will be small deviations in the output
which may lead to a brief interruption of CATV signals.
See the Typical Operating Characteristics for Gain vs.
Control Voltage.
A hysteresis control input is provided to limit dithering
when the optical level is close to a gain-switching point.
The hysteresis level is controlled by the value of RHYST.
Hysteresis is minimum (0.13dB) when this pin is open.
RF Output and Cable Tilt Compensation
With a typical photodiode, the gain at 870MHz is 4dB
higher than at 47MHz. The overall frequency response
of the TIA is within ±0.75dB of a straight line connecting
the values at 47MHz and 870MHz.
Mute
In normal operation, the TTL MUTE pin is held high.
When MUTE is low, the output signal is attenuated by
more than 45dB.
MAX3654
47MHz to 870MHz Analog CATV
Transimpedance Amplifier
6
_______________________________________________________________________________________
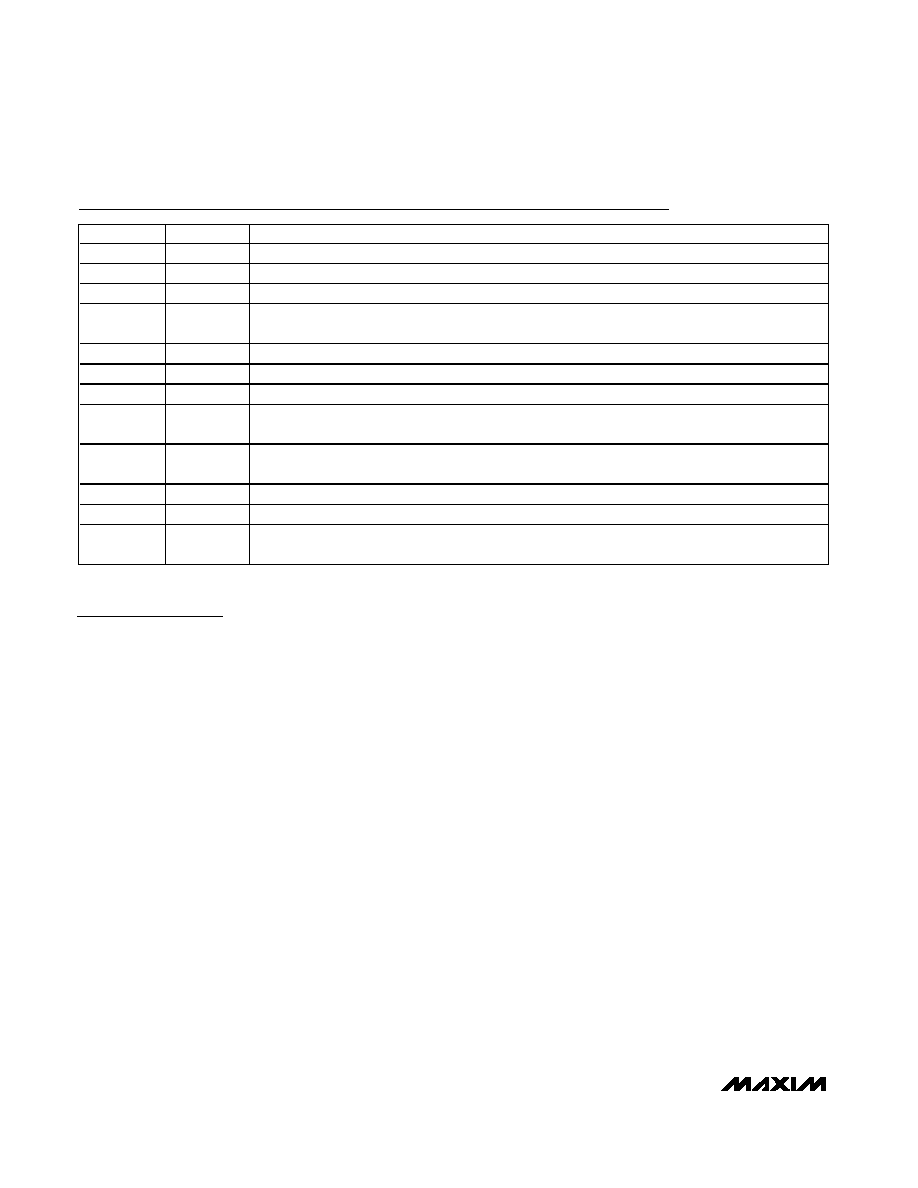
Pin Description
PIN
NAME
FUNCTION
1, 4, 9, 12
VCC
+5.0V Power Supply
2
IN+
Positive Analog Photodiode Input Connection. Typically connected to photodiode cathode.
3
IN-
Negative Analog Photodiode Input Connection. Typically connected to photodiode anode.
5
VAGC
AGC Control Input. Range is 0 to 1.4V. See the Typical Operating Characteristics Gain vs. Control
Voltage graph.
6
MUTE
Mute Control Input, TTL. MUTE < 0.8V to mute output.
7
HYST
AGC Hysteresis Control Input. A resistor from HYST to GND controls the hysteresis level.
8, 14, 16
GND
Ground
10
OUT-
Negative RF Output. The voltage on this pin decreases with increasing optical power when IN+ is
connected to the photodiode cathode.
11
OUT+
Positive RF Output. The voltage on this pin increases with increasing optical power when IN- is
connected to the photodiode anode.
13
TEST1
Reserved for Test. Connect to GND for normal operation.
15
TEST2
Reserved for Test. Connect to GND for normal operation.
EP
Exposed Pad. The exposed pad must be soldered to the circuit-board ground for proper thermal and
electrical performance.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LTC2753ACUK-16#TRPBF | IC DAC 16BIT DUAL 48-QFN |
| DAC8800FSZ-REEL | IC DAC 8BIT OCTAL CMOS 20SOIC |
| VE-25M-IV-F3 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 10V 150W |
| VE-25M-IV-F1 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 10V 150W |
| VE-251-IV-F3 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 12V 150W |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX3654ETE+ | 功能描述:跨阻抗放大器 47-870MHz Alog CATV Transimpedance Amp RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-14 帶寬:3 MHz 工作電源電壓:36 V 電源電流:5.5 mA 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 封裝:Tube |
| MAX3654ETE+T | 功能描述:跨阻抗放大器 47-870MHz Alog CATV Transimpedance Amp RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-14 帶寬:3 MHz 工作電源電壓:36 V 電源電流:5.5 mA 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 封裝:Tube |
| MAX3654EVKIT | 功能描述:跨阻抗放大器 MAX3654 Evaluation Kit RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 封裝 / 箱體:SOIC-14 帶寬:3 MHz 工作電源電壓:36 V 電源電流:5.5 mA 工作溫度范圍:- 40 C to + 85 C 封裝:Tube |
| MAX3656E/D | 功能描述:激光驅(qū)動(dòng)器 RoHS:否 制造商:Micrel 數(shù)據(jù)速率:4.25 Gbps 工作電源電壓:3 V to 3.6 V 電源電流:80 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 85 C 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-16 封裝:Tube |
| MAX3656ETA | 制造商:Maxim Integrated Products 功能描述:- Rail/Tube |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。