- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄25637 > MC80C52EXXX-25/883:D (ATMEL CORP) 8-BIT, MROM, 25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CDIP40 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MC80C52EXXX-25/883:D |
| 廠商: | ATMEL CORP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, MROM, 25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CDIP40 |
| 封裝: | 0.600 INCH, SIDE BRAZED, DIP-40 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 124/141頁 |
| 文件大小: | 7628K |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁第122頁第123頁當(dāng)前第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁
53
2486AA–AVR–02/2013
ATmega8(L)
When switching between tri-state ({DDxn, PORTxn} = 0b00) and output high ({DDxn, PORTxn}
= 0b11), an intermediate state with either pull-up enabled ({DDxn, PORTxn} = 0b01) or output
low ({DDxn, PORTxn} = 0b10) must occur. Normally, the pull-up enabled state is fully accept-
able, as a high-impedant environment will not notice the difference between a strong high driver
and a pull-up. If this is not the case, the PUD bit in the SFIOR Register can be set to disable all
pull-ups in all ports.
Switching between input with pull-up and output low generates the same problem. The user
must use either the tri-state ({DDxn, PORTxn} = 0b00) or the output high state ({DDxn, PORTxn}
= 0b11) as an intermediate step.
Table 20 summarizes the control signals for the pin value.
Reading the Pin Value
Independent of the setting of Data Direction bit DDxn, the port pin can be read through the
PINxn Register Bit. As shown in Figure 22 on page 52, the PINxn Register bit and the preceding
latch constitute a synchronizer. This is needed to avoid metastability if the physical pin changes
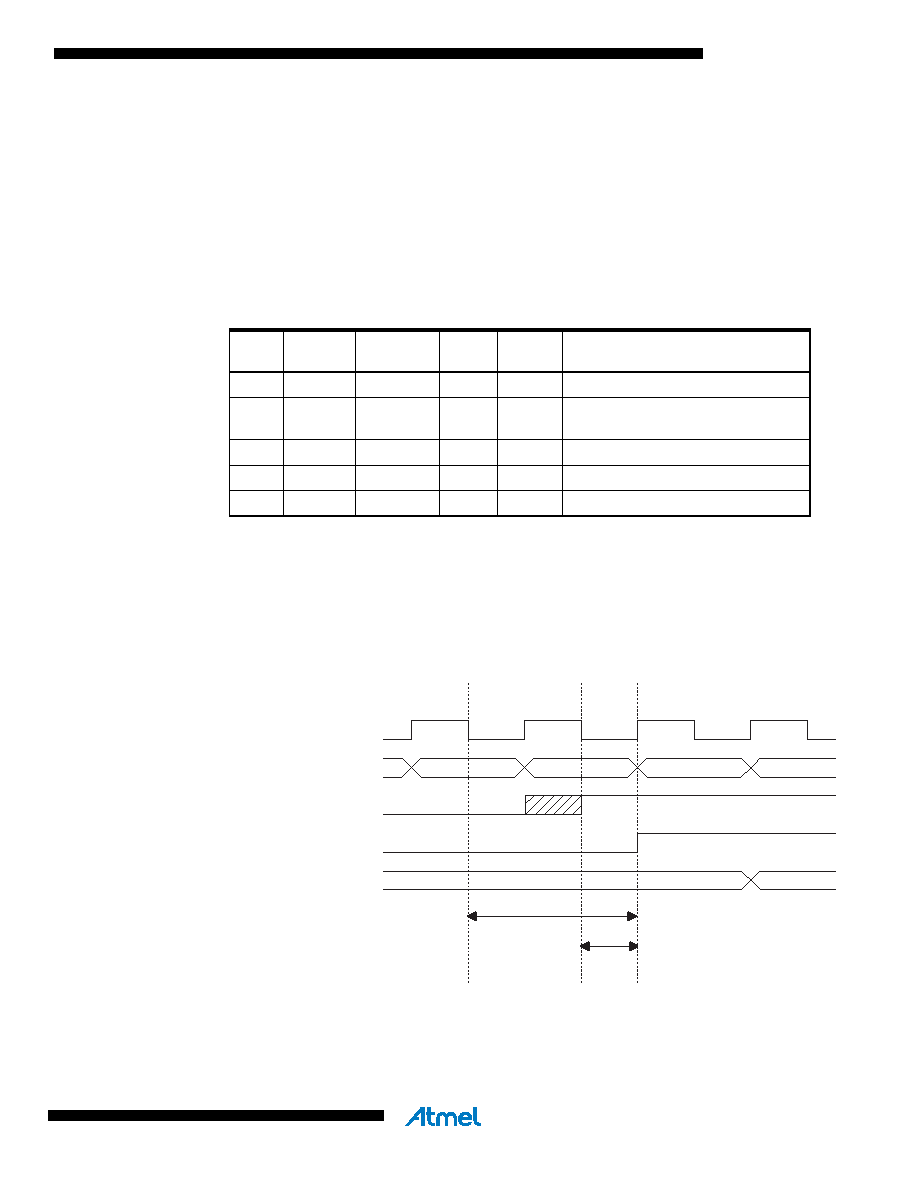
value near the edge of the internal clock, but it also introduces a delay. Figure 23 shows a timing
diagram of the synchronization when reading an externally applied pin value. The maximum and
minimum propagation delays are denoted t
pd,max and tpd,min, respectively.
Figure 23. Synchronization when Reading an Externally Applied Pin Value
Consider the clock period starting shortly after the first falling edge of the system clock. The latch
is closed when the clock is low, and goes transparent when the clock is high, as indicated by the
shaded region of the “SYNC LATCH” signal. The signal value is latched when the system clock
Table 20. Port Pin Configurations
DDxn
PORTxn
PUD
(in SFIOR)
I/O
Pull-up
Comment
0
X
Input
No
Tri-state (Hi-Z)
0
1
0
Input
Yes
Pxn will source current if external
pulled low.
0
1
Input
No
Tri-state (Hi-Z)
1
0
X
Output
No
Output Low (Sink)
1
X
Output
No
Output High (Source)
XXX
in r17, PINx
0x00
0xFF
INSTRUCTIONS
SYNC LATCH
PINxn
r17
XXX
SYSTEM CLK
t
pd, max
t pd, min
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MR80C52EXXX-12/883:R | 8-BIT, MROM, 12 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQCC44 |
| MC80C52XXX-16SHXXX:D | 8-BIT, MROM, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CDIP40 |
| MQ80C52TXXX-30SBR | 8-BIT, MROM, 30 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQFP44 |
| MR83C154XXX-25/883D | 8-BIT, MROM, 25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQCC44 |
| MR83C154CXXX-25P883R | 8-BIT, MROM, 25 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQCC44 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MC80D21000G | 制造商:COR 功能描述:RN |
| MC80F0104 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLERS |
| MC80F0104B | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLERS |
| MC80F0104D | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLERS |
| MC80F0204 | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:8-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCONTROLLERS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。