- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄5658 > MCP621T-E/MNY (Microchip Technology)IC OPAMP SGL 20MHZ 8TDFN PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | MCP621T-E/MNY |
| 廠商: | Microchip Technology |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 16/66頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 0K |
| 描述: | IC OPAMP SGL 20MHZ 8TDFN |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 3,300 |
| 系列: | mCal 技術(shù) |
| 放大器類型: | 通用 |
| 電路數(shù): | 1 |
| 輸出類型: | 滿擺幅 |
| 轉(zhuǎn)換速率: | 10 V/µs |
| 增益帶寬積: | 20MHz |
| 電流 - 輸入偏壓: | 5pA |
| 電壓 - 輸入偏移: | 200µV |
| 電流 - 電源: | 2.5mA |
| 電流 - 輸出 / 通道: | 70mA |
| 電壓 - 電源,單路/雙路(±): | 2.5 V ~ 5.5 V |
| 工作溫度: | -40°C ~ 125°C |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 封裝/外殼: | 8-WFDFN 裸露焊盤 |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 8-TDFN(2x3) |
| 包裝: | 帶卷 (TR) |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁當(dāng)前第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁
2009-2011 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS22188C-page 23
MCP621/1S/2/3/4/5/9
4.0
APPLICATIONS
The MCP621/1S/2/3/4/5/9 family of self-zeroed op
amps is manufactured using Microchip’s state-of-the-
art CMOS process. It is designed for low-cost, low-
power and high-precision applications. Its low supply
voltage, low quiescent current and wide bandwidth
makes the MCP621/1S/2/3/4/5/9 ideal for battery-
powered applications.
4.1
Calibration and Chip Select
These op amps include circuitry for dynamic calibration
of the offset voltage (VOS).
4.1.1
mCal CALIBRATION CIRCUITRY
The internal mCal circuitry, when activated, starts a
delay timer (to wait for the op amp to settle to its new
bias point), then calibrates the input offset voltage
(VOS). The mCal circuitry is triggered at power-up (and
after some power brown-out events) by the internal
POR, and by the memory’s Parity Detector. The
power-up time, when the mCal circuitry triggers the
calibration sequence, is 200 ms (typical).
4.1.2
CAL/CS PIN
The CAL/CS pin gives the user a means to externally
demand a Low-Power mode of operation, then to
calibrate VOS. Using the CAL/CS pin makes it possible
to correct VOS as it drifts over time (1/f noise and aging;
see Figure 2-35) and across temperature.
The CAL/CS pin performs two functions: it places the
op amp(s) in a Low-Power mode when it is held high,
and starts a calibration event (correction of VOS) after a
rising edge.
While in the Low-Power mode, the quiescent current is
quite small (ISS = -3 A, typical). The output is also in a
High-Z state.
During the calibration event, the quiescent current is
near, but smaller than the specified quiescent current
(2.5 mA, typical). The output continues in the High-Z
state, and the inputs are disconnected from the
external circuit, to prevent internal signals from
affecting circuit operation. The op amp inputs are
internally connected to a Common mode voltage buffer
and feedback resistors. The offset is corrected (using a
digital state machine, logic and memory), and the
calibration constants are stored in memory.
Once the calibration event is completed, the amplifier is
reconnected to the external circuitry. The turn-on time,
when calibration is started with the CAL/CS pin, is 5 ms
(typical).
There is an internal 5 M
Ω pull-down resistor tied to the
CAL/CS pin. If the CAL/CS pin is left floating, the
amplifier operates normally.
For the MCP625 dual and the MCP629 quad, there is
an additional constraint on toggling the two CAL/CS
pins close together; see the tCON specification in
Table 1-3. If the two pins are toggled simultaneously, or
if they are toggled separately with an adequate delay
between them (greater than tCON), then the CAL/CS
inputs are accepted as valid. If one of the two pins
toggles, while the other pin’s calibration routine is in
progress, then an invalid input occurs and the result is
unpredictable.
4.1.3
INTERNAL POR
This part includes an internal Power-on Reset (POR) to
protect the internal calibration memory cells. The POR
monitors the power supply voltage (VDD). When the
POR detects a low VDD event, it places the part into the
Low-Power mode of operation. When the POR detects
a normal VDD event, it starts a delay counter, then
triggers a calibration event. The additional delay gives
a total POR turn-on time of 200 ms (typical); this is also
the power-up time (since the POR is triggered at power
up).
4.1.4
PARITY DETECTOR
A parity error detector monitors the memory contents
for any corruption. In the rare event that a parity error is
detected (e.g., corruption from an alpha particle), a
POR event is automatically triggered. This will cause
the input offset voltage to be recorrected, and the op
amp will not return to normal operation for a period of
time (the POR turn-on time, tPON).
4.1.5
CALIBRATION INPUT PIN
A VCAL pin is available in some options (e.g., the single
MCP621) for those applications that need the
calibration to occur at an internally driven Common
mode voltage other than VDD/3.
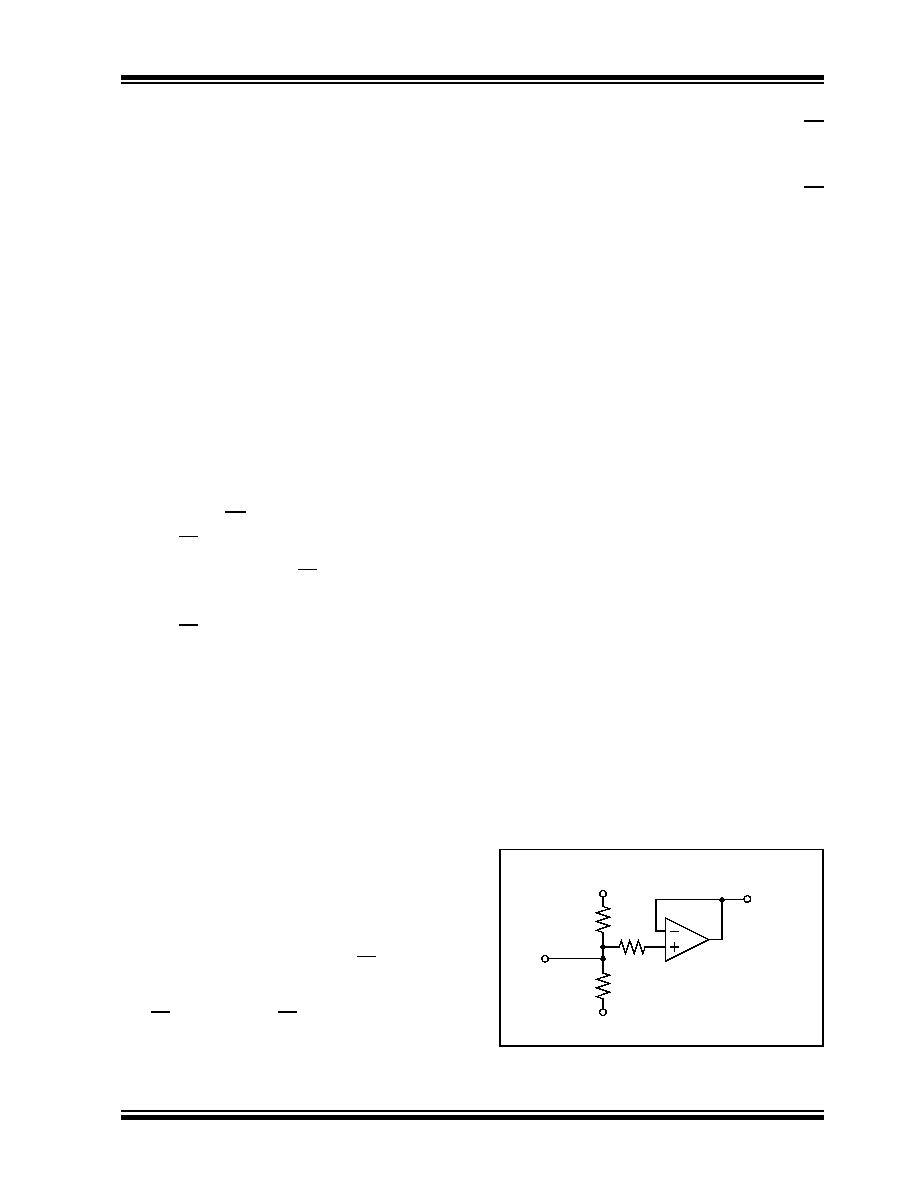
Figure 4-1 shows the reference circuit that internally
sets the op amp’s Common mode reference voltage
(VCM_INT) during calibration (the resistors are
disconnected from the supplies at other times). The
5k
Ω resistor provides overcurrent protection for the
buffer.
FIGURE 4-1:
Common-Mode Reference’s
Input Circuitry.
To op amp during
VCAL
BUFFER
5k
Ω
300 k
Ω
150 k
Ω
VSS
VDD
calibration
VCM_INT
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| CRCW04024R75FKED | RES 4.75 OHM 1/16W 1% 0402 SMD |
| 3428-1502UG | CONN HEADER 20PS R/A SHORT LATCH |
| MCP621T-E/SN | IC OPAMP SGL 2.5V R-R 8-SOIC |
| MCP6L94T-E/ST | IC OPAMP 10MHZ 2.4V 14-TSSOP |
| CRCW04024R70FKED | RES 4.70 OHM 1/16W 1% 0402 SMD |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| MCP622-E/MF | 功能描述:運(yùn)算放大器 - 運(yùn)放 Dual 20MHz OP Auto-cal E temp RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 通道數(shù)量:4 共模抑制比(最小值):63 dB 輸入補(bǔ)償電壓:1 mV 輸入偏流(最大值):10 pA 工作電源電壓:2.7 V to 5.5 V 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-16 轉(zhuǎn)換速度:0.89 V/us 關(guān)閉:No 輸出電流:55 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 125 C 封裝:Reel |
| MCP622-E/SN | 功能描述:運(yùn)算放大器 - 運(yùn)放 Dual 20MHz OP Auto-cal E temp RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 通道數(shù)量:4 共模抑制比(最小值):63 dB 輸入補(bǔ)償電壓:1 mV 輸入偏流(最大值):10 pA 工作電源電壓:2.7 V to 5.5 V 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-16 轉(zhuǎn)換速度:0.89 V/us 關(guān)閉:No 輸出電流:55 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 125 C 封裝:Reel |
| MCP622T-E/MF | 功能描述:運(yùn)算放大器 - 運(yùn)放 Dual 20MHz OP Auto-cal E temp RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 通道數(shù)量:4 共模抑制比(最小值):63 dB 輸入補(bǔ)償電壓:1 mV 輸入偏流(最大值):10 pA 工作電源電壓:2.7 V to 5.5 V 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-16 轉(zhuǎn)換速度:0.89 V/us 關(guān)閉:No 輸出電流:55 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 125 C 封裝:Reel |
| MCP622T-E/SN | 功能描述:運(yùn)算放大器 - 運(yùn)放 Dual 20MHz OP Auto-cal E temp RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 通道數(shù)量:4 共模抑制比(最小值):63 dB 輸入補(bǔ)償電壓:1 mV 輸入偏流(最大值):10 pA 工作電源電壓:2.7 V to 5.5 V 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-16 轉(zhuǎn)換速度:0.89 V/us 關(guān)閉:No 輸出電流:55 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 125 C 封裝:Reel |
| MCP6231-E/MC | 功能描述:運(yùn)算放大器 - 運(yùn)放 SNGL 18V 300 kHz OP E Temp RoHS:否 制造商:STMicroelectronics 通道數(shù)量:4 共模抑制比(最小值):63 dB 輸入補(bǔ)償電壓:1 mV 輸入偏流(最大值):10 pA 工作電源電壓:2.7 V to 5.5 V 安裝風(fēng)格:SMD/SMT 封裝 / 箱體:QFN-16 轉(zhuǎn)換速度:0.89 V/us 關(guān)閉:No 輸出電流:55 mA 最大工作溫度:+ 125 C 封裝:Reel |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。