- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98158 > TA8876FA AUDIO/VIDEO DEMODULATOR, PDSO30 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | TA8876FA |
| 元件分類: | 接收器 |
| 英文描述: | AUDIO/VIDEO DEMODULATOR, PDSO30 |
| 封裝: | 0.375 INCH, 1 MM PITCH, PLASTIC, SSOP-30 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 4/20頁 |
| 文件大小: | 443K |
| 代理商: | TA8876FA |
TA8876FA
2001-05-10
12
Note 7: Detection output bandwidth
PIF input : f = 58.75 MHz, 84 dBV CW.
Measure 2nd AGC terminal voltage and fix the terminal to that voltage using the external power supply.
Then, input the following composite signals to the PIF input.
(1) SG 1 : 58.75 MHz, 84 dBV
(Frequency fixed)
(2) SG 2 : 58.65 MHz~45 MHz, 64 dBV (Frequency variable)
Monitor video output-2 with a spectrum analyzer. Vary SG2 to find frequency f when the detection output will
be 3 dB.
Calculate the difference between that frequency and 58.75 MHz.
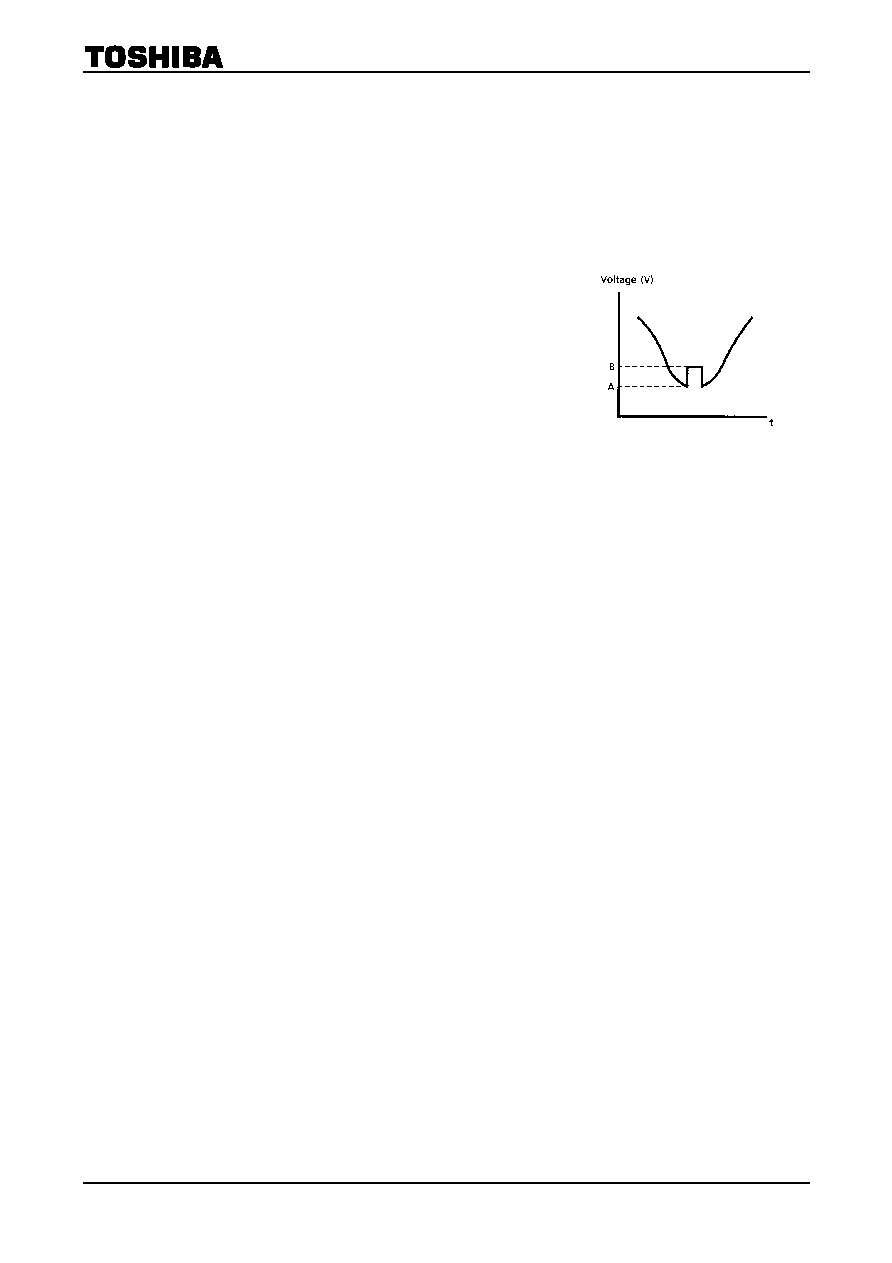
Note 8: Black noise inverter, clamp level
PIF input : f = 58.75 MHz, fm = 15.75 kHz, 30% AM, 84 dBV.
Measure the 2nd AGC terminal voltage and fix the terminal to that
voltage using the external power supply.
Then, gradually raise the 2nd AGC terminal voltage and fix the
voltage when a waveform like that in the accompanying diagram is
output. At that time, the A and B voltages are :
A : Black noise inverter level
B : Black noise clamp level
Note 9: Carrier wave rejection ratio
PIF input : f = 58.75 MHz, fm = 15.75 kHz, 78% AM, 84 dBV.
Monitor video output-2 detection output using a spectrum analyzer.
Measure the ratios of the 15.75 kHz and 58.75 MHz components.
Note 10: Harmonic rejection ratio
Measure as in Note 9, above, and calculate the secondary harmonic level (117.5 MHz component) at video
output-2.
Note 11: Intermodulation
PIF input : Input the following composite signals to the PIF input.
(1) SG 1 : 58.75 MHz (P) 84 dBV
(2) SG 2 : 54.25 MHz (S) 74 dBV
(3) SG 2 : 55.17 MHz (C) 74 dBV
Monitor the video output-2 detection output waveform. Apply external voltage to the 2nd AGC terminal so
that the waveform’s lowest level matches the sync. Tip level.
Using a spectrum analyzer, measure the difference between the level of the chroma signal component of the
video output-2 and the 920 kHz signal component.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TA8880AN | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDIP64 |
| TA8880CN | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDIP64 |
| TA8884AN | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDIP54 |
| TA8889AP | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDIP16 |
| TA8891N | SPECIALTY CONSUMER CIRCUIT, PDIP30 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TA8879 | 制造商:TOSHIBA 制造商全稱:Toshiba Semiconductor 功能描述:1 CHIP NTSC COLOR TV |
| TA8879N | 制造商:TOSHIBA 制造商全稱:Toshiba Semiconductor 功能描述:1 CHIP NTSC COLOR TV |
| TA8880BN | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:IC |
| TA8880CN | 制造商:TOSHIBA 制造商全稱:Toshiba Semiconductor 功能描述:VIDEO, CHROMA, AND SYNC. SIGNAL PROCESSING IC FOR PAL/NTSC/SECAM-SYSTEM COLOR TELEVISIONS |
| TA8884AN | 制造商:TOSHIBA 制造商全稱:Toshiba Semiconductor 功能描述:RGB PROCESSOR IC |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。