- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98282 > TPS54110PWPG4 (TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC) 3.5 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 762 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO20 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | TPS54110PWPG4 |
| 廠商: | TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC |
| 元件分類: | 穩(wěn)壓器 |
| 英文描述: | 3.5 A SWITCHING REGULATOR, 762 kHz SWITCHING FREQ-MAX, PDSO20 |
| 封裝: | GREEN, PLASTIC, HTSSOP-20 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 9/30頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 870K |
| 代理商: | TPS54110PWPG4 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁當前第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁
6
4
5
C3 0.047 F
19
20
VI 5 V
+
C1
470 F
PWRGD_3P3
R7
10 k
U1
TPS54110PWP
R4
71.5 k
C4
0.1 F
C9
10 F
21
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
RT
SYNC
SS/ENA
VBIAS
VIN
PGND
AGND
VSENSE
COMP
PWRGD
BOOT
PH
PWPD
R3
1.74 k
C6
1000 pF
C7
47 pF
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
C8
560 pF
R5
432
R1
10 k
R2
3.74 k
L1
1 H
1
2
3.3 V at 1.5 A
C14 0.047 F
19
20
PWRGD_1P5
R8
10 k
U2
TPS54110PWP
R9
71.5 k
C10
0.1 F
C15
10 F
21
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
RT
SYNC
SS/ENA
VBIAS
VIN
PGND
AGND
VSENSE
COMP
PWRGD
BOOT
PH
PWPD
R6
1.74 k
C5
1000 pF
C11
47 pF
10
9
8
7
3
2
1
C13
560 pF
R12
432
R11
10 k
R10
14.7 k
L2
1 H
1
2
1.5 V at 1.5 A
C2
10 F
C12
10 F
VOUT1
VOUT2
SLVS500C
– DECEMBER 2003 – REVISED FEBRUARY 2011
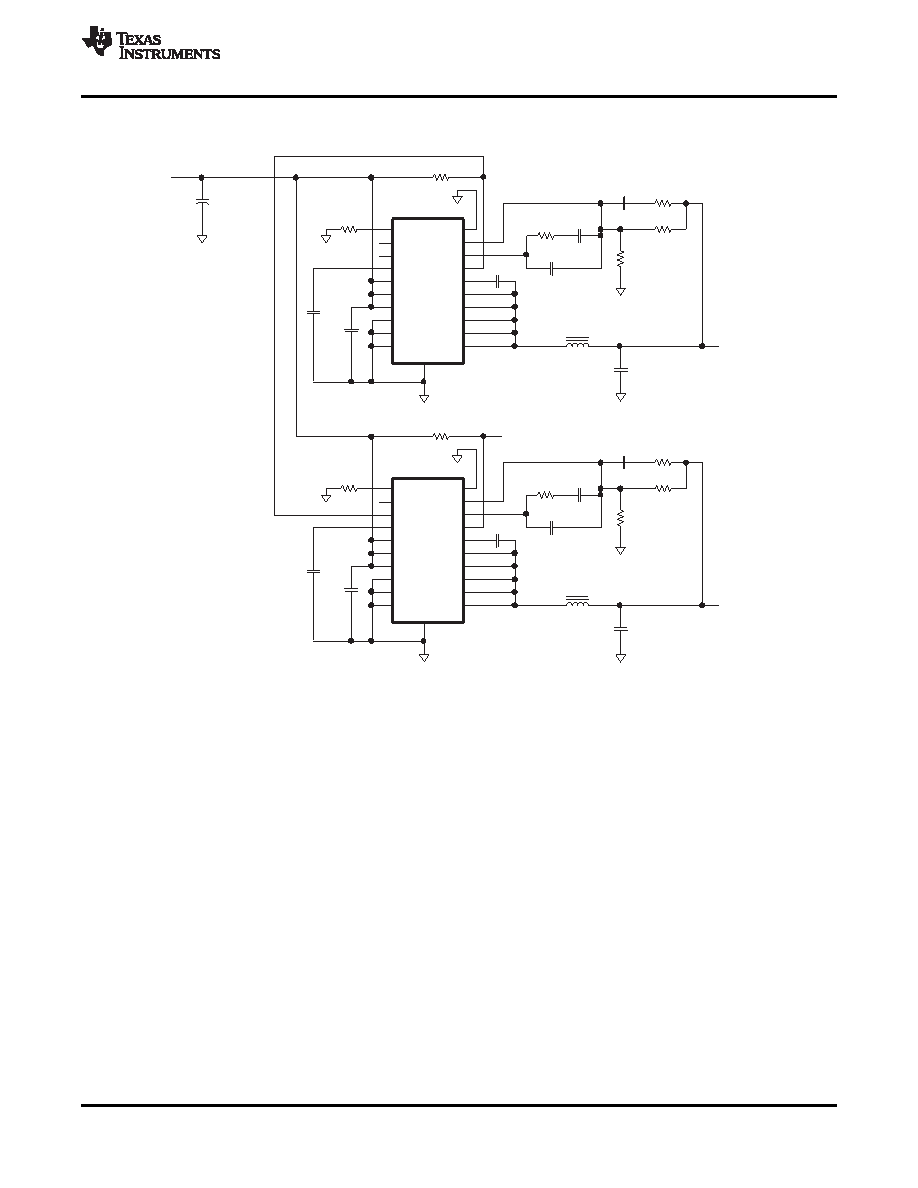
Two-Output Sequenced-Startup Application
Figure 29. TPS54110 Sequencing Application Circuit
In Figure 29, the power-good output of U1 is used as a sequencing signal in a two-output design. Connecting the
PWRGD pin of U1 to the SS/ENA pin of U2 causes the 1.5-V output to ramp up after the 3.3-V output is within
regulation. Figure 30 shows the startup waveforms associated with this circuit.
When VIN reaches the UVLO-start threshold, the U1 output ramps up towards the 3.3-V set point. After the output
reaches 90 percent of 3.3 V, the U1 asserts the power-good signal driving the U2 SS/ENA input high. The output
of U2 then ramps up towards the final output set point of 1.5 V.
2003–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
17
Product Folder Link(s): TPS54110
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。