- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄4212 > XCV405E-7BG560I (Xilinx Inc)IC FPGA 1.8V 560-MBGA PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | XCV405E-7BG560I |
| 廠商: | Xilinx Inc |
| 文件頁(yè)數(shù): | 2/118頁(yè) |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 0K |
| 描述: | IC FPGA 1.8V 560-MBGA |
| 產(chǎn)品變化通告: | FPGA Family Discontinuation 18/Apr/2011 |
| 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)包裝: | 1 |
| 系列: | Virtex®-E EM |
| LAB/CLB數(shù): | 2400 |
| 邏輯元件/單元數(shù): | 10800 |
| RAM 位總計(jì): | 573440 |
| 輸入/輸出數(shù): | 404 |
| 門數(shù): | 129600 |
| 電源電壓: | 1.71 V ~ 1.89 V |
| 安裝類型: | 表面貼裝 |
| 工作溫度: | -40°C ~ 100°C |
| 封裝/外殼: | 560-LBGA,金屬 |
| 供應(yīng)商設(shè)備封裝: | 560-MBGA(42.5x42.5) |
第1頁(yè)當(dāng)前第2頁(yè)第3頁(yè)第4頁(yè)第5頁(yè)第6頁(yè)第7頁(yè)第8頁(yè)第9頁(yè)第10頁(yè)第11頁(yè)第12頁(yè)第13頁(yè)第14頁(yè)第15頁(yè)第16頁(yè)第17頁(yè)第18頁(yè)第19頁(yè)第20頁(yè)第21頁(yè)第22頁(yè)第23頁(yè)第24頁(yè)第25頁(yè)第26頁(yè)第27頁(yè)第28頁(yè)第29頁(yè)第30頁(yè)第31頁(yè)第32頁(yè)第33頁(yè)第34頁(yè)第35頁(yè)第36頁(yè)第37頁(yè)第38頁(yè)第39頁(yè)第40頁(yè)第41頁(yè)第42頁(yè)第43頁(yè)第44頁(yè)第45頁(yè)第46頁(yè)第47頁(yè)第48頁(yè)第49頁(yè)第50頁(yè)第51頁(yè)第52頁(yè)第53頁(yè)第54頁(yè)第55頁(yè)第56頁(yè)第57頁(yè)第58頁(yè)第59頁(yè)第60頁(yè)第61頁(yè)第62頁(yè)第63頁(yè)第64頁(yè)第65頁(yè)第66頁(yè)第67頁(yè)第68頁(yè)第69頁(yè)第70頁(yè)第71頁(yè)第72頁(yè)第73頁(yè)第74頁(yè)第75頁(yè)第76頁(yè)第77頁(yè)第78頁(yè)第79頁(yè)第80頁(yè)第81頁(yè)第82頁(yè)第83頁(yè)第84頁(yè)第85頁(yè)第86頁(yè)第87頁(yè)第88頁(yè)第89頁(yè)第90頁(yè)第91頁(yè)第92頁(yè)第93頁(yè)第94頁(yè)第95頁(yè)第96頁(yè)第97頁(yè)第98頁(yè)第99頁(yè)第100頁(yè)第101頁(yè)第102頁(yè)第103頁(yè)第104頁(yè)第105頁(yè)第106頁(yè)第107頁(yè)第108頁(yè)第109頁(yè)第110頁(yè)第111頁(yè)第112頁(yè)第113頁(yè)第114頁(yè)第115頁(yè)第116頁(yè)第117頁(yè)第118頁(yè)
Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays
Module 2 of 4
DS025-2 (v3.0) March 21, 2014
6
R
— OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE — OBSOLETE —
Table 5 shows the depth and width aspect ratios for the
block SelectRAM. The Virtex-E block SelectRAM also
includes dedicated routing to provide an efficient interface
with both CLBs and other block SelectRAM modules. Refer
to XAPP130 for block SelectRAM timing waveforms.
Programmable Routing Matrix
It is the longest delay path that limits the speed of any
worst-case design. Consequently, the Virtex-E routing
architecture and its place-and-route software were defined
in a joint optimization process. This joint optimization mini-
mizes long-path delays, and consequently, yields the best
system performance.
The joint optimization also reduces design compilation
times because the architecture is software-friendly. Design
cycles are correspondingly reduced due to shorter design
iteration times.
Local Routing
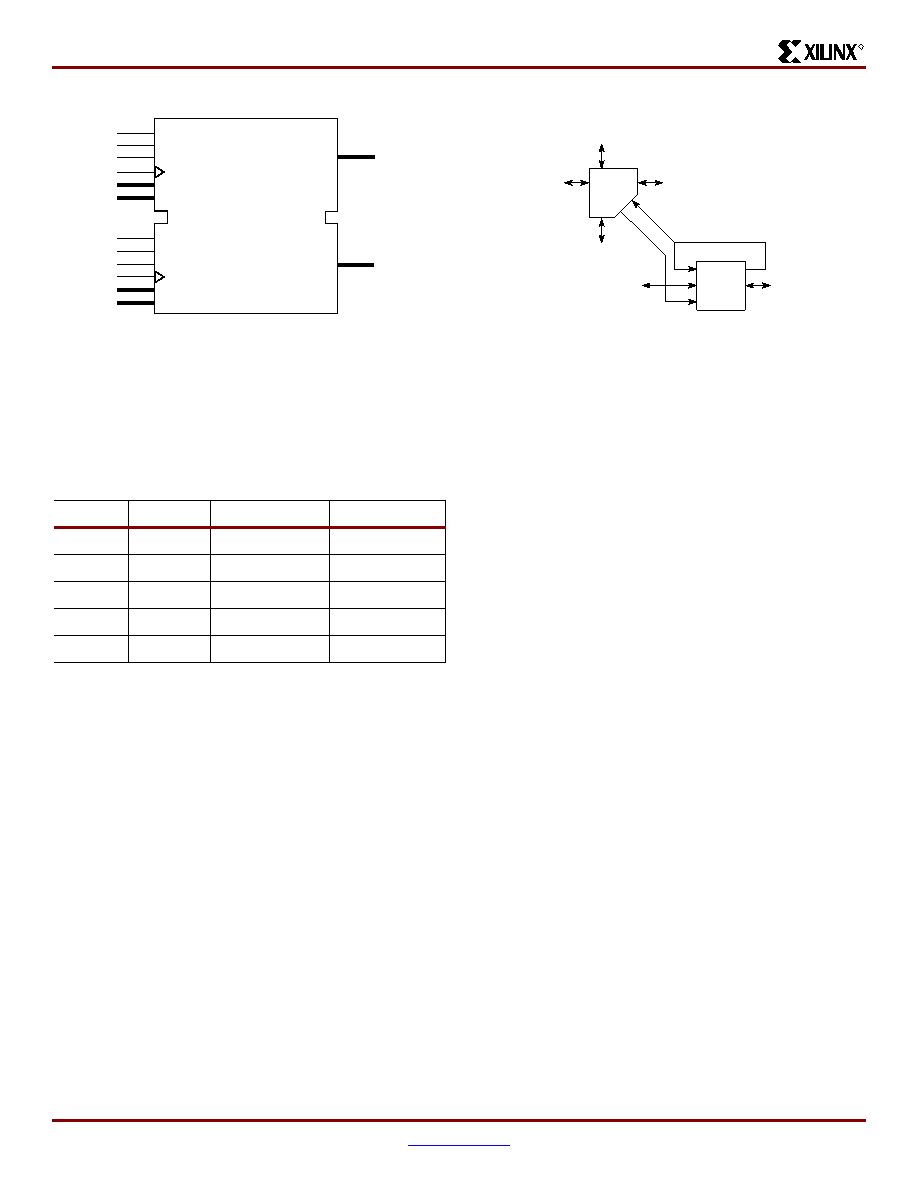
The VersaBlock, shown in Figure 7, provides local routing
resources with the following types of connections:
Interconnections among the LUTs, flip-flops, and GRM
Internal CLB feedback paths that provide high-speed
connections to LUTs within the same CLB, chaining
them together with minimal routing delay
Direct paths that provide high-speed connections
between horizontally adjacent CLBs, eliminating the
delay of the GRM
.
General Purpose Routing
Most Virtex-E signals are routed on the general purpose
routing, and consequently, the majority of interconnect
resources are associated with this level of the routing hier-
archy. The general routing resources are located in horizon-
tal and vertical routing channels associated with the CLB
rows and columns. The general-purpose routing resources
are listed below.
Adjacent to each CLB is a General Routing Matrix
(GRM). The GRM is the switch matrix through which
horizontal and vertical routing resources connect, and
is also the means by which the CLB gains access to
the general purpose routing.
24 single-length lines route GRM signals to adjacent
GRMs in each of the four directions.
72 buffered Hex lines route GRM signals to another
GRMs six-blocks away in each one of the four
directions. Organized in a staggered pattern, Hex lines
are driven only at their endpoints. Hex-line signals can
be accessed either at the endpoints or at the midpoint
(three blocks from the source). One third of the Hex
lines are bidirectional, while the remaining ones are
uni-directional.
12 Longlines are buffered, bidirectional wires that
distribute signals across the device quickly and
efficiently. Vertical Longlines span the full height of the
device, and horizontal ones span the full width of the
device.
I/O Routing
Virtex-E devices have additional routing resources around
their periphery that form an interface between the CLB array
and the IOBs. This additional routing, called the VersaRing,
facilitates pin-swapping and pin-locking, such that logic
redesigns can adapt to existing PCB layouts. Time-to-mar-
ket is reduced, since PCBs and other system components
can be manufactured while the logic design is still in prog-
ress.
Figure 6: Dual-Port Block SelectRAM
Table 5:
Block SelectRAM Port Aspect Ratios
Width
Depth
ADDR Bus
Data Bus
1
4096
ADDR<11:0>
DATA<0>
2
2048
ADDR<10:0>
DATA<1:0>
4
1024
ADDR<9:0>
DATA<3:0>
8
512
ADDR<8:0>
DATA<7:0>
16
256
ADDR<7:0>
DATA<15:0>
WEB
ENB
RSTB
CLKB
ADDRB[#:0]
DIB[#:0]
WEA
ENA
RSTA
CLKA
ADDRA[#:0]
DIA[#:0]
DOA[#:0]
DOB[#:0]
RAMB4_S#_S#
ds022_06_121699
Figure 7: Virtex-E Local Routing
XCVE_ds_007
CLB
GRM
To
Adjacent
GRM
To Adjacent
GRM
Direct
Connection
To Adjacent
CLB
To Adjacent
GRM
To Adjacent
GRM
Direct Connection
To Adjacent
CLB
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| XC4VLX80-10FF1148I | IC FPGA VIRTEX-4LX 1148FFBGA |
| XC4VLX80-11FFG1148C | IC FPGA VIRTEX-4 LX 80K 1148FBGA |
| XC4VLX80-10FFG1148I | IC FPGA VIRTEX-4 LX 80K 1148FBGA |
| XCV600E-8FG900C | IC FPGA 1.8V C-TEMP 900-FBGA |
| XCV600E-7FG900I | IC FPGA 1.8V I-TEMP 900-FBGA |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| XCV405E-7BG676C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-7BG676I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-7BG900C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-7BG900I | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| XCV405E-7FG404C | 制造商:XILINX 制造商全稱:XILINX 功能描述:Virtex-E 1.8 V Extended Memory Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
發(fā)布緊急采購(gòu),3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。