- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄224800 > PSD4235G2V-C-12UI (意法半導(dǎo)體) Flash In-System-Programmable Peripherals for 16-Bit MCUs PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | PSD4235G2V-C-12UI |
| 廠商: | 意法半導(dǎo)體 |
| 英文描述: | Flash In-System-Programmable Peripherals for 16-Bit MCUs |
| 中文描述: | Flash在系統(tǒng)可編程外設(shè)的16位微控制器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 10/93頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 503K |
| 代理商: | PSD4235G2V-C-12UI |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁當(dāng)前第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁
Preliminary Information
PSD4000 Series
15
9.0
The
PSD4000
Functional
Blocks
As shown in Figure 1, the PSD4000 consists of six major types of functional blocks:
t Memory Blocks
t PLD Blocks
t Bus Interface
t I/O Ports
t Power Management Unit
t JTAG-ISP Interface
The functions of each block are described in the following sections. Many of the blocks
perform multiple functions, and are user configurable.
9.1 Memory Blocks
The PSD4000 has the following memory blocks:
The main Flash memory
Secondary Flash memory
SRAM.
The memory select signals for these blocks originate from the Decode PLD (DPLD) and
are user-defined in PSDsoft.
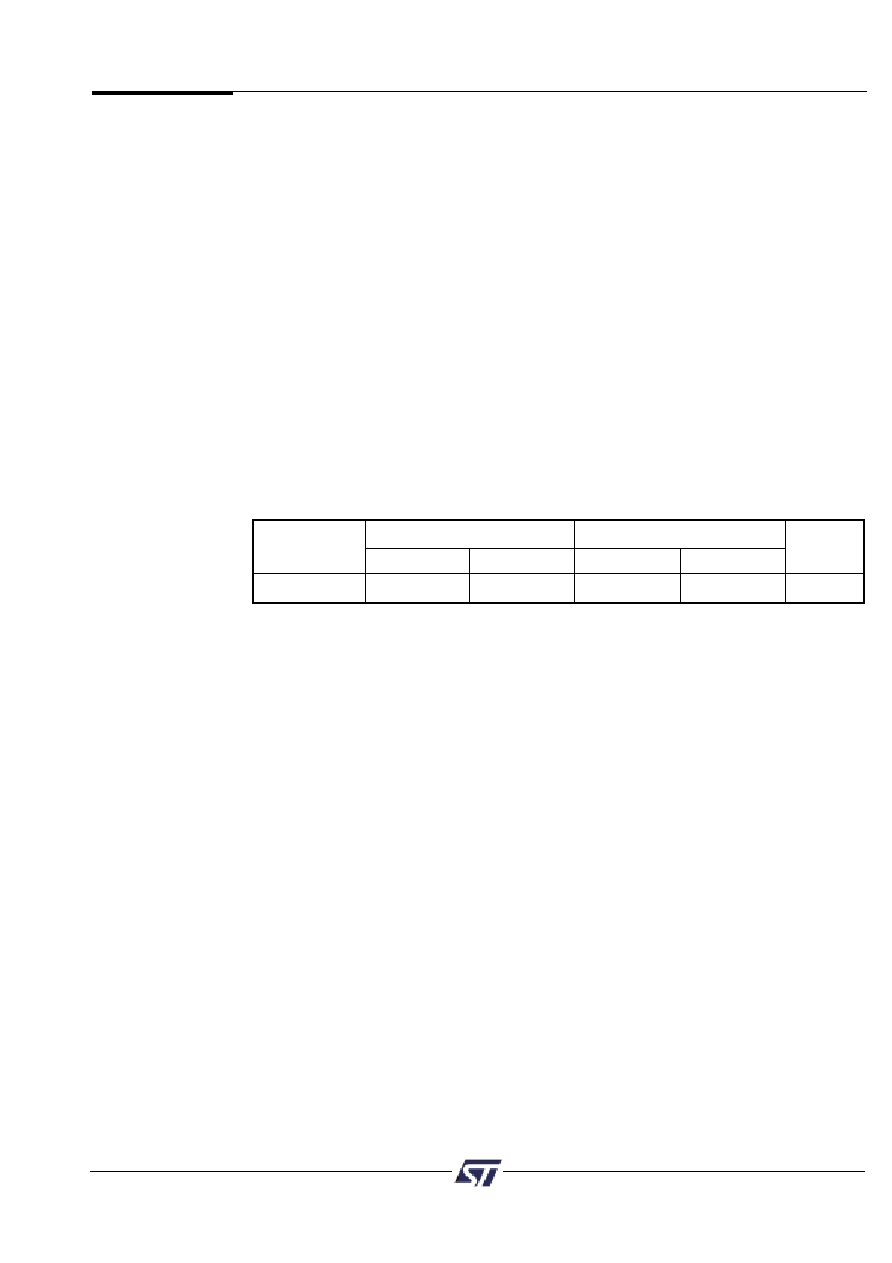
Table 7 summarizes which versions of the PSD4000 contain which memory blocks.
Main Flash
Secondary Flash
Device
Flash Size
Sector Size
Block Size
Sector Size
SRAM
PSD4135G2
512KB
64KB
32KB
8KB
Table 7. Memory Blocks
9.1.1 Main Flash and Secondary Flash Memory Description
The main Flash memory block is divided evenly into eight sectors. The secondary Flash
memory is divided into four sectors of eight Kbytes each. Each sector of either memory
can be separately protected from program and erase operations.
Flash memory may be erased on a sector-by-sector basis and programmed word-by-word.
Flash sector erasure may be suspended while data is read from other sectors of memory
and then resumed after reading.
During a program or erase of Flash, the status can be output on the Rdy/Bsy pin of Port
PE4. This pin is set up using PSDsoft.
9.1.1.1 Memory Block Selects
The decode PLD in the PSD4000 generates the chip selects for all the internal memory
blocks (refer to the PLD section). Each of the eight Flash memory sectors have a
Flash Select signal (FS0-FS7) which can contain up to three product terms. Each of the
four Secondary Flash memory sectors have a Select signal (CSBOOT0-3) which can
contain up to three product terms. Having three product terms for each sector select signal
allows a given sector to be mapped in different areas of system memory. When using a
microcontroller (80C51XA) with separate Program and Data space, these flexible select
signals allow dynamic re-mapping of sectors from one space to the other before and after
IAP.
9.1.1.2 The Ready/Busy Pin (PE4)
Pin PE4 can be used to output the Ready/Busy status of the PSD4000. The output on the
pin will be a ‘0’ (Busy) when Flash memory blocks are being written to, or when the Flash
memory block is being erased. The output will be a ‘1’ (Ready) when no write or erase
operation is in progress.
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PSD4235G2V-C-15B81 | Flash In-System-Programmable Peripherals for 16-Bit MCUs |
| PSD4825 | |
| PSD4850 | |
| PSD4890 | |
| PSD4810 | |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PSD4256G6V-10UI | 功能描述:CPLD - 復(fù)雜可編程邏輯器件 3.3V 8M 100ns RoHS:否 制造商:Lattice 系列: 存儲(chǔ)類型:EEPROM 大電池?cái)?shù)量:128 最大工作頻率:333 MHz 延遲時(shí)間:2.7 ns 可編程輸入/輸出端數(shù)量:64 工作電源電壓:3.3 V 最大工作溫度:+ 90 C 最小工作溫度:0 C 封裝 / 箱體:TQFP-100 |
| PSD4-36 | 制造商:Tamura Corporation of America 功能描述: |
| PSD-45 | 制造商:MEANWELL 制造商全稱:Mean Well Enterprises Co., Ltd. 功能描述:45W DC-DC Single Output Switching Power Supply |
| PSD-45_11 | 制造商:MEANWELL 制造商全稱:Mean Well Enterprises Co., Ltd. 功能描述:45W DC-DC Single Output Switching Power Supply |
| PSD-45A-05 | 功能描述:線性和開關(guān)式電源 30W 5Vout 6A Input 9.2-18VDC RoHS:否 制造商:TDK-Lambda 產(chǎn)品:Switching Supplies 開放式框架/封閉式:Enclosed 輸出功率額定值:800 W 輸入電壓:85 VAC to 265 VAC 輸出端數(shù)量:1 輸出電壓(通道 1):20 V 輸出電流(通道 1):40 A 商用/醫(yī)用: 輸出電壓(通道 2): 輸出電流(通道 2): 安裝風(fēng)格:Rack 長(zhǎng)度: 寬度: 高度: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。