- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄368671 > TMS320C242FNA 16-Bit Digital Signal Processor PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | TMS320C242FNA |
| 元件分類: | 數(shù)字信號(hào)處理 |
| 英文描述: | 16-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
| 中文描述: | 16位數(shù)字信號(hào)處理器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 16/66頁 |
| 文件大小: | 803K |
| 代理商: | TMS320C242FNA |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁當(dāng)前第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁
TMS320C242
DSP CONTROLLER
SPRS063B – DECEMBER 1997 – REVISED DECEMBER 1999
16
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
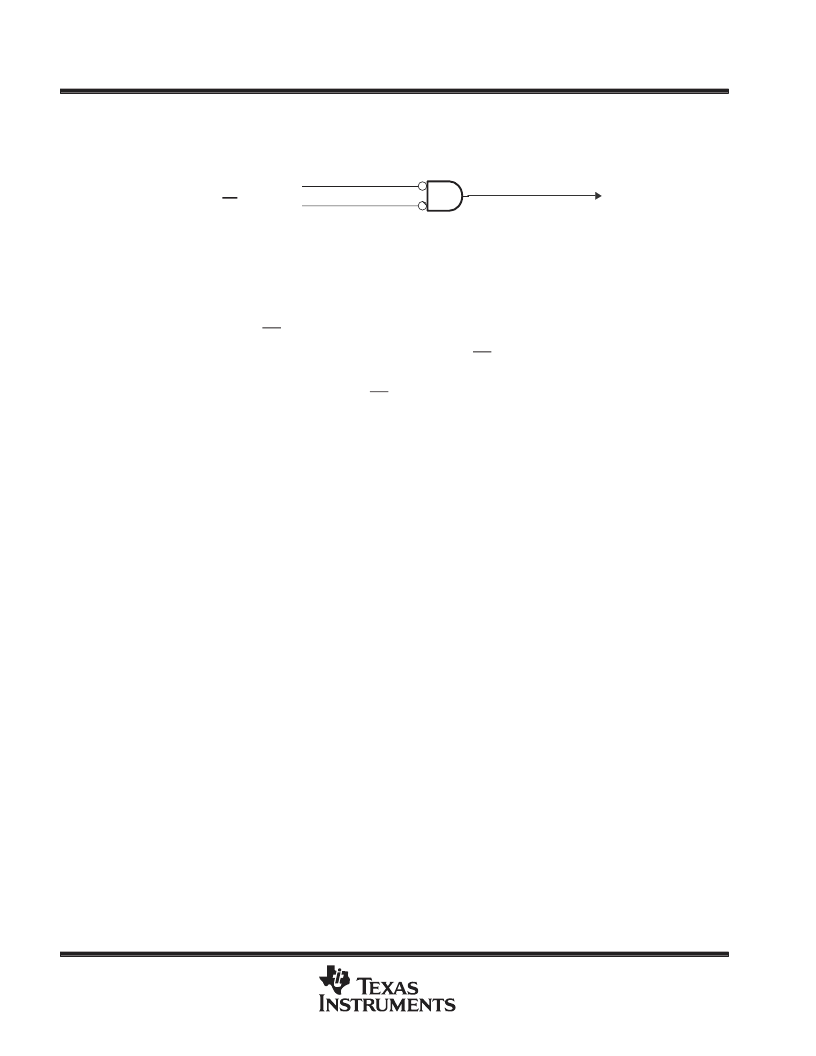
reset
The reset operation ensures an orderly startup sequence for the device. There are two possible causes of a
reset, as shown in Figure 4.
Signal
Reset
System Reset
Watchdog Timer Reset
External Reset (RS) Pin Active
Figure 4. Reset Signals
The two possible reset signals are generated as follows:
Watchdog timer reset.
A watchdog-timer-generated reset occurs if the watchdog timer overflows or an
improper value is written to either the watchdog key register or the watchdog control register. (Note that
when the device is powered on, the watchdog timer is automatically active.) The watchdog timer reset is
reflected on the external RS pin also.
Reset pin active.
To generate an external reset pulse on the RS pin, a low-level pulse duration of at least
one CPUCLK cycle is necessary to ensure that the device recognizes the reset signal.
Once watchdog reset is activated, the external RS pin is driven (active) low for a minimum of eight CPUCLK
cycles. This allows the TMS320x24x device to reset external system components.
The occurrence of a reset condition causes the TMS320x24x to terminate program execution and affects
various registers and status bits. During a reset, RAM contents remain unchanged, and all control bits that are
affected by a reset are initialized to their reset state.
hardware-generated interrupts
The ’24x CPU supports one nonmaskable interrupt (NMI) and six maskable prioritized interrupt requests. The
’24x devices have many peripherals, and each peripheral is capable of generating one or more interrupts in
response to many events. The ’24x CPU does not have sufficient interrupt requests to handle all these
peripheral interrupt requests; therefore, a centralized interrupt controller is provided to arbitrate the interrupt
requests from all the different sources. Throughout this section, refer to Figure 5 .
A
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TMS320C241 | 16-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
| TMS320C242FNS | 16-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
| TMS320C242PGA | 16-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
| TMS320C242PGS | 16-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
| TMS320C30GEL | 32-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| TMS320C242FNS | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:16-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
| TMS320C242PG | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:DSP CONTROLLER |
| TMS320C242PGA | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:16-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
| TMS320C242PGS | 制造商:未知廠家 制造商全稱:未知廠家 功能描述:16-Bit Digital Signal Processor |
| TMS320C25 | 制造商:TI 制造商全稱:Texas Instruments 功能描述:SECOND-GENERATION DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。