- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄45045 > M3826AMFA-XXXFP 8-BIT, MROM, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | M3826AMFA-XXXFP |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, MROM, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| 封裝: | PLASTIC, LQFP-100 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 78/93頁 |
| 文件大?。?/td> | 996K |
| 代理商: | M3826AMFA-XXXFP |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁當前第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁
Rev.2.00
May. 24, 2006
page 8 of 90
REJ03B0028-0200
3826 Group (A version)
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
The 3826 group uses the standard 740 family instruction set. Re-
fer to the table of 740 family addressing modes and machine
instructions or the 740 Family Software Manual for details on the
instruction set.
Machine-resident 740 family instructions are as follows:
The FST and SLW instruction cannot be used.
The STP, WIT, MUL, and DIV instruction can be used.
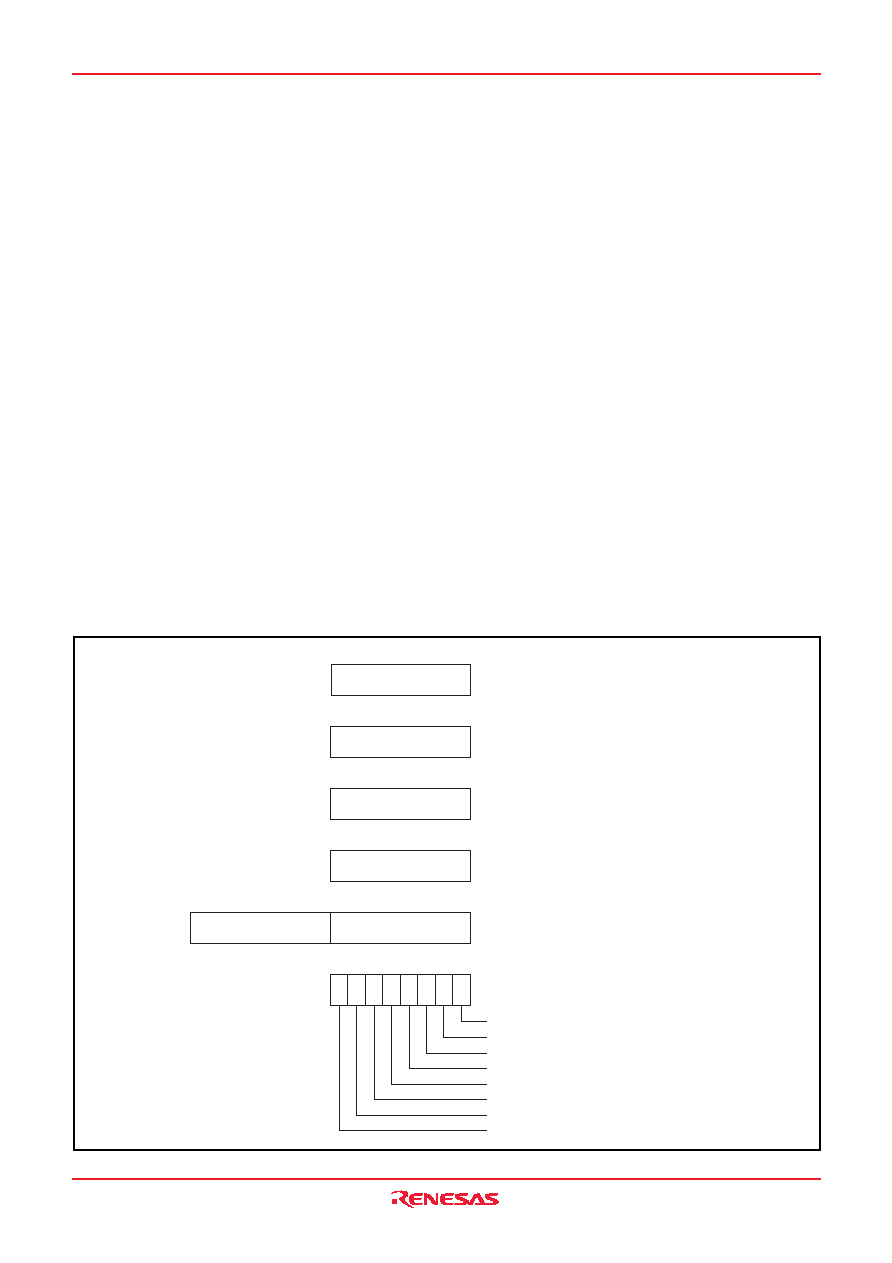
The central processing unit (CPU) has six registers. Figure 6
shows the 740 Family CPU register structure.
[Accumulator (A)]
The accumulator is an 8-bit register. Data operations such as
arithmetic data transfer, etc., are executed mainly through the ac-
cumulator.
[Index Register X (X)]
The index register X is an 8-bit register. In the index addressing
modes, the value of the OPERAND is added to the contents of
register X and specifies the real address.
[Index Register Y (Y)]
The index register Y is an 8-bit register. In partial instruction, the
value of the OPERAND is added to the contents of register Y and
specifies the real address.
[Stack Pointer (S)]
The stack pointer is an 8-bit register used during subroutine calls
and interrupts. This register indicates start address of stored area
(stack) for storing registers during subroutine calls and interrupts.
The low-order 8 bits of the stack address are determined by the
contents of the stack pointer. The high-order 8 bits of the stack
address are determined by the stack page selection bit. If the
stack page selection bit is “0” , the high-order 8 bits becomes
“0016”. If the stack page selection bit is “1”, the high-order 8 bits
becomes “0116”.
Figure 9 shows the operations of pushing register contents onto
the stack and popping them from the stack. Table 6 shows the
push and pop instructions of accumulator or processor status reg-
ister.
Store registers other than those described in Figure 9 with pro-
gram when the user needs them during interrupts or subroutine
calls.
[Program Counter (PC)]
The program counter is a 16-bit counter consisting of two 8-bit
registers PCH and PCL. It is used to indicate the address of the
next instruction to be executed.
Fig. 6 740 Family CPU register structure
A
Accumulator
b7
b0
b7
b15
b0
b7
b0
X
Index register X
Y
Index register Y
S
Stack pointer
PCL
Program counter
PCH
N V T B D I Z C
Processor status register (PS)
Carry flag
Zero flag
Interrupt disable flag
Decimal mode flag
Break flag
Index X mode flag
Overflow flag
Negative flag
相關PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| M3826AMFA-XXXGP | 8-BIT, MROM, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M3826AMFA-XXXGP | 8-BIT, MROM, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M38268MCA-XXXGP | 8-BIT, MROM, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M3826AMFA-XXXFP | 8-BIT, MROM, 10 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| M3826AMFLXXXGP | 8-BIT, MROM, 4 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
相關代理商/技術參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| M3826-BK001 | 制造商:Alpha Wire 功能描述: |
| M3826-BK002 | 制造商:Alpha Wire 功能描述: |
| M3826-BK005 | 制造商:Alpha Wire 功能描述: |
| M3826-BK199 | 制造商:Alpha Wire 功能描述: |
| M3826-BLACK-100 | 制造商:Alpha Wire 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。