- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄370021 > PSD813F4V -200V 100kRad Hi-Rel Single P-Channel TID Hardened MOSFET in a SMD-2 package; A IRHNA597260 with Standard Packaging PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號(hào): | PSD813F4V |
| 英文描述: | -200V 100kRad Hi-Rel Single P-Channel TID Hardened MOSFET in a SMD-2 package; A IRHNA597260 with Standard Packaging |
| 中文描述: | Flash在系統(tǒng)編程(ISP)外設(shè)的8位微控制器 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 11/103頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1185K |
| 代理商: | PSD813F4V |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁當(dāng)前第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁
11/103
PSD81XFX, PSD83XF2, PSD85XF2
PSD8XXFX ARCHITECTURAL OVERVIEW
PSD8XXFX devices contain several major func-
tional blocks. Figure 3 shows the architecture of
the PSD8XXFX device family. The functions of
each block are described briefly in the following
sections. Many of the blocks perform multiple
functions and are user configurable.
Memory
Each of the memory blocks is briefly discussed in
the following paragraphs. A more detailed discus-
sion can be found in the section entitled “MEMO-
RY BLOCKS“ on page 18.
The 1 Mbit or 2 Mbit (128K x 8, or 256K x 8) Flash
memory is the primary memory of the PSD8XXFX.
It is divided into 8 equally-sized sectors that are in-
dividually selectable.
The optional 256 Kbit (32K x 8) secondary Flash
memory is divided into 4 equally-sized sectors.
Each sector is individually selectable.
The optional SRAM is intended for use as a
scratch-pad memory or as an extension to the
MCU SRAM. If an external battery is connected to
Voltage Stand-by (V
STBY
, PC2), data is retained in
the event of power failure.
Each sector of memory can be located in a differ-
ent address space as defined by the user. The ac-
cess times for all memory types includes the
address latching and DPLD decoding time.
Page Register
The 8-bit Page Register expands the address
range of the MCU by up to 256 times. The paged
address can be used as part of the address space
to access external memory and peripherals, or in-
ternal memory and I/O. The Page Register can
also be used to change the address mapping of
sectors of the Flash memories into different mem-
ory spaces for IAP.
PLDs
The device contains two PLDs, the Decode PLD
(DPLD) and the Complex PLD (CPLD), as shown
in Table 2, each optimized for a different function.
The functional partitioning of the PLDs reduces
power consumption, optimizes cost/performance,
and eases design entry.
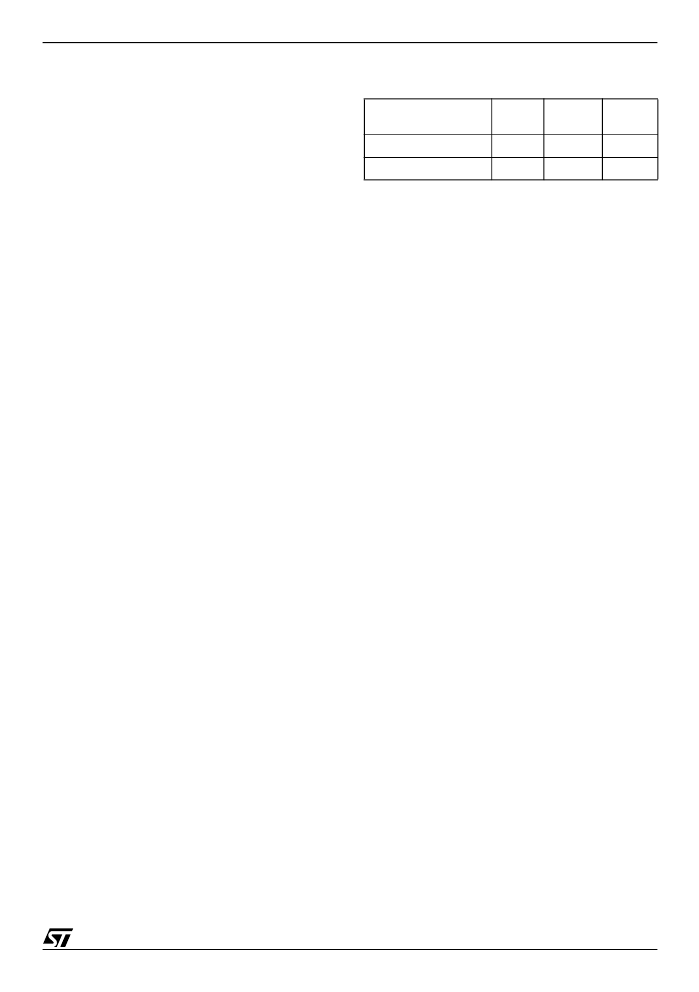
Table 2. PLD I/O
The DPLD is used to decode addresses and to
generate Sector Select signals for the PSD8XXFX
internal memory and registers. The DPLD has
combinatorial outputs. The CPLD has 16 Output
Macrocells (OMC) and 3 combinatorial outputs.
The PSD8XXFX also has 24 Input Macrocells
(IMC) that can be configured as inputs to the
PLDs. The PLDs receive their inputs from the PLD
Input Bus and are differentiated by their output
destinations, number of product terms, and mac-
rocells.
The PLDs consume minimal power. The speed
and power consumption of the PLD is controlled
by the Turbo bit in PMMR0 and other bits in the
PMMR2. These registers are set by the MCU at
run-time. There is a slight penalty to PLD propaga-
tion time when invoking the power management
features.
I/O Ports
The PSD8XXFX has 27 individually configurable I/
O pins distributed over the four ports (Port A, B, C,
and D). Each I/O pin can be individually configured
for different functions. Ports can be configured as
standard MCU I/O ports, PLD I/O, or latched ad-
dress outputs for MCUs using multiplexed ad-
dress/data buses.
The JTAG pins can be enabled on Port C for In-
System Programming (ISP).
Ports A and B can also be configured as a data
port for a non-multiplexed bus.
MCU Bus Interface
PSD8XXFX interfaces easily with most 8-bit
MCUs that have either multiplexed or non-multi-
plexed address/data buses. The device is config-
ured to respond to the MCU’s control signals,
which are also used as inputs to the PLDs. For ex-
amples, please see the section entitled “MCU Bus
Interface Examples“ on page 43.
Name
Inputs
Outputs
Product
Terms
Decode PLD (DPLD)
73
17
42
Complex PLD (CPLD)
73
19
140
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PSD813F5V | -60V 100kRad Hi-Rel Single P-Channel TID Hardened MOSFET in a SMD-2 package; Similar to IRHNA9064 with optional Total Dose Rating of 300kRads |
| PSD86 | THREE PHASE RECTIFIER BRIDGE |
| PSF101 | WORLD MAGNETICS ULTRA SENSITIVEPRESSURESWITCHES |
| PSG61 | 4 KEY BI-BI CALL |
| PSM-100KPD | Pressure sensor module/Gauge,Differential |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| PSD813F4VA-15J | 功能描述:SPLD - 簡(jiǎn)單可編程邏輯器件 U 511-PSD813F2VA-15J RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 邏輯系列:TICPAL22V10Z 大電池?cái)?shù)量:10 最大工作頻率:66 MHz 延遲時(shí)間:25 ns 工作電源電壓:4.75 V to 5.25 V 電源電流:100 uA 最大工作溫度:+ 75 C 最小工作溫度:0 C 安裝風(fēng)格:Through Hole 封裝 / 箱體:DIP-24 |
| PSD813F4VA-15U | 功能描述:SPLD - 簡(jiǎn)單可編程邏輯器件 U 511-PSD813F2VA-15U RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 邏輯系列:TICPAL22V10Z 大電池?cái)?shù)量:10 最大工作頻率:66 MHz 延遲時(shí)間:25 ns 工作電源電壓:4.75 V to 5.25 V 電源電流:100 uA 最大工作溫度:+ 75 C 最小工作溫度:0 C 安裝風(fēng)格:Through Hole 封裝 / 箱體:DIP-24 |
| PSD813F5-12JI | 制造商:WSI 功能描述: |
| PSD813F5-15JI | 制造商:WSI 功能描述: |
| PSD813F5-15U | 制造商:WSI 功能描述: 制造商:WSI 功能描述:1M X 1 FLASH, 27 I/O, PIA-GENERAL PURPOSE, PQFP64 |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復(fù)。