- 您現(xiàn)在的位置:買賣IC網(wǎng) > PDF目錄98145 > ST72T774S9T1 (STMICROELECTRONICS) 8-BIT, OTPROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 PDF資料下載
參數(shù)資料
| 型號: | ST72T774S9T1 |
| 廠商: | STMICROELECTRONICS |
| 元件分類: | 微控制器/微處理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 |
| 封裝: | TQFP-44 |
| 文件頁數(shù): | 122/144頁 |
| 文件大小: | 1280K |
| 代理商: | ST72T774S9T1 |
第1頁第2頁第3頁第4頁第5頁第6頁第7頁第8頁第9頁第10頁第11頁第12頁第13頁第14頁第15頁第16頁第17頁第18頁第19頁第20頁第21頁第22頁第23頁第24頁第25頁第26頁第27頁第28頁第29頁第30頁第31頁第32頁第33頁第34頁第35頁第36頁第37頁第38頁第39頁第40頁第41頁第42頁第43頁第44頁第45頁第46頁第47頁第48頁第49頁第50頁第51頁第52頁第53頁第54頁第55頁第56頁第57頁第58頁第59頁第60頁第61頁第62頁第63頁第64頁第65頁第66頁第67頁第68頁第69頁第70頁第71頁第72頁第73頁第74頁第75頁第76頁第77頁第78頁第79頁第80頁第81頁第82頁第83頁第84頁第85頁第86頁第87頁第88頁第89頁第90頁第91頁第92頁第93頁第94頁第95頁第96頁第97頁第98頁第99頁第100頁第101頁第102頁第103頁第104頁第105頁第106頁第107頁第108頁第109頁第110頁第111頁第112頁第113頁第114頁第115頁第116頁第117頁第118頁第119頁第120頁第121頁當前第122頁第123頁第124頁第125頁第126頁第127頁第128頁第129頁第130頁第131頁第132頁第133頁第134頁第135頁第136頁第137頁第138頁第139頁第140頁第141頁第142頁第143頁第144頁
ST72774/ST727754/ST72734
79/144
4.6 USB INTERFACE (USB)
4.6.1 Introduction
The USB Interface implements a low-speed
function interface between the USB and the ST7
microcontroller. It is a highly integrated circuit
which
includes
the
transceiver,
3.3
voltage
regulator, SIE and DMA. No external components
are needed apart from the external pull-up on
USBDM for low speed recognition by the USB
host.
4.6.2 Main Features
s
USB Specification Version 1.0 Compliant
s
Supports Low-Speed USB Protocol
s
Two or Three Endpoints (including default one)
depending on the device (see device feature list
and register map)
s
CRC
generation/checking,
NRZI
encoding/
decoding and bit-stuffing
s
USB Suspend/Resume operations
s
DMA Data transfers
s
On-Chip 3.3V Regulator
s
On-Chip USB Transceiver
4.6.3 Functional Description
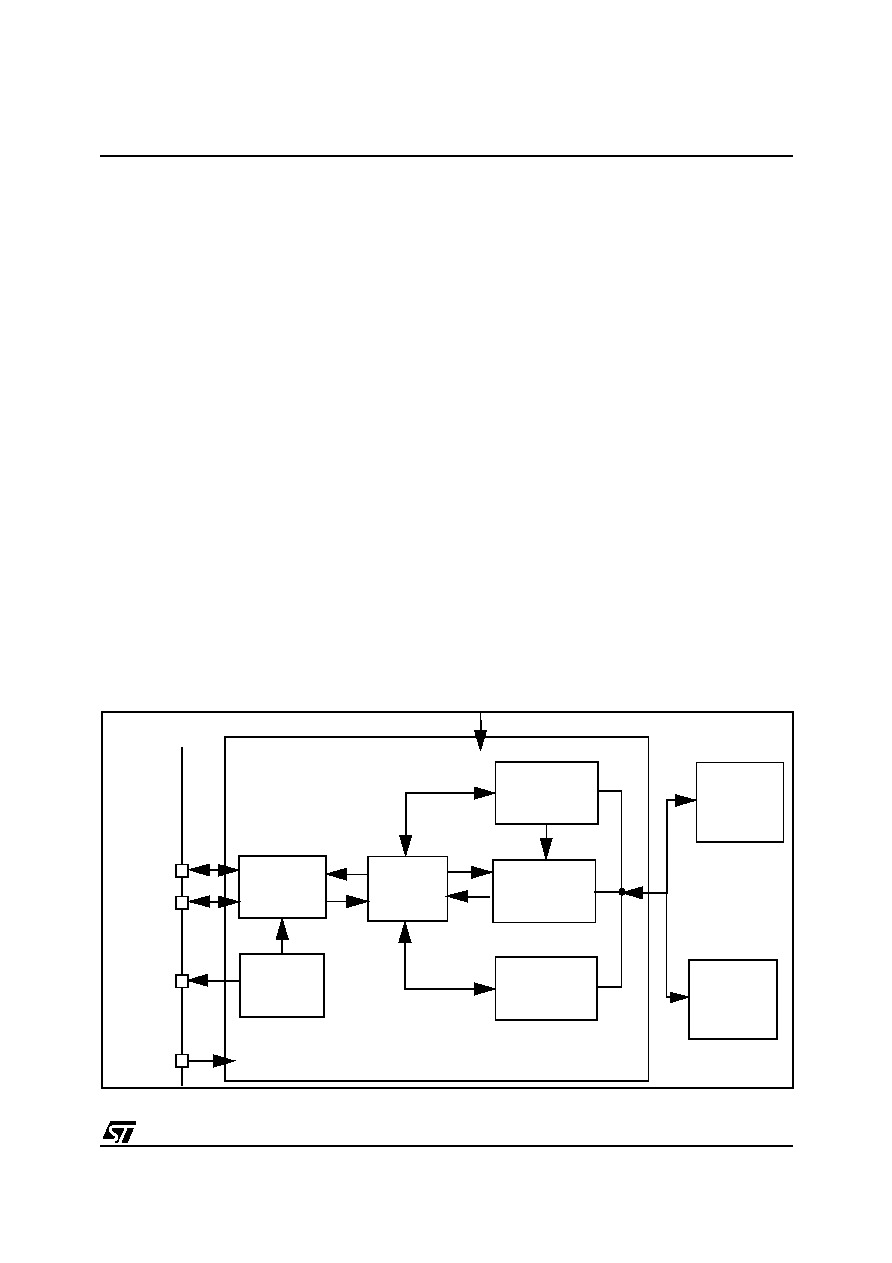
The block diagram in Figure 50, gives an overview
of the USB interface hardware.
For general information on the USB, refer to the
“Universal Serial Bus Specifications” document
available at http//:www.usb.org.
Serial Interface Engine
The SIE (Serial Interface Engine) interfaces with
the USB, via the transceiver.
The
SIE
processes
tokens,
handles
data
transmission/reception,
and
handshaking
as
required by the USB standard. It also performs
frame formatting, including CRC generation and
checking.
Endpoints
The
Endpoint
registers
indicate
if
the
microcontroller is ready to transmit/receive, and
how many bytes need to be transmitted.
DMA
When a token for a valid Endpoint is recognized by
the USB interface, the related data transfer takes
place, using DMA. At the end of the transaction, an
interrupt is generated.
Interrupts
By
reading
the
Interrupt
Status
register,
application software can know which USB event
has occurred.
Figure 50. USB block diagram
CPU
MEMORY
Transceiver
3.3V
Voltage
Regulator
SIE
ENDPOINT
DMA
INTERRUPT
Address,
and interrupts
USBDM
USBDP
USBVCC
6 MHz
REGISTERS
data busses
USBGND
相關(guān)PDF資料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ST7294C6B6 | 8-BIT, MROM, 4 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP28 |
| ST72T94C6M6 | 8-BIT, OTPROM, MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO28 |
| ST72C171K2B6 | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP32 |
| ST72E85A5G0 | 8-BIT, UVPROM, 4.332 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CQFP80 |
| ST72F321J9T7 | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 |
相關(guān)代理商/技術(shù)參數(shù) |
參數(shù)描述 |
|---|---|
| ST730 | 制造商:IRF 制造商全稱:International Rectifier 功能描述:PHASE CONTROL THYRISTORS Hockey Puk Version |
| ST7-30 | 制造商:SUPERWORLD 制造商全稱:Superworld Electronics 功能描述:POWER TRANSFORMER |
| ST-7300 | 制造商:GC Electronics 功能描述: |
| ST730186-3 | 制造商:KEMET Corporation 功能描述: 制造商:KET 功能描述: |
| ST730268-1 | 制造商:KEMET Corporation 功能描述: 制造商:KET 功能描述: |
發(fā)布緊急采購,3分鐘左右您將得到回復。